* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download How is the STAT3 pathway activated?
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Complement system wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Inflammation wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
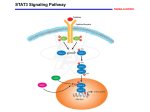
STAT3 and the Immune System Maureen Sherry Lynes February 29, 2012 Overview STAT family; STAT3 signaling and structure Role of STAT3 revealed by tissue specific knockouts STAT3 and the anti-tumor immune response Therapeutic approaches for targeting STAT3 Paper discussion The STAT Family of Transcription Factors 7 mammalian STAT proteins latent cytoplasmic transcription factors Important in a wide range of physiological processes STAT1 STAT2 STAT3 STAT4 STAT5A STAT5B STAT6 Impaired interferon response; increased susceptibility to tumors Impaired interferon response Embryonic lethal Impaired Th1 differentiation due to loss of Il-12 responsiveness Impaired mammary gland development (decreased prolactin response) Impaired growth (growth hormone signaling impaired) Impaired Th1 differentiation due to loss of Il-4 responsiveness Adapted from Darnell and Levy, 2002 How is the STAT3 pathway activated? •Cytokines, growth factors •Secreted by diverse cell types in response to diverse processes •Receptor specific QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Minegishi et al 2011 The STAT3 Signaling Pathway Negative Regulation of STAT3 signaling 1. Cytoplasmic phosphatases 2. SOCs proteins 3. Pias Proteins 4. STAT3ß Domain Structure of STAT3 Q uickTim e™ and a decom pr essor ar e needed t o see t his pict ur e. Figure 1.2. Domain structure of the STAT proteins. STAT3 Target Genes Growth (C-myc, cyclin D) Apoptosis (Survivin, bcl-xl) STAT3 Differentiation Angiogenesis (VEGF) Immortalization (hTERT) Tissue Specific STAT3 Knockouts •Brain: obesity, inability to control temperature, diabetes •Skin: impaired wound healing, resistance to skin cancer •Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells: loss of pluripotency QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. •Lung •Macrophages and Neutrophils •Liver •Th17 development Gao et al, 2004. STAT3 and the Acute Phase Response •Liver: site of integration of signals from tissue, toxins and bacterial products in blood, etc • Macrophages in the periphery: cytokine release •Hepatocytes respond to cytokines (IL-6, IL-1 for example) and upregulate appropriate response proteins (clotting, innate responses to bacterial infection, toxins, etc) •Hepatocyte deletion of STAT3- polymicrobial sepsis LPS injection or cecal ligation and puncture: Sakamori et al 2007 QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Similar bacterial load; decreased acute phase proteins, increased inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6 and TNFa STAT3 in macrophages and neutrophils •STAT3 deleted in cells expressing lysozyme M •Mice were susceptible to LPS-induced endotoxic shock •Macrophages constitutively activated QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Takeda et al, 1999. STAT3 in macrophages and neutrophils •STAT3 -/- macrophages are resistant to IL-10 •IL-10 normally dampens macrophage activation and response •LysmCre STAT3 mice develop chronic enterocholitis QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. STAT3 in the lung epithelium • House dustmite extract: induces allergic inflammation in the lung, as well as STAT3 activation •Lung specific STAT3 KO: appears normal •STAT3 lung KO: decreased airway hyperresponsiveness, immune infiltration upon HDM challenge QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Simeone et al, 2007. STAT3 in Th17 Differentiation •CD4+, defense against extracellular bacteria, fungi •Pathogenic autoimmune responses •Celiac, IBD, etc QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Fischer 2008 STAT3 in hyper IgE syndrome activation QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. DNA binding QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. STAT3 in hyper IgE syndrome QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Recurrent skin and lung infections (Th17, lung epithelial defects?) Activation, Duration, and extent of STAT3 signaling is tightly regulated •Brain: obsesity, inability to control temperature, diabetes •Skin: impaired wound healing, resistance to skin cancer •Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells: loss of pluripotency •Lung- promotes allergic inflammation •Macrophages and Neutrophilsprevents constitutve activation, •Liver: actue phase response; integration of signals from tissues •Th17 differentiation Gao et al, 2004. STAT3 and tumorigenesis STAT3 is constitutively activated in many human cancers Inappropriately activated or overexpressed Prevents apoptosis, stimulates migration, stimulates proliferation, increases angiogenesis Upregulates cytokines that perpetuate STAT3 activation in the tumor and surrounding tissue Wang, Rich et al. Stem Cells 2009 DN STAT3 induces melanoma regression in a mouse model Transfection of B16 tumors with dominant negative STAT3 induces tumor regression Bystander effect: regression disproportionate to transfection QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Niu et al Cancer Research 1999 STAT3 Suppresses Anti-Tumor Immunity Cultured B16 cells transfected with DN STAT3: increased production of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines (TNFa, RANTES, IP-10) In vivo: enhances macrophage and neutrophil infiltration QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Wang et al Nature Med 2004 STAT3 Suppresses Anti-Tumor Immunity Yu et al Nature Reviews 2007 STAT3 as a therapeutic target STAT3 as a therapeutic target Activation EGFR antibodies; small molecules Jak inhibitors Multi-receptor kinase inhibitors Protein-protein interactions Small molecules to prevent dimerization phosphoTyr peptides DNA binding Double stranded oligonucleotides Nuclear translocation, natural inhibitors Summary STAT3 is a cytokine and growth factor activated transcription factor STAT3 has a wide range of functions, both anti and pro inflammatory depending on the tissue and physiological context STAT3 is also involved in disease states, such as asthma, colitis, and cancer STAT3 can suppress anti-tumor immunity STAT3 directed therapeutics is an active area of research QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture.