* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mid-Year Review - The Bronx High School of Science
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
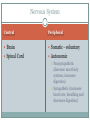
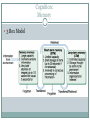
Mid-Year Review Psychological Perspectives Wave One: Introspection Structuralism (Wilhelm Wundt): mind operates by combining subjective emotion and objective sensations Functionalism Wave Two: Gestalt – view person’s total experience and did not separate behavior from thought (Max Wertheimer) – little impact on current theories Wave Three: Psychoanalysis – examination of unconscious mind (Freud); repression, defense mechanisms Wave Four: Behaviorism – scientific approach using observable outcomes. John watson, Ivan Pavlov, Skinner Wave Five: Multiple Perspectives – eclectic Psychological Perspectives: Multiple Perspectives Humanist: Maslow, Carl Rogers – stress individual choice and free will Psychoanalytic Biopsychology (neuroscience) – explain psychology as strictly biological processes (genes, neurotransmitters, structure, etc.) Evolutionary (Darwinian) – psychology in terms of natural selection Behavioral Cognitive – Jean Piaget, Erikson, etc. – examine thoughts and behaviors in terms of interpreting, processing and remembering information Social-cultural (sociocultural) – examine based on cultural influences Research Methods: Study Designs Case study – single or small group observed; highly detailed Correlational – examine relationships between variables Naturalistic – observe without interaction with participants Cross sectional – snapshot in time (correlation) Longitudinal – repeated measures of group of people Experimental – assign participants to control or experimental groups (causation) Experimental Design Random sampling – selection process of randomly choosing people from a target population to make your group under study Random assignment/Randomization – randomly assigning participants to control or experimental groups. People have equal chance of being put into each group Types of Bias Confounding – some third variable influences a relationship between two other variables (may make relationship eventhough not there or mask a relationship) Experimenter bias Response bias (social desirability) Hawthorne effect – people perform differently or better when known under observation Placebo Effect Overcoming Bias Blind or Double blind Placebo Counter balancing Statistics Measure of Central Tendency (middle) Mean, Median, Mode Measures of Spread Range, Variance, Standard deviation (average distance from the mean) SD: 68%, 95%, 99% Z-score: way to compare scores between different distributions 1 Z score = 1 Standard deviation Compare different distributions by comparing z score for values comparing Example: Mean 1 = 90, SD 1 = 2; Mean 2 = 80, SD 2 = 7 Statistics Continued Correlation coefficient – measure of relationship (-1 to 1) Scatter plot – graphical representation of relationship between 2 variables Positively skewed – mostly low, some high (outliers) Negatively skewed – mostly high, some low (outliers) Inferential Statistics P – value: 0.05 standard to compare your calculated p-value. If your value is less than 0.05 the relationship is statistically significant T-test – compare distributions using means; compare continuous data Chi-square – compare categorical data Ethics IRB – institutional review board Animal Research Clear scientific purpose Best chosen for question (can use cells not animal?) Cared for and housed in humane way Acquired animals legally Experiment must ensure least amount of suffering Human Research No coercion Informed consent Confidentiality Risk (Cost – benefit analysis) Debriefing Neuroscience (Biopsychological): Biological Basis for Behavior Neuroanatomy/Structure of the Neuron Dendrites – information in Interact with sense receptors Interact with neurotransmitters (receptors) Cell body/Soma – contains nucleus, synthesizes proteins/neurotransmitters Axon – carries action potential Myelin Sheath – fatty substance that insulates part of the axon and increases the speed/velocity of the action potential Terminal buds – information out (release neurotransmitters) Synapse – gap between dentrites and terminal bud of two neurons Communication in and between neurons Action potential Threshold Depolarization – Sodium channels open Repolarization – Potassium channels open Refractory period – sodium-potassium pump re-establishes the resting membrane potential All or none potential All action potentials look exactly the same Stimulus strength differentiated by number and frequency of action potentials Neurotransmitters Chemicals that diffuse across the synapse and interact with specific receptors on dendrites Review specific neurotransmitters Other information Afferent/sensory neuron Interneuron Efferent/Motor neuron Reflexes Nervous System Central Peripheral Brain Somatic - voluntary Spinal Cord Autonomic Parasympathetic (decrease most body systems, increases digestion) Sympathetic (increases heart rate, breathing and decreases digestion) Techniques to Study the Brain Lesions – damage or removal of brain tissue EEG – record brain wave activity CAT – x ray; structure not function PET – radioactive glucose; function MRI – structure not function fMRI – structure and function Brain Structure Hindbrain Sits on top of spine Medulla – control breathing, blood pressure, heart rate Pons – involved in facial expression Cerebellum – balance and coordination Midbrain Reticular formation – controls body arousal and ability to focus Damaged fall into deep coma Forebrain Thalamus – relay information from senses to different parts of brain Hypothalamus – controls body temperature, hunger, thirst, sexual arousal and endocrine system Cerebral Cortex Recent development in brain tissue Cognition Areas of the Cerebral Cortex Hemispheres: specialization of function (split-brain patients) Lobes Frontal Prefrontal – thought, inhibition (Phineas Gage) Broca’s area – controls speech Temporal Wernicke’s area – interprets written and spoken speech Hearing Parietal Somatosensory cortex (motor and sensory cortex) Occipital vision Other Brain Plasticity – ability to create new pathways/neural connections Neural networks – highly branching connections between many neurons; increased processing power Endocrine system Hypothalamus Pituitary Adrenal Testes/Ovaries Learning Classical Conditioning Ivan Pavlov John Garcia and Robert Koelling – Taste Aversion UCS, UCR, CS, CR Operant Conditioning Edward Thorndike (law of effect) Skinner: reinforcement vs. punishment