* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PPT
Battle of New Bern wikipedia , lookup
Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
East Tennessee bridge burnings wikipedia , lookup
Fort Fisher wikipedia , lookup
List of American Civil War generals wikipedia , lookup
Blockade runners of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Ulysses S. Grant and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Antietam wikipedia , lookup
Cavalry in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Secession in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Texas in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Seven Pines wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Wilson's Creek wikipedia , lookup
Lost Cause of the Confederacy wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Shiloh wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Lewis's Farm wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Namozine Church wikipedia , lookup
Baltimore riot of 1861 wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Bull Run wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Gaines's Mill wikipedia , lookup
Economy of the Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Pacific Coast Theater of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Confederate privateer wikipedia , lookup
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
Anaconda Plan wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
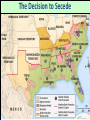
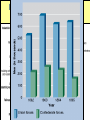
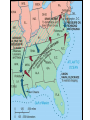
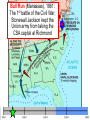
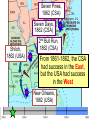
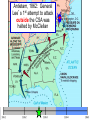
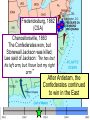
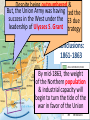
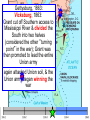
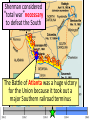
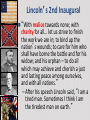
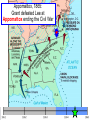
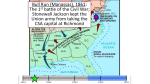
The Civil War: 1861 -- 1865 (Unit III, Segment 2 of 3) Essential Question: – What factors led to the outbreak of the Civil War? Warm-Up Question: – If the Union had more troops, industry, & transportation when the Civil War began, what should their war strategy be? Secession of the Southern States Lincoln's election in 1860 brought the Southern states to the point of secession and Lincoln to a fateful question: Should he allow peaceful secession or should he coerce the rebels to stay in the Union? First Inaugural Address “In your hands, my dissatisfied fellow countrymen, and not in mine, is the momentous issue of civil war. The government will not assail you. You can have no conflict without being yourselves the aggressors. You have an oath registered in Heaven to destroy the government, while I shall have the most solemn one to ‘preserve, protect, and defend it.” “I am loath to close. We are not enemies, but friends. We must not be enemies. Though passion may have strained, it must not break our bonds of affection. The mystic chords of memory, stretching from every battlefield and patriot grave to every living heart and hearthstone all over this broad land, will yet swell the chorus of the Union when again touched, as surely they will be, by the better angels of our nature.” Secession in the South The failed Crittenden Lincoln’s election led to in 1860 Compromise secession by 7 states in the Deep South but that didCarolina not Fort Sumter, South necessarily mean “civil war” Two things had to happen first: –One last failed attempt to reconcile the North & South –The North had to use its military to protect the Union TheNortherners Upper South did notthe view Some thought Lincoln’s election as aoff death sentence U.S. would be better if the & was did not secede South allowed to immediately peacefully SC seceded on secede The entire Deep South Dec 20,1860 seceded by Feb 1861 “Lame duck” Buchanan took no action to stop the South from seceding The Decision to Secede The CSA constitution resembled the U.S., but Secession & the Formation of the with 4 key changes: (1) it protected states’ On Feb 4, 1861, the Confederate rights, (2) guaranteed slavery, (3) referenced Confederate States of America of America weretariffs formed God, & (4)States prohibited protective Mississippi Senator Jefferson Davis was elected CSA president When Lincoln was elected in 1860, The4 more Start of the Civil 1861 Southern states seceded in& 7 Southern states seceded fromWar, the Union 1861 LincolnStates calledof forAmerica military formed the when Confederate volunteers to “preserve the Union” The Civil War began when Fort Sumter was fired upon by Confederate