* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download White blood cells
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
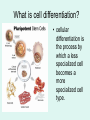
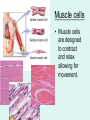
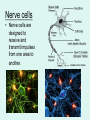
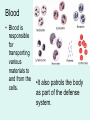
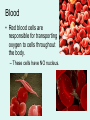
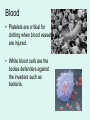
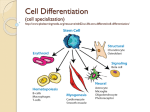
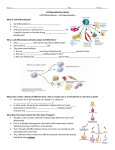
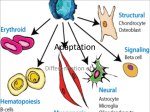
It’s Friday – yay!! Please do the following: • pick up the handout from the front table • pick up glue and a highlighter • have out your notebook Observe the two types of cells. List 4 – 6 similarities and differences on the left page of your notebook . Not all cells are created equal… • We know the difference between a plant and animal cell, but are all plants and animals exactly the same? Why Not? Cell Differentiation What makes us so different, but still the same. http://www.youtube.co m/watch?v=cyaVEotY sY0 How to “mark the text” 1. # the paragraphs 2. Circle vocabulary 3. Highlight definitions 4. Underline facts What is cell differentiation? • cellular differentiation is the process by which a less specialized cell becomes a more specialized cell type. Why differentiate cells? • Because the various cells of each plant and animals need to perform different functions! – Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. How do cells differentiate? • Cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. – Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome • Different cells use different parts of the genetic information they contain – Example: Muscle cells differ from blood cells because different genes are activated Some different plant cells • Roots, Stems, and leaves need to perform different functions, so the cells will be different. Leaf cells • Leaves main role is performing photosynthesis (absorb nutrients from the air & generate glucose using energy from the sun) • protect cells from drying out Plant Stem Cells • Plant Stem cells need to be able to transport water and nutrients to various parts of the plant. • These cells form clusters of tubes for transport. – The tubes are known as Xylem and Phloem. – They provide structure for the plant (thick cell walls), just like the skeleton provides structure for animals. Root cells • Root cells need to be able to grow in the search for and absorb water & minerals. Some different animal cells • Blood, muscle, and epithelium need to perform different functions, so the cells will be different. Muscle cells • Muscle cells are designed to contract and relax allowing for movement. Nerve cells • Nerve cells are designed to receive and transmit impulses from one area to another. Blood • Blood is responsible for transporting various materials to and from the cells. •It also patrols the body as part of the defense system. Blood • Red blood cells are responsible for transporting oxygen to cells throughout the body. – These cells have NO nucleus. Blood • Platelets are critical for clotting when blood vessels are injured. • White blood cells are the bodies defenders against the invaders such as bacteria. • Epithelial cells make up the tissues covering the body as well as lining the organs and cavities of the body. • Acts as a protective barrier! Epithelial cells