* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Defense against disease, immune response
Kawasaki disease wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Behçet's disease wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Plant disease resistance wikipedia , lookup
Vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Childhood immunizations in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Social immunity wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Autoimmunity wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Herd immunity wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Multiple sclerosis research wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Schistosoma mansoni wikipedia , lookup
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
Transmission (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Germ theory of disease wikipedia , lookup
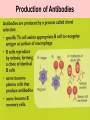
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
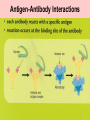
Sociality and disease transmission wikipedia , lookup
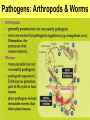
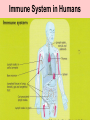
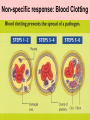
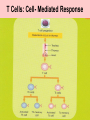
Detecting & Responding 2 Unit 3 Biology Area of Study 2 1 Physical and Chemical Barriers to infection 2 Defence against infection: Plants 3 Defence against infection: Humans 4 Detecting ‘Self’ & ‘Nonself’ Molecules 5 Infection and Disease 6 Pathogens: Bacteria 7 Pathogens: Fungi, Yeasts, Protozoa 8 Pathogens: Arthropods & Worms 9 Pathogenic Agents: Viruses, viroids and Prions 10 Transmission of Pathogens 11 Recognition 12 Disease – Terminology 1 Infection - growth of organism within body of host Chronic disease - long-term infection Acute disease - infection occurs suddenly, is short term Parasite - organism living on or in another organism, gains benefit, provides nothing. Not necessarily pathogenic. Carrier - person lacking particular disease but host to transmittable causative agent. Host - organism or cell on or in which a specific parasite lives 13 Disease – Terminology 2 Recognition Host - second host necessary in addition to host for completion of life cycle Vector - insect or other animal transmitting pathogenic organism from host to host Virulence - degree to which an organism can cause disease Pathogen - organism able to cause disease in host 14 Disease – Terminology 3 Recognition Epidemic - many people in region develop specific infectious disease over short period Pandemic - people world-wide develop specific disease as it spreads from origin relatively quickly Antibiotic - naturally occurring substances that inhibit growth or destroy bacteria & other micro-organisms Designer drug - drug constructed to inhibit activity of pathogen by fitting into 15 its active site Immune Response 16 Immune System in Humans 17 Function of the immune System 18 Innate Immunity 19 Cells of Immune System 20 Non-specific response: Inflammation 21 Non-specific response: Blood Clotting 22 Non-specific response: Phagocytosis 23 Immune response: Complement 24 Specific Immunity 25 B Cells: Humoral Response 26 T Cells: Cell- Mediated Response 27 Antigens 28 Antibodies 29 Production of Antibodies 30 Antigen-Antibody Interactions 31 Disorders of the Immune Response 32 Failures of the Immune System 33 Acquired Immunity 34 Active & Passive Immunity 35 Active & Passive Immunity 36