soldiers Fort Sumter Flag The Civil War Soldier Northern Advantages At the outbreak of the Civil War, the North had lots of advantages: – Larger population for troops – Greater industrial capacity – Huge edge in RR transportation Problem for the North: – Had to invade the South to win – Difficult to maintain enthusiasm & support for war over time Resources of the Union and the Confederacy, 1861 Southern Advantages Although outnumbered & less industrial, South had advantages: – President Davis knew that they did “King Cotton” not have to “win” the war; the diplomacy South only had to drag out the fight & make the North quit – Had the best military leaders – England & France appeared more Robert E. willing“Stonewall” J.E.B. to support the South Lee Jackson Stuart Union Strategy The Union strategy during the war was called the Anaconda Plan: – Blockade the coast, seize the Mississippi River to divide the South, & take Richmond – Exploit South’s dependency on foreign trade & its inability to manufacture weapons – Relied on Northern advantages in population, industry, & military production Take control of the Mississippi River Take the CSA capital at Richmond Ulysses Grant in the West Divide the West from South Blockade the Southern coast George McClellan was in charge of Army of the Potomac Confederate Strategy The Confederate strategy during the war was an Offensive / Defense: – Protect Southern territory from “Northern aggression” but attack into Union territory when the opportunity presents itself – Get Britain & France to join their cause because of European dependency on “King Cotton” – Drag out the war as long as possible to make the North quit Political Leadership During the Civil War During the Civil War, During the Civil War, President Lincoln used President Jefferson Davis The national government in the USA & CSA “emergency powers” to had a difficult time: relied on volunteer armies in the beginning, but protect “national security”: •The CSA Constitution soon needed conscription (draft) to supply their •Suspended habeas corpus protected states’ rights armies(Laws withrequiring troops evidence so state governors could before citizens can be jailed) refuse to send him money •Closed down newspapers or troops • that did not support the war •CSA currency inflated by 7,000% New York City Draft Riots Fighting the Civil War 1861-1865 Fighting the Civil War: 18611865 From 1861 to mid-1863, the Confederate army was winning the Civil War: – Defensive strategy carried out by superior Southern generals like Robert E. Lee & “Stonewall” Jackson – Disagreements among military & political leaders in the North Bull Run (Manassas), 1861: The 1st battle of the Civil War; Stonewall Jackson kept the Union army from taking the CSA capital at Richmond Seven Pines, 1862 (CSA) Seven Days, 1862 (CSA) Shiloh, 1862 (USA) 2nd Bull Run, 1862 (CSA) From 1861-1862, the CSA had success in the East, but the USA had success in the West New Orleans, 1862 (USA) Antietam, 1862: General Lee’s 1st attempt to attack outside the CSA was halted by McClellan Antietam, 1862 Even though the Battle of Antietam ended without a clear winner, it had important effects on the North: – The battle convinced Britain & France not to support the Confederacy in the war – The battle convinced Lincoln that the time was right to make the emancipation of slaves the new focus of the war for the North Battle of Antietam “Bloodiest Single Day of the War” 23,000 casualties Emancipation Proclamation After Antietam, Lincoln issued the Emancipation Proclamation: “…all persons held as slaves – This executive orderwithin freedany allState or designated of a State, the people slaves inpart Confederate territories whereof shall then be in rebellion against the – It did notshall free in the border United States, beslaves then, thenceforward, and forever and theitExecutive states,free; however gave the North Government of the United a new reason fightStates, including the military and naval authority thereof, will – Inspired Southern toofescape recognize and maintain theslaves freedom such which Southern whites to persons, andforced will do no act or acts to repress such worry persons,about or anytheir of them, in any efforts farms they may make for their actual freedom...” States Impacted by the Emancipation Proclamation Lincoln, “The Great Emancipator” Escaped slaves in NC coming into Union lines African-American Recruiting Poster The Famous 54th Massachusetts African Americans in Civil War battles Fredericksburg, 1862 (CSA) Chancellorsville, 1863 The Confederates won, but Stonewall Jackson was killed; Lee said of Jackson: “He has lost his left arm, but I have lost my right