Primary reinforcers: food, water, rest Secondary reinforcers: learn has value (money, power, etc.) Token economy Negative reinforcement v. negative punishment Negative reinforcement – remove a negative stimulus to increase a behavior Negative punishment – negative stimulus given to reduce a behavior Reinforcement schedules Fixed ratio – reinforced after set number of behaviors Fixed interval – reinforced after preset time Variable ratio – reinforced after variable number of behavior done Variable interval reinforced after varied times Variable schedules more resistant to extinction Ratio schedules promote higher response Contingency Models of Classical Conditioning Contiguity – more times two things are paired the greater the learning that takes place (Pavlov) Contingency – cognition plays a role in learning (Robert Rescorla) Observational Learning Albert Bandura Bobo Doll Other types of learning Latent (Edward Toleman) – rats learn a maze without reinforcement Insight (Wolfgang Kohler) – realize answer/solution to a problem (Ah ha moment) Cognition: Memory 3 Box Model Sensory Memory Iconic memory Echoic memory Selective attention – encode what we pay attention to Short Term Memory George Miller and Magic Number of 7 Improve: Chunking: grouping info into chunks to remember more Mnemonic device: ROYGBIV Rehearse Long Term Memory Episodic: specific events Semantic: general knowledge of the world, stored facts, meanings Procedural: skills and how to perform them Explicit/declarative: conscious memories/facts or events Implicit/nondeclarative: unintentional memories, do not realize you have these memories Eidetic: photographic memory Long term potentiation: strengthen connections between each other Levels of Processing Deep: recall better Shallow Retrieval Recognition: matching current event or fact with one already in memory (multiple choice questions) Recall: retrieve from external cues Primacy Effect (Hermann Ebbinghaus): recall things at beginning of list Recency Effect: recall things at end of list Serial Position Effect: combination of primacy and recency effect Tip of Tongue Phenomenon explained by semantic network theory Flashbulb memory: encoded because of importance to person Retrieval Continued Mood-congruent: greater to recall an item when mood matches the mood when event happened State-dependent: recall events better if in the same state of consciousness Constructive Memory Reconstructed memories may be false. May remember wrong: add or delete details Forgetting Retroactive Interference: learning new info interferes with recalling old info Proactive Interference: Older info interferes with recalling new info Anterograde Amnesia: cannot encode new memories Cognition: Language Phonemes: smallest units of sound Morphemes: smallest unit of sound with meaning Syntax: grammar of language Language Acquisition Babbling Holophrastic/ One word stage Telegraphic/ Two word stage Overgeneralization/Overregularization: misapplication of grammar rules Noam Chomsky: Language acquisition device (innate ability to learn language) Benjamin Whorf: Linguistic relativity hypothesis – language might control or limit our thinking Thinking and Creativity Concepts Prototype: most typical example of a concept Problem Solving Algorithm: rule that guarantees the right solution Heuristics: rule of thumb Availability: judge situation based on previous similar situation, may lead to wrong conclusion Representativeness: judging a situation based on how similar the aspects are to prototypes the person holds Belief Bias: illogical conclusions to confirm pre- existing belief Belief Perseverance: tendency to maintain a belief even after evidence presented that contradicts the belief Impediments to Problem Solving Rigidity Example: functional fixidness Confirmation bias: look for evidence to confirm belief and ignore other evidence Framing: how the problem is presented Creativity Wolfang Kohler: Insight learning Convergent thinking: One answer Divergent thinking: many potential answers Developmental Psychology Nature (Genetics) v. Nurture (Environment) Prenatal Development: Teratogens Fetal Alcohol Syndrome Drugs, Alcohol Motor/Sensory Development Reflexes 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Rooting: touch cheek turn head to feed Sucking Grasping Moro: splay arms and legs if “dropped” Babinski:toes spread when foot touched Parenting Konrad Lorenz: Imprinting (innate in some organisms) Harry Harlow: Monkeys raised with cloth and wire mothers. Spend time with one that comforts not feeds. Importance of sense of safety Ainsworth Secure attachment: confident explore when parent around, cry when leave and come to parents when return Avoidant attachment: resist being held, explore with parent around, do not go to parents for comfort Anxious/Ambivalent attachment: ambivalent to parents Parenting Styles Diana Baumrind Authoritarian: strict rules and punishment Authoritative: consistent standards, reasonable Permissive: no clear rules or enforcement of rules Uninvolved Stage Theories Jean Piaget Erikson Freud Vygotsky Jean Piaget Cognitive Development Sensorimotor: explore world with senses Object permanence (8 months) Preoperational: (2 – 7 years) Egocentric: Lack theory of mind: all think and feel like me Concrete operational Conservation of mass, volume and number Formal operational Abstract thinking Logical reasoning Criticism of Piaget Information processing model – continuous and not in discrete stages Vygotsky and Zone of proximal development Erikson and all his stages Trust v. mistrust Autonomy v. shame and doubt Initiative v. guilt Industry v. inferiority Identify v. role confusion Intimacy v. isolation Generativity v. stagnation Integrity v. despair Kohlberg and Morality Pre-conventional: make decisions to avoid punishment; decisions limited to own interest Conventional: look at moral choice through the eyes of others, what is right and wrong Postconventional: rights and values of an individual life (any individual) Criticism of Kohlberg Carol Gilligan Gender impacts how view situation so males not more moral than females Freud Stages of Development Oral: pleasure through mouth Oral fixation Anal: conflict around anus (toilet training) Anal fixation Phallic Oedipus complex: boy secretly in love with mother Electra complex: girl secretly in love with father Latency Genital: focus of pleasure through genitals Gender Development Biopsychological: neurological differences leads to gender Social-cognitive: own thoughts and social interactions guide development of gender Gender schemas Gender roles