* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Respiratory system
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
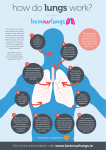
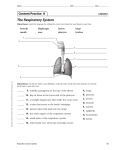
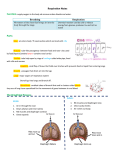
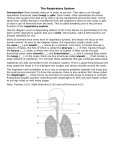
By: Madison Knode, Emma Starkey, Carley Robinson Fred It supplies the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to the rest of the body. The Lungs… • • • • • • Facts A pair of organs that are the site of oxygen absorption. They are light pink. Full of air They are surprisingly light. Takes up most of the area in your chest. It wraps around your heart. Main Function Respiration- The process of oxygen entering your body, and carbon dioxide leaving your body. The Trachea… • • • • Facts The trachea is also called the windpipe. This tube leads from the top of the neck, below the voice box, and down towards the lungs. It is surprisingly flexible, stretching to be 4 or 5 inches long. Its made up of 16 to 20 cartilage rings in the shape of a “C”. Main Function The trachea allows air to travel passed the larynx and to the bronchi. The Bronchi… Facts • The bronchi is the branches of the windpipe/trachea that lead into the lungs. • Each bronchi enters its lung and begins on a series of branches, called bronchial or respiratory tree. Main Function The bronchi conducts air into the lungs. The Diaphragm… Facts • A sheet of muscle underneath the lungs of mammals that helps draw air to the lungs. • A dome shaped muscle that moves up and down to expand or contract lungs. Main Function Contracts so the lungs can inhale oxygen. Then releases for the lungs to exhale carbon dioxide. The Alveoli… What is it??? The alveoli is inside of the lungs and is where the waste (carbon dioxide) goes so that our lungs can exhale the harmful waste. So basically it is the container of which hold carbon dioxide until it is exhaled. Diseases… So many things can go wrong with this system. The respiratory system is very vulnerable to toxins and diseases. In some cases the patient is unable to breath properly. Like with pneumonia, it causes your lungs to fill up with fluid and then you cant get enough air into your lungs. Relationships… The respiratory system provides the body with oxygen and supplies the blood with oxygen. Then the circulatory system sends the blood to all the other systems throughout the body. Without this system you would not be able to function or live. Nervous System!! The nervous system is responsible for sending, receiving, and processing new impulses throughout the body. What are they?? Central Nervous System Brain- Controls all thoughts and actions, your brain is the source of everything you do. Peripheral Nervous System Sensory Organs-Composed of neurons, which convert environmental stimuli to electrical signals and glialike cells. Spinal Cord-The main nerve extending from the base of the brain along inside of the back bone. Motor Neurons-A neuron that carries an impulse from the brain or spinal cord to a muscle, where it simulates contractions. A Neuron… Diseases… Parkinson’s Disease Parkinson’s disease is a progressive disorder that is caused by a generation of nerve cells in the Part of the brain called the substantia nigra, which controls movement. Then the nerve cells die therefore you are then unable to control movement of certain parts of your body. Treatment The patients are treated with medication to relieve symptoms of the disease. Symptoms • Tremor • Involuntary movements of the hands, arms, legs and jaw. • Unsteady walk or balance • Depression • Muscles rigidity, or stiffness of the limbs. Relationships • Skeletal System: the brain regulates the position of bones by controlling muscles. • Cardiovascular System: the brain regulates heart rate and blood pressure. • Muscular System: the brain controls contractions of muscles • Endocrine System: the hypothalamus controls the pituitary gland and other endocrine glands. • Lymphatic Systems: The brain can simulate defense mechanisms against infection. • Respiratory System: the brain regulates breathing rate. • Digestive System: Provide the building blocks for some neurotransmitters. The brain controls drinking and feeding behaviors. • Urinary System: The brain controls urination. • Integumentary System: Nerves control muscles connected to hair follicles. Citations!! • • • • • www.becomehealthynow.com www.google.com http://faculty.washington.edu/ www.neurosurgerytoday.org www.innerbody.com