* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download and NK T cells
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Major histocompatibility complex wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
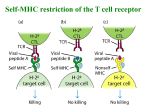
I. T Cells II. Invariant TCR T Cells T Cells in Autoimmune and Infectious Disease T cells can account for 30% of the T cell infiltrate in MS lesions (Wucherpfennig, K. W., et. al. PNAS 89:4588). T cells expand from 5 to 17% of PBMCs in patients during acute stages of P. Falciparum (Ho, M. et. al. Infect Immun. 62: 855–862). Similar T cell expansion has been observed in M. Tuberculosis infection and Chron’s disease. KO Mice Reveal a Unique role for Gamma Delta T Cells Infections agents can be lethal Gram-positive Nocardia asteroides Causes Lethal Infection in T Cell KO Mice Tam et. al., Infection & Immunity, 2001 69:6165. Lung Sections of Mice Infected with Aerosolized Gram-positive N. asteroides B6 -/- KO Neutrophils in -/- mice N. asteroides (dark blue stain) Tam et. al., Infection & Immunity, 2001 69:6165. KO mice reveal a unique role for Gamma Delta T cells Certain infections can be lethal. Most infections reveal inflammatory defects in KO mice. Pathological outcome is different than that of KO mice—which usually die upon infectious challenge. Skin wound healing is impaired. T Cells Distribute Differently Then T Cells Anatomically located lining the epithelial tissues Small numbers (1-2% of cells) found in the lymphoid tissues, spleen and lymph nodes might play a role early in the immune response Skin (V5 V1) Reproductive Tract Respiratory Tract Small Intestine (IELs) What do Gamma Delta TCRs recognize? CDR3 Length Distribution of Immune Receptor Chains B cell receptor Ag T cell receptor MHC T cell receptor Ag ? Ed Rock, et. al. What do Gamma Delta TCRs recognize? MHC class II, IEk. LBK5* T cell clone recognizes backbone residues of class II IEk and recognition is independent of the presented peptide. Important residues for LBK5 stimulation *LBK5 was generated from immunization with non-MHC matched splenocytes. Significance of IEk Recognition? Unlike MHC restricted T cell clones, peptide does not confer reactivity of LBK5 to IEk. Gamma delta T cells recognize antigens in a fundamentally different way than T cells. Gamma delta development seems to be normal in b2m-/- and MHC II negative mice, which suggest that the many of the TCR ligands are not conventional MHC molecules. What do Gamma Delta TCRs Recognize? MHC class II, IEk HSV-gI envelope protein HSV-1 gI envelope protein is left on the cell surface Viral DNA TgI4* T Cell Clone is Stimulated by Plate Bound HSV-gI Protein Cell lysis blocked by -TCR and -gI mAbs. *TgI4 was recovered from mice inoculated (I.V.) with HSV-1. Sciammas, R. et. al. J. Exp. Med 185:1969 Significance of HSV-gI Interaction? Like B cell Ig receptors, TCRs can recognize protein directly without need for processing and presentation upon MHC molecules. HSV-1 TgI4 Cytolitic activity T Cell TCR gI envelope protein is left on the cell surface Viral cDNA What do Gamma Delta TCRs Recognize? MHC class II, IEk gI HSV envelope protein Non-classical MHC T22/T10 T22 Tetramer Binds High Frequencies of T Cells T22 tetramer Non-immunized mice •T22 can’t present antigens because of its ‘truncated’ MHC barrel. TCR Crowley, M. et. al. Science 2000, 287:314 •T22 is upregulated on APCs upon CFA immunization or LPS stimulation. •Affinity measurements can be made between G8 TCR and T22. Significance of T22 Recognition? Self or ‘natural’ ligand This ligand is not recognized by TCRs, suggesting that the TCR recognize nonoverlapping ‘cues’ through the TCR. Significance of T22 Recognition? T cell Status of immune system Frequency1 T10/T22- specific T cells ~ 1/250 MHC/peptide specific T cells (not primed) ~ 1/1,000,000 MHC/peptide specific T cells (Immunized; effector phase) ~1/2-1/100 High frequencies = fast immune responses to ligand What do Gamma Delta TCRs recognize? MHC class II, IEk gI HSV envelope protein Non-classical MHC T22/T10 Small phosphate antigens Small Alkyl-Phosphate Antigens are Secreted by Bacteria and Also Expressed in Mammalian Tissues. Small phosphate antigens stimulate human and monkey V2 V2 T cells (Shen, Science, 295:2255-8). V2 V2 T cells expand (15-60%) in response to a variety of infectious