arm” After Antietam, the Confederates continued to win in the East Despite being outnumbered & But, the Union Army under-equipped, the was CSA having dominated the successininthe theEast Westfrom under the fighting 1861-1863 due of Ulysses S. Grant strategy toleadership better generals & a defensive Conclusions: 1861-1863 By mid-1863, the weight of the Northern population & industrial capacity will begin to turn the tide of the war in favor of the Union Fighting the Civil War: 18631865 When the Civil War began, most expected the fighting to end quickly, but the war lasted until 1865 due to: – The commitment of the Union & Confederacy to “total war” – Excellent Southern generals like Robert E. Lee – Improved, industrial weaponry New Weapons but Old Tactics • New weapons: – Long-range artillery & the Gatling gun (1st machine gun) – Cone-shaped bullets & grooved barrel rifles for more accuracy – Ironclad naval ships like the USS Monitor & CSS Virginia • Old tactics such as massed formations & frontal assaults – Led to huge casualty rates Dead on the Battlefield Dead on the Battlefield Fighting “Total War” Women took gov’t jobs as Women’s most st The Civil War was the world’s 1 roleA bookkeepers, clerks & prominent secretaries; as nurses on “total of war” in which the entire number women alsowas served as spies theCSA) battlefield: (Rose Greenhow, economy was devoted to distributing medical supplies, winning: organizing hospitals, & –North & South employed offering comfort to female workers to meet supply wounded or dying soldiers demands Ex. Clara Barton future founder of the American Red Cross The Tide of the War Turns in 1863 By 1863, the Confederacy was having difficulty sustaining the fight: – Attempts to lure Britain & France into the war had failed – The Union blockade, limited Southern manufacturing, & lack of grain fields left CSA soldiers illsupplied – To pay for the war, the CSA printed money leading to massive inflation Gettysburg, 1863: In July,Vicksburg, Robert E Lee decided to 1863: take advantage of his access victory at Grant cut off Southern to Chancellorsville & attackthe Mississippi River & divided Northern soil two to end the war South into halves quickly by the crushing Union (considered other “turning morale point” in the war); Grant Gettysburg proved to be was the then promoted the entire turning pointto oflead the war; Lee Union army was halted, the CSA never again attacked Union soil, & the Union army began winning the war Gettysburg Address The to principles thatthat ourthe We need make sure government founded upon Union wins the were Civil War in order to preserve our form of gov’t This Civil War is a test to see if these principles will last, because other republics have failed Fighting the Civil War: 18631865 Under Grant’s leadership, the Union army was more aggressive & committed to destroy the South’s will to fight: – Grant appointed William T. Sherman to lead the Southern campaign – Sherman destroyed everything of value to the South & emancipated slaves during his “march to the sea” Sherman considered “total war”necessary to defeat the South The Battle of Atlanta was a huge victory for the Union because it took out a major Southern railroad terminus Lincoln’s 2nd Inaugural “With malice towards none; with charity for all… let us strive to finish the work we are in; to bind up the nation’s wounds; to care for him who shall have borne the battle and for his widow; and his orphan – to do all which may achieve and cherish a just and lasting peace among ourselves, and with all nations.” – After his speech Lincoln said, “I am a tired man. Sometimes I think I am the tiredest man on earth.” Appomattox, 1865: Grant defeated Lee at Appomattox ending the Civil War On April 9, 1865, Lee surrendered to Grant at Appomattox Courthouse, ending the fighting of Civil War Ford’s Theater (April 14, 1865) The Assassin John Wilkes Booth The Assassination WANTED~~!! “Now He Belongs to the Ages!” -- Edwin M. Stanton, Secretary of War Funeral March The Execution Effects of the War Effects of the Civil War: – 620,000 troops were dead; More than any other U.S. war – The 13th Amendment was ratified in 1865 ending slavery – The war forever ended the states’ rights argument – The South was destroyed; A plan was needed to admit Southern states back into the Union Conclusions The turning point of the war: 1863 – The Civil War began as a conflict “to preserve the Union,” but by 1863 it became a war for human liberty (Emancipation Proclamation was issued) – The South dominated the early campaigns of the war due, but by 1863 (Gettysburg & Vicksburg) the weight of Northern industry & population wore down the South