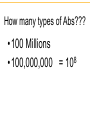* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 03 Formation and Gen..
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
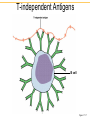
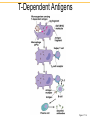
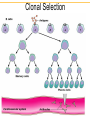
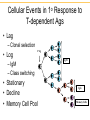
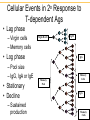
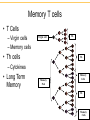
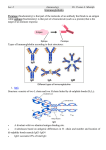
IgG IgM IgA IgD IgE Clonal Selection • Bone marrow gives rise to B cells. • Mature B cells migrate to lymphoid organs. • A mature B cells recognizes epitopes. Hallmarks of the Immune Response • Self/Non-self Discrimination • Memory • Specificity A. Self/non-self discrimination - One characteristic feature of the specific immune system is that it normally distinguishes between self and non-self and only reacts against non-self. B. Memory - A second feature of the specific immune response is that it demonstrates memory. The immune system "remembers" if it has seen an antigen before and it reacts to secondary exposures to an antigen in a manner different than after a primary exposure. Generally only an exposure to the same antigen will illicit this memory response. C. Specificity - A third characteristic feature of the specific immune system is that there is a high degree of specificity in its reactions. A response to a particular antigen is specific for that antigen or a few closely related antigens T-independent Antigens B cell Figure 17.17 Self-tolerance • Body doesn't make Ab against self • Clonal deletion –The process of destroying B and T cells that react to self antigens T-Dependent Antigens Figure 17.16 Clonal Selection Cellular Events in 1o Response to T-dependent Ags • Lag – Clonal selection • Log 1o Ag – IgM – Class switching • Stationary • Decline • Memory Cell Pool IgM IgG Memory Cells Cellular Events in 2o Response to T-dependent Ags • Lag phase – Virgin cells – Memory cells Virgin B cell • Log phase IgG – Pool size – IgG, IgA or IgE • Stationary • Decline – Sustained production IgM Memory Pool Memory Cells IgG Memory Cells Memory T cells • T Cells – Virgin cells – Memory cells Virgin cell • Th cells Th Th – Cytokines • Long Term Memory Memory Pool Memory Cells Th Memory Cells Animation of cell selection TORTORA • FUNKE • CASE Immunoglobulin Genetics IgG IgM IgA IgD IgE How many types of Abs??? • 100 Millions 8 • 100,000,000 = 10 Immunoglobulin Genetics History • Same C region could associate with many V regions – IgG Ab with different specificities • Same V region could associate with many C regions – Same idiotype on IgG and IgM Ab • V and C regions coded for by separate genes Light Chain Gene Families Germ line gene organization Lambda light chain genes; n=30 V1 L P L V2 P L Vn J 1 P C 1 J 2 E J 3 C 2 E C 3 J 4 E C 4 E Kappa light chain genes; n=300 L P V1 L P V2 L P Vn J 1 J 2 J 3 J 4 J 5 C E Light Chain Gene Families Gene rearrangement and expression L V 1 P L V 2 P V n L P L V 1 P L V 2 J4 J 5 P L V J DNA C Primary transcript RNA L V J C mRNA Translation DNA C E E RNA Processing C E DNA Rearrangement Transcription J 1 J 2 J 3 J 4 J 5 RNA L V J C Protein Transport to ER V J C Protein V C