* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Endocrine System
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
History of catecholamine research wikipedia , lookup
Endocrine disruptor wikipedia , lookup
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
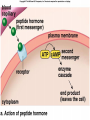
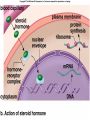
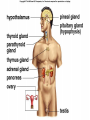
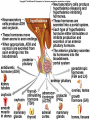
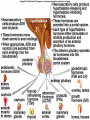
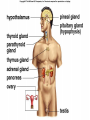
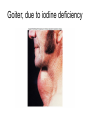
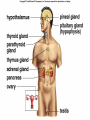
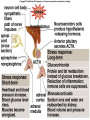
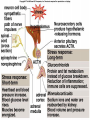
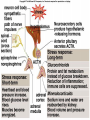
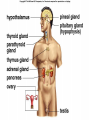
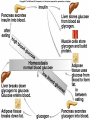
Endocrine System Hormones Endocrine glands • Endocrine glands make hormones • Hormones are chemical messengers transported in the bloodstream. • Hormones bring about a response, or change, in cells with matching receptors called target cells. Pituitary Gland • • • • • • • Master gland Located just below the brain Growth hormone (GH) Prolactin (‘lact-’ means milk) Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH) Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) Growth Hormone Growth hormone Pituitary Gland • Luteinizing Hormone (LH) • Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) • Oxytocin Thyroid gland • Located in the neck region • Makes thyroid hormone that regulates the rate of metabolism in the body • Iodine is needed for thyroid hormone Goiter, due to iodine deficiency Adrenal gland • Small glands located just on top of the kidneys • Inner portion is called the adrenal medulla • Makes epinephrine (aka adrenaline) and norepinephrine • Responsible for the fight or flight response Adrenal gland • Outer portion of the gland is the adrenal cortex • Cortisol helps the body conserve and store energy; suppresses the immune response; is anti-inflammatory Adrenal gland • The adrenal cortex also makes aldosterone • Results in sodium reabsorption from the kidneys to the bloodstream Pancreas • Located just below the stomach • Makes insulin that lowers blood glucose by taking it out of the bloodstream and into cells, such as brain cells • Diabetes Mellitus is due to not enough insulin, or the inability to respond to insulin Diabetes Mellitus • Type I, aka Insulin-dependent Diabetes is an autoimmune disease that attacks the insulin-producing cells of the pancreas • Type II, aka adult-onset Diabetes has a heavy hereditary component. Often associated with poor diet and obesity. • The last type of diabetes is called gestational diabetes associated with pregnancy.