* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Bell Ringer - North Penn School District
Electoral reform in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Native American civil rights wikipedia , lookup
Larry C. Johnson wikipedia , lookup
Article Five of the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Jim Crow laws wikipedia , lookup
James Weldon Johnson wikipedia , lookup
Reconstruction era wikipedia , lookup
Fifteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
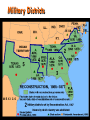
AMENDMENT 13th 14th 15th YEAR RATIFIED 1865 1867 1870 Congress (even though Johnson vetoed it) President Grant •All citizens were granted “equal protection of the laws” •It defined a citizen as “all persons born or naturalized in the United States” •It did not include Native Americans •It forbade states to “deprive any person of life, liberty, or property without due process of law.” •If a state denied any male citizen who was 21 years old (or older) the right to vote, that state would have its representation in Congress reduced •It forbade any state to deny any citizen the right to vote because of “race, color, or previous servitude.” •It did not apply to Native Americans or women WHO IT WAS President Lincoln RATIFIED UNDER DETAILS •Banned slavery and involuntary servitude, except as punishment for crime •Necessary because the emancipation proclamation did not free all slaves Lincoln and Reconstruction “with malice [harm] towards none, charity for all” – Lincoln - Confederate officials pardoned (forgiven of their crimes) - Freedmen’s Bureau established Freedmen’s Bureau Government agency set up to help former slaves who wanted to learn to read and write and set up their own communities Freedmen’s Bureau Ex-slaves and poor whites were aided by the federal government Gave them clothing and food Helped them to look for jobs Provided medical care for over 1 million people Set up schools – first funding of all black colleges (Howard University) With Johnson in charge… - - - Promised to return Confederate property in exchange for pledging loyalty to the United States Southern states set up new state gov’ts – many refused to ratify 13th amendment Southern states pass “black codes” which limit freedoms of former slaves and criminalize AfricanAmerican life Black Codes Excerpts from Codes of Mississippi: African-Americans … must have written proof of employment at all times are forbidden to meet in unsupervised groups cannot carry any form of weapon OR RISK INCARCERATION! (prison confinement and labor) Civil Rights Act 1866 All persons born in the United States were citizens (except Native Americans) But not Native Americans… Stated all citizens were entitled to equal rights (regardless of race) Johnson vetoes and Congress overrides Proposed 14th amendment but hit resistance by South and president RADICAL RECONSTRUCTION 1867 *Divided South into 5 military districts *Planter class lost right to vote Before Southern states could reenter union they must: th 1) Ratify 14 amendment (citizenship) 2) Allow African-American men to vote (15th amendment) 3) Disband state governments and write new state constitutions Military Districts What was not done? Land reform! Suggestion of 40 acres and a mule (Sherman) never realized Why is economic independence so important? Most of the new delegates writing southern state constitutions were Republican poor white farmers nicknamed Scalawags (scoundrels) for going along with the “radical” plan Carpetbaggers: People who headed South carrying only a cheap suitcase, known as a “carpetbag” Some African-American delegates as well Johnson fights back and so does Congress! Tenure of Office Act – prohibited Johnson from firing government officials without approval from Senate 1868 – Johnson fires Secretary of War Stanton over disagreements Leads to impeachment hearings against Johnson – acquitted by a single vote! Think about it… How does your plan compare to what the actual Congress voted to do during the Reconstruction period? Evaluate their decisions – was enough done?