* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Reconstruction
Fourteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Lost Cause of the Confederacy wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Fifteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Disenfranchisement after the Reconstruction Era wikipedia , lookup
Reconstruction era wikipedia , lookup
Radical Republican wikipedia , lookup
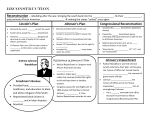
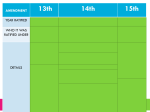
Reconstruction How to put the Union back together? Reconstruction • 1865 - 1877 • The period of rebuilding the South and restoring the Southern states to the Union after the Civil War 1 Andrew Johnson 2 • Lincoln’s VicePresident • Became 17th President when Lincoln was killed • Favored a generous plan to re-admit Southern states • Personally pardoned over 13,000 former Confederates Radical Republicans 3 • Believed that the main goal of Reconstruction should be the total restructuring of society to guarantee black people true equality • Opposed Lincoln’s plan and Johnson’s plan Freedmen’s Bureau Created by Congress in 1865 (after vetoed by President Andrew Johnson) Functioned as a division of the War Dept Supplied clothing, food, and medical supplies to war refugees Redistributed land abandoned or seized during the war Educated more than 250,000 freed slaves Discontinued in 1872 with pressure from white southerners 4 A Freedmen’s Bureau School A Freedmen’s Bureau School Black Codes 5 • Laws in Southern states that restricted the rights of freed blacks – Curfews (in doors by sunset) – Vagrancy laws (fined or whipped for not working) – Labor contracts (must sign and work for a year or lose all wages) – Land restrictions (could not rent or own house in town) th 13 Amendment 1865 Abolishes slavery 6 th 14 Amendment 7 1868 Defines citizenship to include African Americans Guarantees equal protection under the law for all citizens th 15 Amendment 1870 Citizens can not be denied the right to vote based on race, religion, color, or previous condition of servitude 8 Reconstruction Act 9 1867 - Passed by Radical Republicans in Congress Put the South under military rule Ordered states to create new constitutions All states had to allow black males to vote Required southern states to ratify 14th Amendment and to guarantee equal rights to all citizens Johnson’s Impeachment • Johnson opposed equal rights for African Americans • He fired his Secretary of War, Edwin Stanton, who was a friend of the Radicals • May 1868, Johnson was acquitted in the Senate by only one vote 10 Carpetbaggers Northern Republicans who moved to the South during Reconstruction Sometimes carried cheap suitcases made of scraps of carpet Insulting nickname used by Southerners who resented Northerners coming to profit on their misery 11 Carpetbag – a travel bag made from a scrap of carpet “Carpetbagger” coming from the North to profit from conditions in the South Scalawags Insulting name used by Southerners to refer to southern white Republicans whom they thought were traitors to the South 12 Sharecroppers 13 Workers who lived on land owned by others and farmed it for a share of the crops at harvest time. Many had to pay a planter for housing or food, which usually left them in debt every year. Tenant Farmers Rented land Grew and sold their own crops. Had a higher social status than sharecroppers. Sometimes saved enough money to buy their own land. 14 Ku Klux Klan Secret society of former Confederate leaders and plantation owners. Goal was to keep Blacks from gaining equality. Used terror and violence. 15 Solid South 16 Political changes after 1872 Ex-Confederates and other white Southern Democrats form a political force which blocks Republican Reconstruction policies and reforms. Marks the end of Republican control of the South. Compromise of 1877 17 The election of 1876 was nearly a tie in the popular and electoral votes. Southern Democrats agreed to give the election to Republican Rutherford B. Hayes if he agreed to Remove all remaining federal troops from the South. Give huge amounts of federal funding to build southern railroads. Rutherford B. Hayes Electoral Vote (185) Sates Won (20) Popular Vote (4,034,311) Percentage (47.9%) Samuel Tilden (184) (18) (4,288,546) (51%)