* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 8thCivilWarPPTStudent
Battle of Roanoke Island wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Cumberland Church wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fredericksburg wikipedia , lookup
Texas in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Sailor's Creek wikipedia , lookup
Arkansas in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Union blockade wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Island Number Ten wikipedia , lookup
Second Battle of Corinth wikipedia , lookup
Battle of White Oak Road wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Appomattox Station wikipedia , lookup
Galvanized Yankees wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Perryville wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Port Royal wikipedia , lookup
Blockade runners of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Stones River wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Wilson's Creek wikipedia , lookup
East Tennessee bridge burnings wikipedia , lookup
Red River Campaign wikipedia , lookup
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Antietam wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Fort Fisher wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Shiloh wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Gaines's Mill wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Cedar Creek wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Seven Pines wikipedia , lookup
Battle of New Bern wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Lewis's Farm wikipedia , lookup
Confederate privateer wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Bull Run wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
Anaconda Plan wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Namozine Church wikipedia , lookup
Western Theater of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Economy of the Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
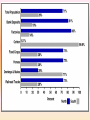
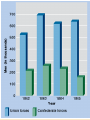
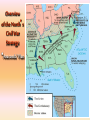
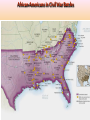
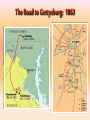
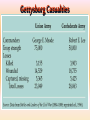
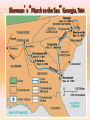
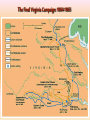
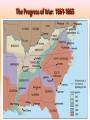
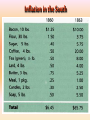
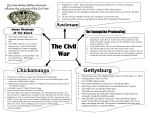
Georgia and the American Experience Chapter 8: The Civil War, A Nation in Conflict Study Presentation Georgia and the American Experience Section Section Section Section 1: 2: 3: 4: The The Life Life Road to War War on the Battlefield for the Civil War Soldier During the Civil War Section 1: The Road to War • Essential Question – What strategies were selected to win the Civil War? Section 1: The Road to War • What words do I need to know? – conscription – blockade – blockade runner – King Cotton Diplomacy – strategy The Leaders of the Confederacy Pres. Jefferson Davis VP Alexander Stevens The North Initiates the Draft, 1863: Conscription: “A rich man’s war, but a poor man’s fight.” Lincoln’s Generals Winfield Scott Joseph Hooker George McClellan, Ulysses S. Grant The Confederate Generals “Stonewall” Jackson George Pickett Nathan Bedford Forrest Robert E. Lee The War Begins • April 10, 1861, Major General P.G.T. Beauregard leads bombardment of Fort Sumter, in Charleston Harbor • Federal troops and laborers inside Fort Sumter surrender on April 13 • Arkansas, North Carolina, Tennessee, and Virginia secede from the Union • President Abraham Lincoln calls for 75,000 troops to put down the rebellion and protect Washington Assembling Armies • Most soldiers volunteered at first, but later men were conscripted (drafted to serve in the armies) • Some men received bounties (money) to sign up; some signed up, received the bounty, then deserted • Poorer men sometimes accepted money to fight in place of wealthier men who didn’t want to serve North vs. South in 1861 North South Advantages ? ? Disadvantages ? ? Resources, North and South • North had more people from which to create and resupply armies • North had more factories, better railroad system, the most number of males in the region, and most of the nation’s wealth • South had more experienced military leaders, and were highly motivated to defend their familiar homeland to win independence Railroad Lines, 1860 Resources: North & the South Men Present for Duty in the Civil War Blockade Strategy • Union blockaded all Southern ports to prevent cotton exports and imports of weaponry from Great Britain and France • Privately operated blockade runners successfully slipped past Union ships to ship goods to and from Europe during the war • The Union Navy included many ironclads (armored ships) Other Wartime Strategies • “Anaconda Plan”: To squeeze Confederacy to death by capturing the Mississippi River and cutting off Louisiana, Texas, and Arkansas • Capturing Richmond, the capital, might have ended the war early, but General Robert E. Lee’s Confederate Army prevented that for years Overview of the North’s Civil War Strategy: “Anaconda” Plan The “Anaconda” Plan Late War Strategy • Destroy Confederate armies on the battlefield • Lay waste to the Southern land, so that civilians would call for an end to the war • General William T. Sherman’s “March to the Sea” through Georgia was successful in the “lay waste to land” strategy Southern Strategies • Wear down the Union armies, which would hasten the northerners’ desire to end the war • Use swift raiders to help break the Union blockade • King Cotton Diplomacy: Temporarily stop exports to England and France to inspire those nations to help break the Union blockade; France and England instead starting importing Egyptian cotton Click to return to Table of Contents. Section 2: The War on the Battlefield • ESSENTIAL QUESTION – What were the major battles that took place in Georgia? Section 2: The War on the Battlefield • What words do I need to know? – Chickamauga – Atlanta Campaign – Emancipation Proclamation Battle of Fort Pulaski-April 1862 Battle of Antietam • fought on September 17, 1862, near Sharpsburg, Maryland, and Antietam Creek, • It was the first major battle in the American Civil War to take place on Northern soil • It was the bloodiest single-day battle in American history, with about 26,000 casualties. • Union Victory and the Confederates retreat to Virginia Battle of Antietam “Bloodiest Single Day of the War” September 17, 1862 23,000 casualties Freeing the Slaves • Lincoln issued the Emancipation Proclamation on September 22, 1862 • Document gave the Southern Confederacy a choice: Quit the war and keep slavery alive or keep fighting and slaves would be forever free • Deadline was January 1, 1863 • The Confederate leaders continued the war and the slaves were declared free by the United States government in 1863 The Emancipation Proclamation The Famous 54th Massachusetts Robert G. Shaw Robert G. Shaw African-Americans in Civil War Battles Battle of Gettysburg Generals Union Confederate George Meade Robert E. Lee The Road to Gettysburg: 1863 Battle of Gettysburg “Turning Point” • fought in and around the town of Gettysburg, Pennsylvania, • The largest number of casualties in the American Civil War on BOTH sides • Is frequently cited as the war's turning point. • Union Maj. Gen. George Gordon Meade defeated attacks by Confederate Gen. Robert E. Lee, ending Lee's invasion of the North. Gettysburg Casualties Union Battle of Chickamauga William S. Rosecrans Confederate Braxton Bragg The Battle of Chickamauga • September 1863 • Seven miles south of Chattanooga, Tennessee • Chattanooga was major railroad center • Union troops were driven back to Chattanooga; Confederates did not follow-up on their victory • TWO most important reasons for this battle: 1. Largest Union defeat in western theater of CW 2. Due to South’s victory, General Bragg focused on recapturing Chattanooga • Union reinforcements later recaptured Chattanooga The Atlanta Campaign • Late Spring/Early Summer 1864: Sherman’s Union Army fought series of battles against Joseph E. Johnston’s Confederate Army • Confederates continued to retreat further southward into Georgia • June 1864: Sherman attacked Johnston at Kennesaw Mountain; Sherman lost but continued toward Atlanta • July 1864: John Bell Hood replaced Johnston, battled Sherman, then concentrated defenses in Atlanta The Battle of Atlanta • Sherman surrounded the city and laid siege • Hood wanted to lure Sherman into the city to fight, but that didn’t work • Fighting continued during July and August 1864 • Hood and Atlanta’s citizens finally vacate the city on September 1 • Sherman burns the city in mid-November then begins his march toward Savannah and the sea The March to the Sea • Sherman’s Union army destroys everything in its path, 300 miles from Atlanta to Savannah • A sixty mile-wide area is burned, destroyed, and ruined during a two-month period • Estimated losses exceeded $100 million • Captured, but did not burn, Savannah in December 1864 • Loaded and shipped $28 million worth of cotton, stored in Savannah, to the North Sherman’s “March to the Sea” Georgia, 1864 The Civil War Ends • January 13, 1865: Fort Fisher in North Carolina captured;the last Confederate blockade-running port • General Robert E. Lee’s Army of Virginia cannot defeat Union General U.S. Grant at Petersburg; he surrenders his army at Appomattox Courthouse on April 9, 1865 • Confederate President Jefferson Davis flees and is eventually captured in Irwinville, Georgia The Final Virginia Campaign: 1864-1865 Surrender at Appomattox: April 9, 1865 The Progress of War: 1861-1865 Civil War Casualties in Comparison to Other Wars Inflation in the South Jefferson Davis is captured… Confederate Civil War Prisons • One of the Confederate prisons for Union soldiers was in Andersonville, Georgia. • Prisoners were only given shelter that they could piece together themselves and there was not enough food, water, and medical supplies. • During its operation, almost 13,000 Union prisoners died. • Prison commander Captain Henry Wirz was executed for “excessive cruelty” in 1865. Union Civil War Prisons • The harsh prison conditions were not only found in the South. • A Union prison for Confederate soldiers was in Elmira, New York. • One-fourth of the 12, 123 Confederate prisoners died there. • Many prisoners faced malnutrition, exposure to cold, and poor medical conditions.