* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Immune System
Embryonic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Antiviral drug wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Regeneration in humans wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
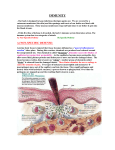
Immune System The body’s defense system Three Level Approach to Problem Level I - Non-Specific Defense: Prevent entry • Skin • Mucous Membrane • Secretions of skin and mucous membranes Level 2 – Non-Specific Defense: Search/Destroy at point of attack foreign objects • White blood cells • Antimicrobial proteins • Inflammatory response Damaged cells release chem. Signals: histamines protoglandins Capillaries dilate More permeability Clotting elements (Platelets) appear Clotting begin Phagocytic leukocytes enter region Attracted to chem. sig. Leukocytes consume pathogens and cell debris by phagocytosis Level 3 - Specific Defense: Complex system of interacting cells (immune pathway) Pathogen Macrophage T- Cell B-Cell Antibodies Lymphatic system (Protection 3) Lymph nodes, spleen, tonsils, thymus gland, appendix Lymph node – contains lymphocytes (T-cells, B-cells) Type of white blood cell -Filters pathogens that defends the body -Armpits,neck, intestines…. -get big when infection present Macrophages identify germs When a germ invades our bodies, macrophages gobble up the germ and display its surface shape, or antigen, for other immune cells to see. Helper T cells direct the defense Helper T cells spot the foreign antigen on the macrophage and begin to multiply. They alert other white blood cells and direct the body's defense. B cells make antibodies B cells start to make chemicals called antibodies. Antibodies lock onto foreign antigens making it easier for other immune cells to destroy them. Killer T cells destroy germs Alerted by helper T cells, killer T cells multiply and destroy the invading germs. Working together, our white blood cells can usually destroy invading germs. Antibody An antibody is a protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects like bacteria and viruses. Each antibody recognizes a specific antigen unique to its target. Antibody Immunity • Antigen – the foreign invader surface proteins (recognized phagocytes/lymphocytes) – When an antigen is present, body produces ___________ antibodies in response, that are specific (complementary) to that antigen (shape matches!) Check out the cartoon http://www.nyscience.org/whataboutaids/whatis/immune/content.html What? I don’t understand! • Macrophage eats pathogen (puts antigen on surface) • Proteins from antigen are expressed on macrophage surface • T-cells recognize these antigen proteins as non-self and start signaling • Some become Killer T-cells – secrete enzymes directly into infected cells and kill them • Others become Helper T-cells which stimulates more Killer T-cell growth, and stimulates growth of B-cells and their production of antibodies (helper T-cells are like the conductor of an orchestra – telling everyone when and how to play) Vaccines (Active immunity)– viral protein without genetic Info. (either from outside of envelope or the capsid protein itself) Prepares immune system for future Attacks, gives time to build up defense (helps Acquired Immunity) Vaccines • • • • Inactivated bacteria or virus Provokes immune response but not the disease or illness Memory cells react faster to second exposure Some pathogens mutate too quickly to be eliminated by vaccines Antibiotics • Chemicals produced by other organisms (like other bacteria or fungi) that kill/inhibit bacterial growth (not viruses!) • Eg. Penicillin, Ampicillin…. • Harms/prevents formation of bacterial cell wall (makes holes) – causes water to flow in [from high to low concentration, remember?] and kills bacterium.