* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SECESSION AND THE CIVIL WAR
Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Bull Run wikipedia , lookup
Secession in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Seven Pines wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Shiloh wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Gaines's Mill wikipedia , lookup
Texas in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Fort Fisher wikipedia , lookup
Reconstruction era wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Namozine Church wikipedia , lookup
Galvanized Yankees wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Lewis's Farm wikipedia , lookup
Photographers of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Ulysses S. Grant and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Economy of the Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Lost Cause of the Confederacy wikipedia , lookup
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
Anaconda Plan wikipedia , lookup
Baltimore riot of 1861 wikipedia , lookup
Pacific Coast Theater of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Confederate privateer wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Jubal Early wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
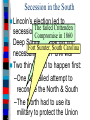
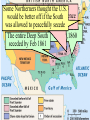
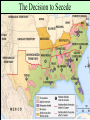
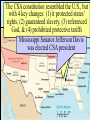
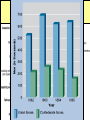
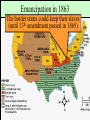
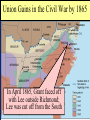
Secession & the Outbreak of the Civil War Secession in the South Lincoln’s election led to The failed Crittenden secessionCompromise by 7 statesinin1860 the Deep South but that did not Fort Sumter, South Carolina necessarily mean “civil war” Two things had to happen first: –One last failed attempt to reconcile the North & South –The North had to use its military to protect the Union Upper South didthe notU.S. view Some The Northerners thought Lincoln’s election a death sentence would be better off as if the South & did not secede immediately was allowed to peacefully secede SC seceded on The entire Deep South Dec 20,1860 seceded by Feb 1861 The Decision to Secede The CSA constitution resembled theofU.S., Secession & the Formation the but with 4 key changes: (1) it the protected states’ On Feb 4, 1861, Confederate Confederate States of America rights, (2) guaranteed slavery, (3) referenced States of America were formed God, & (4) prohibited protective tariffs Mississippi Senator Jefferson Davis was elected CSA president Fort Sumter, South Carolina In April 1861, a skirmish at Fort Sumter, SC led to the 1st shots fired of the Civil War Adjusting to Total War Northern Advantages At the outbreak of the Civil War, the North had lots of advantages: –Larger population for troops –Greater industrial capacity –Huge edge in RR transportation Problem for the North: –Had to invade the South to win –Difficult to maintain enthusiasm & support for war over time Resources of the Union and the Confederacy, 1861 Southern Advantages Although outnumbered & less industrial, South had advantages: –President Davis knew that they did not have to “win” the war; the South only had to drag out “King Cotton” the fightdiplomacy & make the North quit –Had the best military leaders –England & France appeared Robert E “Stonewall” J.E.B. Lee more willing Jackson to support Stuart the South Winfield Scott’s Anaconda Plan Southern strategy was an “offensive defense”: Take the CSA capital drag control out the war & strategically attack the Take of the at Richmond North toRiver destroy Northern morale Mississippi Ulysses Grant in the West Divide the West from South Blockade the Southern coast George McClellan was in charge of Army of the Potomac Political Leadership During the Civil War Davis was less Lincoln effective: expanded his –concerned powers: mainly with –declared military duties martial law –neglected the –imprisoned economy “subversives” –obstructed by –briefly closed state governors down a few who resisted newspapers conscription Fighting the Civil War From 1861-1863, the South consistently beat the North due to poor Union leadership & the Southern defensive strategy The Civil War 1st battle was Bull Run (Manassas, VA) on The U.S. & CSA forces fought to a July 21, 1861; “On to Richmond” campaign draw at Antietam in Sept 1862—the was repulsed by “Stonewall” Jackson single bloodiest day of the Civil War Fighting “Total War” Women took gov’t jobs as bookkeepers, clerks & secretaries; Cone-shaped bullets &A number of womenst The Civil War was the world’s 1 also served as spies (Rose Greenhow, CSA) grooved barrel rifles Massive frontal assaults and massed “total war” in which the entire Repeatingwith rifles formations as & many as 100,000 soldiers economy was devoted to winning: the Gatling gun –North & South Shrapnel, booby traps, drafted soldiers & land mines –North & South employed female workers to meet supply demands Women’s most prominentold roletactics, were as nurses –New weapons, & on the battlefield: distributing medical sheer numbers of troops in supplies, organizing hospitals, & offering battletoled to massive comfort wounded or dyingcasualties soldiers Battle of the Ironclads (1862): CSS Virginia vs. USS Monitor Confederate ironclad CSS Virginia was built using the remains of the USS Merrimack USS Monitor was a revolutionary design: rotating turret & low profile Confederate Prison Camp in Andersonville, GA Union Prison Camp at Andersonville, GA Built to hold 10,000 prisoners; but held