* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Oncolytic virus wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Central nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Acquired characteristic wikipedia , lookup
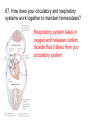
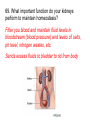
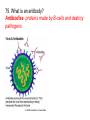
67. How does your circulatory and respiratory systems work together to maintain homeostasis? Respiratory system takes in oxygen and releases carbon dioxide that it takes from you circulatory system. 68. What endocrine gland and hormone it produces regulates metabolism? Thyroid gland- The function of the thyroid gland is to take iodine, found in many foods, and convert it into thyroid hormones: thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). Every cell in the body depends upon thyroid hormones for regulation of their metabolism 69. What important function do your kidneys perform to maintain homeostasis? Filter you blood and maintain fluid levels in bloodstream (blood pressure) and levels of salts, ph level, nitrogen wastes, etc. Sends excess fluids to bladder to rid from body 70. How does a vaccine provide you with immunity? Vaccines artificially produce acquired immunity 1. Vaccine- substance that contains antigen of a pathogen 2. Causes immune system to produce memory cells 3. You can make antibodies right away if infected 71. Where does chemical digestion of food begin? In your mouth 72. What type of pathogens do antibiotics work on or not work on? Bacteria or fungi, but NOT on viruses 73. What are your body’s non-specific defenses against pathogens? Inflammatory response- characterized by swelling, redness, pain, itching, and increased warmth at affected site Reacts to every pathogen the same way 74. What are your body’s specific defenses against pathogens? Immune response is triggered when immune system detects a pathogen (2 types of immune response) •Cell-mediated immunity- when lymphocytes (not antibodies) themselves defend the body. •Humoral Immunity- also called antibodymediated immunity Antigens- protein markers on surfaces of cells and viruses that help immune system identify a foreign cell or virus 75. What is an antibody? Antibodies- proteins made by B-cells and destroy pathogens 76. What is an antigen? Antigens- protein markers on surfaces of cells and viruses that help immune system identify a foreign cell or virus 77. What are the three types of neurons? (Diagram and label the correct pathway) • Sensory neurons- detect stimuli and transmit signals to brain and spinal cord • Interneurons- make up brain and spinal cord and receive and process information • Motor neurons-pass messages from nervous system to organs and muscles 78. What is a feedback loop and how is it similar to a thermostat in your house? It operates by doing the opposite (negative) of what it senses. If senses it is to hot, it tries to cool down, to cold, tries to warm up. 79. How are the nervous system and endocrine system similar? Different? Both regulate and control you body Nervous system- fast acting and “hard wired” Endocrine system- slower acting chemical signals carried in your bloodstream throughout the body. Control process that occur over long periods of time (hair growth, aging, sleep patterns, etc.) 80. Why is a virus not considered a living thing? It needs a host cell to reproduce (cannot reproduce by itself)