agents. Reactivity is mediated through the TCR and the CDR3 is important for reactivity (Bukowski, J. I. 161:286) Cell contact is required (Morita, Immunity 3:495). No processing is required (fixed cells + small phosphate antigen = stimulation) (Morita, Immunity 3:495). Significance of Small Phosphate TCR Recognition? Ligands can either be self or foreign. Small phosphates are produced by the nucleotide salvage pathway, during cellular stress (i.e. heat shock, starvation, etc.) (Constant, P. Science 264:267). Suggesting that T cells monitor cellular stress. Other Reports of TCR Ligands MICA – a non classical MHC that is upregulated on tumor cells and upon heat shock (Wu, J. et. al. J. I. 169:1236). CD1c- No addition of antigen is required (Spada F et. al. JEM March 2000). Hsp60 has been reported to be stimulatory. Qa-1b can stimulate T cells. T Cell Summary T cells can recognize self (MHC and MHClike) and foreign ligands (HSV-gI, small phosphate antigens). Many of the ligands are up regulated on the surface of cells upon infection or stress. Taken together T cells might ‘see’ cell surface perturbations in homeostasis through their TCR and regulate the immune response. T Cell T22 Small phosphate antigens LPS Cell ‘Non-homeostatic’ Cell Viral derived surface Antigens II. Invariant TCR T cells. Invariant TCR T cells clonally/oligoclonally express TCRs with a limited P/N/Junctional CDR3 diversity. High frequencies are found in specific tissues. NK T cells, DETC T cells, MAIT cells. Invariant NK T cells (iNK T cells) Defined as being reactive to CD1d. Express the invariant V and limited V TCRs. iNK T cells represent the majority of T cells found in the liver. 1-3% found in the spleen. Express markers found on NK cells. V TCR sequences of CD1d restricted iNK T cells Mouse V14 P/N TGT GTG GTG GGC GCA C 1 TGT GTG GTG GGC CVVG 2 TGT GTG GTG GG DRGSA G CVVG GTA GAT AGA GGT TCA GCC CVV CVVG Human V24 CVVS GAT AGA GGT TCA GCC DRGSA 3 TGT GTG GTG 4 TGT GTG GTG GG J281 C TGT GTA GAT AGA GGT TCA GCC GAT AGA GGT TCA GCC VDRGSA T GAC D P/N AGA GGT TCA GCC RGSA JQ DRGST Lantz, O. and Bendelac, A., J. Exp. Med. 180:1097, 1994. What do the iNK T cells recognize? CD1d plus…. An unidentified endogenous self-glycolipid antigen. •-GlcCer synthase KO APCs fail to stimulate galcer/CD1d1 restricted NK T cells (Stanic et al. PNAS, 2003). •Selected by CD1, CD8, CD4, positive cells in the thymus (Nat Immunol. 2:971). -Galactosylceramide and iNK T cells -carbon linkage • CD1 family of B2m dependent class Ib proteins that can present a variety of lipid antigens to CD1 restricted T cells. • 80% of NK T cells (NK1.1+) in both mouse and human express an invariant TCR (mV14-J281, hV24-JQ) that recognize CD1d loaded with -GalCer. • Mammalians do not synthesize -GalCer which is derived from sea sponges. -Galcer is likely a structural mimic of a ‘self’ or ‘natural’ ligand. iNK T cells are specific for CD1d1 -Galcer Loaded with a-Galcer 1000 0.029 Not preloaded 1.35 0 2.09e-3 100 PhyEry PhyEry CD1d tetramer 100 1000 10 1 10 1 13.8 0.1 0.1 84.8 1 10 Fluor 100 TCR 1000 12.6 0.1 0.1 87.4 1 10 Fluor 100 1000 iNK T cell function Rapidly (within 1-2 hours) secrete IFN- and/or IL-4 upon stimulation in vivo (Yoshimoto T J. Exp. Med. 179:1285). J281-/- mice lack iNK T cells and have delayed immune responses to a variety of infectious agents. Dendritic Epidermal T cells (DETCs) promote wound healing -/B6 Jameson et. al. Science 296:747 What is the DETC TCR ligand? We don’t know…. Heat shocked keratinocytes stimulate DETC cells in a TCR dependent fashion (Haravan, W. Science 252:1430). This ligand is not sensitive to trypsin treatment (unpublished results), therefore is most likely not a protein. Table summarizing invariant T cell phenotypes Cell NK T MAIT DETC Conserved in Mouse and Man? iTCR (mouse) Development is dependent upon: Yes Va14Ja281 CD4+,CD8+, CD1+ Thymocytes Yes Va19Ja33 B cells, MR1+, Microbial Flora Vg5 Vd1 Conformationally dependent fetal TCR expression No Ligand Location Autoreactive Negatively selected? ? (similar to aGalcer) Liver, Spleen Yes ?(No in most models) ? Gut Lamina Propria Yes ? Yes ? (Yes, in some models) ? (not a protein) Skin First line of Defense Invariant and gamma delta T cells respond quickly to antigenic stimulus. Should these T cells be classified as being apart of the innate immune system or not?