more than 32,000 Union POWs Mobilizing the Home Fronts The draft was unpopular among Southern Both&the North antiwar & South faced governors Northern, “Copperheads” problems supporting the war: –Both sides began running out of troops; in 1862, the North & South began conscription (draft) –Funding the war was difficult; both sides printed paper money (greenbacks) to accommodate spending needs; led to runaway inflation (9,000% in the South) The Coming of Emancipation At the beginning of the war, the North was fighting to preserve the Union, not to abolish slavery By mid-1862, many Northerners called for immediate emancipation –Congress refused a gradual plan –Many thought immediate freedom for slaves would lure England & France into alliance –Southern victories pressured the North to “strike back” The Emancipation Proclamation Union “success” at Antietam led Lincoln to issue the Emancipation Proclamation on January 1, 1863: –Lincoln freed all slaves in Confederate territories –This did not free a single slave but Passed it gaveafter thethe North new Civil a War ended on the Jan 31, 1865 reason fight Civil War –Inspired slaves to flee North Pushed for the 13th Amendment Emancipation in 1863 The border states could keep their slaves (until 13th amendment passed in 1865) The Tide Turns in 1863 By New earlyYork 1863, North Citythe Draft Riot & South both faced morale problems: –South—economic & diplomatic collapse, runaway slaves, & many yeomen refused to fight –North—consistent losses against Lee, draft riots in NYC, anti-war “Copperheads” played on war failures & racial anxieties Fight to the Finish But by 1863, the war began to turn in favor of the North: –Northern supremacy in industry & manpower began to take its toll on the exhausted South –The North began enlisting blacks into the Union army; 200,000 fought as soldiers & many others served as labor in the Northern war effort Grant began a siege on Richmond and… Due to Grant’s success in the west, In Lincoln July 1863, General Grant took Vicksburg made Grant supreme commander & of gained control of the Mississippi River Union army in 1864; Grant devised a strategy to invade the South on all fronts The Civil War Lee ledSherman an attackbegan into the William hisNorth, lostsea” at Gettysburg; 1st “marchbut to the (Atlanta to North’s Savannah) real victoryofinmilitary the east value & destroyed everything Now we are engaged in a The world will little —that we here highly Gettysburg Address great civil war, testing But,or in long a larger sense, note remember resolve that these dead whether that nation, or any ItFour is rather for us to be score and seven we can not dedicate, what we say here, but shall not have died in nation so conceived and soit here dedicated to the years ago our we not consecrate, dedicated, canforget longnation, endure. cancan never what vain—that this great task remaining forefathers brought We are met on a great battlewe can not hallow this they did here. It is fora under God, shall have before us—that field of that war. Wefrom have forth on this continent, ground. For the brave us the living, rather, to new birth of freedom— come tohonored dedicate adead portion of these we a new nation, men, living and dead, be dedicated hereresting to the and that government of that field, as a final take increased devotion conceived in Liberty, who struggled place for those who here unfinished work which the people, byhere, the to that cause for which and dedicated to the gave their lives that that have consecrated it far they whoand fought here people, for the they gave the last full nation might live. Itall is proposition that abovethus our poor power have far so nobly people, shall not perish altogether fitting andequal. proper measure of devotion— men are created tofrom add or detract. advanced. the earth. that we should do this. Election of 1864 Meanwhile, Lincoln faced a tough re-election in 1864 against General George McClellan: –War failures were a key issue –Radical Republicans considered dropping Lincoln from the ticket But, when Atlanta fell during Sherman’s “March to the Sea,” nd In his 2 inaugural address, Lincoln promised Lincoln regained support and was a Reconstruction Plan for the Union with “malice towards none reelected & charity for all” overwhelmingly Union Gains in the Civil War by 1865 In April 1865, Grant faced off with Lee outside Richmond; Lee was cut off from the South On April 9, 1865, Lee surrendered to Grant at Appomattox Courthouse, ending the fighting of Civil War The Death of Lincoln Northern celebration was short lived; On April 14, 1865, Lincoln was shot by pro-Southerner John Wilkes Booth Effects of the War Effects of the War Social changes: –618,000 troops were dead –Women in both the North & South were forced to take on more non-domestic roles –13th Amendment ended slavery –Nativism decreased as many immigrants fought in Civil War EndedEffects the Southern argument of the War over nullification & states’ rights Political changes: –The Civil War established that the national gov’t is supreme over the states –With no Southern opposition, Republicans passed new laws: Homestead Act (1862), Morrill Act (1862), a protective tariff, land grants to RR companies, & a national banking system Conclusions The turning point of the war: 1863 –The Civil War began as a conflict “to preserve the Union,” but by 1863 it became a war for human liberty (Emancipation Proclamation was issued) –The South dominated the early campaigns of the war due, but by 1863 (Gettysburg and Vicksburg) the weight of Northern industry & population wore down the South