* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Reconstruction
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Fifteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Reconstruction era wikipedia , lookup
Radical Republican wikipedia , lookup
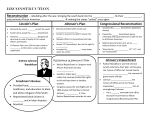
Reconstruction Chapter 16 Post war Problems Politically – How do you put the nation back together? Economically – How do you keep the nation from utter economic ruin? Social – How do you ease the hard feelings of the populous? – What will happen to the 4 million slaves that are now free? – What will the future hold for all people? Changes during the War 1862 – Pacific Railway Act gave huge grants of land to build the transcontinental railroad Land grants and federal subsidies were major source of funding Abraham Lincoln’s Plan Ten Percent Plan – 10% of the 1860 voters swear allegiance – Accept 13th Amendment – All except high-ranking civil and military leaders could be pardoned Bring the South back in as soon as possible Lincoln pocket vetoed the WadeDavis Bill Wade-Davis Bill July 1864 – created by Ben Wade (OH) & Henry Davis (MD) 1. Majority of white male citizens participate in creation of new government 2. To vote or be a constitutional conventions delegate men had to take an “iron-clad” oath 3. All Confederate officers ranking higher than a Lieutenant and civil officers would be considered non-citizens The Defeated South Many former slaves worked on abandoned plantations leased to Northern investors Sherman had given some 40 acre plots Congress created the Freedman’s Bureau – March 1865 – Provided food, medicine, schools/colleges for freed slaves and white refugees 13th Amendment – abolished slavery (1865) Andrew Johnson Background V.P. only during 2nd term Compromise to get Democrats to vote for Lincoln (Republican) Former War Democrat from Tennessee – sympathized with fellow white Southerners and committed to white supremacy Not the statesman that Lincoln was Andrew Johnson and Presidential Reconstruction Restrict reconstruction to the executive branch Restore the Union quickly Restore property rights to Southerners who swear allegiance to the Union Johnson’s Actions Granted amnesty to most Southern states while Congress was not in session Pardoned many of the political elite in the South if they swore allegiance to the Union High confederate officials, former federal officials, and West Point/Annapolis grads initially were not pardoned Ex-Confederates with taxable property > $20,000 personal appeal to President for voter rights Three Factions Northern Democrats = supported Johnson didn’t want racial equality Conservative Republicans = wanted limited federal role in the Reconstruction Radical Republicans = wanted to transform the South The Radical Republican Vision Punish the South Thaddeus Stevens, Charles Sumner Remake the South more like the North Wanted land redistribution to former slaves Wanted to exclude CSA officers and soldiers from political offices Favored black suffrage and rights of freed people Congressional Reconstruction Angry at Johnson’s plan and Southern black codes, the Senate proposed stronger legislation: Civil Rights Act of 1865 -Extended the power of Freedmen’s Bureau -Vetoed by Johnson and overridden by Congress 14th Amendment (1867) -Defined citizenship and protected that right! -Punished former Confederates 15th Amendment (1870)– right to vote regardless of race, color or former servitude Congressional Reconstruction Military Reconstruction Act of 1867 (First Reconstruction Act) -Passed over Johnson’s veto -Divided South into 5 military districts -Each run by a UNION military general with dictatorial powers To be “readmitted” to the Union: -States drafted Constitution granting black suffrage (in other words; they had to ratify the 14th & 15th Amendments) 3 Steps Towards Impeachement Final Straw =Tenure of Office Act Sec. of War Edwin Stanton One vote short of conviction The Election of 1868 Ulysses S. Grant – Republican Horatio Seymour - Democrat “Waving the Bloody Shirt” – Republican tactic of reminding Northern voters of Union casualties Blaming the South & Democrats for the war Moving About Black Codes – laws to restrict the freedom of blacks Radical Republicans very upset by these After Grant’s election he wanted to legalize voting for African Americans Result: 15th Amendment White Resistance and “Redemption” Re-establishing white supremacy & social order Redeemers = Conservative Democrats who gained control of southern states Violence & Intimidation: KKK – Ku Klux Klan Act The African-American Family Society based family and church Males took on more family authority but women continued to work outside the home Allowed to practice religion without interference Education – Freedman’s Bureau taught many First Black colleges established The Origins of African-American Politics Primary goals: equality before the law and guarantee of suffrage (right to vote) Five states had more blacks than whites Political organizations form New leaders emerge and get elected Prevented from voting by – Threats & intimidation – Poll taxes, grandfather clauses, literacy tests Land and Labor after Slavery Spread of sharecropping and tenant farming Most wanted to be self-sufficient farmers Not a real change from slavery and in some ways worse Southern Reconstruction Major issue: how to get things back to normal Confirmed the federal government was supreme over individual states Carpetbaggers & Scalawags – Whites who support republicans Grant Scandals Credit Mobilier – stealing Union Pacific Railroad – Congress investigates & is bribed to keep quiet Whiskey Ring – not paying tax, tax collectors being paid off Indian trading posts – Sec. of War being extorted to allow man to remain in charge Speculation in the gold market – James Fiske & Jay Gould Weakening Equality Slaughterhouse cases: said 14th Amendment only applied to national citizenship – not state citizenship U.S. v. Reese & U.S. v. Cruikshank – only applied to discrimination by the states The Age of Capital Rapid Industrialization – railroad boom Rise of monopolies & big business Mining & Oil Reconstructing the States: A Mixed Record Civil Rights Act of 1875 – outlawed racial discrimination in public places Idealism fades – Democrats gain strength Republican vision of modern South does not become reality Cotton prices spiral downward – South becomes an impoverished region Liberal Republicans and the Election of 1872 Old radicals die off Many appalled by corruption of the party Liberal Republicans call for return to limited government Propose Civil Service reform The Depression of 1873 Longest Depression in history to this point Clashes between labor and management High unemployment, falling prices on goods The Electoral Crisis of 1876 Samuel Tilden – Democrat Rutherford B. Hayes – Republican & war hero Disputed electoral votes Electoral Commission Compromise of 1877 Hayes – president End of military presence in South Appoint a Democrat to his cabinet Spend federal money on internal improvements in the South Other Chinese Exclusion Act – prohibited Chinese immigration to the U.S. for 10 years Thomas Nast – political cartoonist – Harper’s Weekly