* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Civil War
Texas in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Wilson's Creek wikipedia , lookup
List of American Civil War generals wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Antietam wikipedia , lookup
Ulysses S. Grant and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Lost Cause of the Confederacy wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Lewis's Farm wikipedia , lookup
Economy of the Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Cavalry in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Baltimore riot of 1861 wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Shiloh wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Seven Pines wikipedia , lookup
Maryland Campaign wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Namozine Church wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Cedar Creek wikipedia , lookup
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Bull Run wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Gaines's Mill wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Confederate privateer wikipedia , lookup
Pacific Coast Theater of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Anaconda Plan wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
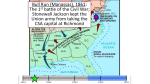
The Civil War: 1861—1865 I. The Civil War A. The Start of the Civil War, 1861 1. When Lincoln was elected in 1860, 7 Southern states __________________________ from the Union & formed the __________________________________________ of America 2. The Civil War began when _______________________________________ was fired upon by Confederate soldiers 3. 4 more Southern states seceded in 1861 when Lincoln called for military volunteers to “_____________________” B. Strategies & Advantages 1. The Union strategy during the war was called the _____________________ Plan: a. ____________________ the coast, seize the Mississippi River to _______________ the South, & take Richmond b. Exploit South’s dependency on foreign trade & its inability to _________________________________ weapons c. Relied on Northern advantages in ________________________, _____________________, & military 2. The Confederate strategy during the war was an _____________________________________________________: a. Protect Southern territory from “Northern aggression” but _______________________ into Union territory when the opportunity presents itself b. Get ______________ & ______________ to join their cause because of European dependency on “King Cotton” c. ______________________ the war as long as possible to make the North quit C. Political Leadership During the Civil War 1. During the Civil War, President Lincoln used “______________________________” to protect “national security”: a. Suspended _____________________________________ (Laws requiring evidence before citizens can be jailed) b. Closed down ___________________________ that did not support the war 2. During the Civil War, President _______________________________________ had a difficult time: a. The CSA Constitution protected _____________________________________ so state governors could refuse to send him money or troops b. CSA _______________________ inflated by 7,000% 3. The national government in the USA & CSA relied on _____________________________ armies in the beginning, but soon needed _______________________________ (draft) to supply their armies with troops II. Fighting the Civil War: 1861-1863 A. From 1861 to mid-1863, the Confederate army was ____________________ the Civil War: 1. Defensive strategy carried out by superior Southern generals like ___________________ & ___________________ 2. ___________________________ among military & political leaders in the North B. Battles: 1. ___________________________ (Manassas), 1861: The 1st battle of the Civil War; Stonewall Jackson kept the Union army from taking the CSA capital at Richmond 2. From 1861-1862, the CSA had success in the _______________, but the USA had success in the _______________ 3. Antietam, 1862 a. Antietam, 1862: General Lee’s 1st attempt to invade ____________________ the CSA was halted by McClellan b. Even though the Battle of ________________________ ended without a clear winner, it had important effects on the North: (i) The battle convinced Britain & France not to __________________ the Confederacy in the war (ii) The battle convinced Lincoln that the time was right to make the ___________________________ of slaves the new focus of the war for the North 4. After Antietam, Lincoln issued the _______________________________________: a. This executive order freed all slaves in __________________________________ territories b. It did not free slaves in the ______________________________ but it gave the North a new reason fight c. Inspired Southern slaves to _______________________ which forced Southern whites to worry about their farms 5. After Antietam, the Confederates continued to ____________ in the East C. Conclusions: 1861-1863 1. Despite being __________________________ & under-equipped, the CSA dominated the fighting in the East from 1861-1863 due to better generals & a ______________________ strategy 2. But, the Union Army was having success in the West under the leadership of _______________________________ 3. By mid-1863, the weight of the Northern ____________________________ & industrial capacity will begin to turn the tide of the war in favor of the Union III. Fighting the Civil War: 1863-1865 A. When the Civil War began, most expected the fighting to end ________________, but the war lasted until 1865 due to: 1. The commitment of the Union & Confederacy to “________________________” 2. Excellent Southern generals like Robert E. Lee & Stonewall Jackson 3. Improved, industrial weaponry; New weapons but old _________________: a. Long-range artillery & the Gatling gun (1st ______________________ gun) b. Cone-shaped bullets & grooved barrel rifles for more ______________________ c. _______________________ naval ships like the USS Monitor & CSS Virginia d. Old tactics such as massed formations & frontal assaults; Led to huge _______________________ rates B. The Tide of the War Turns in 1863 1. By 1863, the Confederacy was having difficulty _______________________________ the fight: a. Attempts to lure Britain & France into the war had _____________________ b. The Union blockade, limited Southern manufacturing, & lack of grain fields left CSA soldiers _______________ c. To pay for the war, the CSA _____________________ money leading to massive inflation 2. Gettysburg, 1863: a. In July, Robert E Lee decided to take advantage of his victory at Chancellorsville & attack __________________ soil to end the war quickly by crushing Union ________________ b. Gettysburg proved to be the ______________________________ of the war; Lee was halted, the CSA never again attacked ____________________ soil, & the Union army began ______________________ the war 3. _________________________, 1863: Grant cut off Southern access to Mississippi River & __________________ the South into two halves; Grant was then promoted to lead the entire Union army 4. Gettysburg Address C. Fighting the Civil War: 1863-1865 1. Under Grant’s leadership, the Union army was more ___________ & committed to destroy the South’s will to fight: a. Grant appointed William T. _______________________ to lead Southern campaign b. Sherman destroyed everything of value to the South & emancipated slaves during his “____________________” c. Sherman considered “total war” ___________________________ to defeat the South d. The Battle of ______________________ was a huge victory for the Union because it took out a major Southern ___________________ terminus 2. The election of 1864: a. Lincoln faced a tough ________________________ campaign against George McClellan b. The North’s war _________________________ were the key election issue c. When Atlanta fell during Sherman’s “March to the Sea,” Lincoln was overwhelmingly reelected d. In his 2nd inaugural address, Lincoln promised a Reconstruction Plan for the Union with “__________________ towards none & ______________________ for all” 3. Appomattox, 1865: Grant defeated Lee at ________________________________ ending the Civil War 4. From 1863-1865, the lack of Southern resources & _____________________ as well as the Northern advances into the South led to the end of the Civil War 5. Northern celebration was short lived; On April 14, 1865, Lincoln was shot by ______________________________ D. Effects of the Civil War: 1. __________________________ troops were dead; More than any other U.S. war 2. The ____________ Amendment was ratified in 1865 ending slavery 3. The war forever ended the ___________________________ argument 4. The South was destroyed; A _______________ was needed to admit Southern states back into the Union