* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download tissues.
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
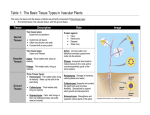
Lecture PLANTS TISSUES Authors as. Kernychna I.Z. Plan 1.Meristematic tissues. 2. Dermal tissues. 3. Secretory tissues. 4. Parenchyma. In the body plants cells not isolated, but placed groups - on the basis of community of origin, structure and functions. These groups of cells name tissues. Many classification Living and dead; meristematic and constant; Simple and complex; Primary and secondary The tissues of a plant are organized into three tissue systems: the dermal tissue system, the ground tissue system, and the vascular tissue system Simple tissues are: Classification tissues Parenchyma Chlorenchyma Collenchyma Sclerenchyma Complex tissues are: DERMAL XYLEM PHLOEM Meristematic tissues: the cells are small, the cells walls are thin, cells have large nuclei, vacuoles are absent or very small, and there are no intercellular spaces. Plants have four types of meristems: apical, lateral, intercalary, and wound (or regeneration). Dermal tissues cover the plant body There are two types of dermal tissue: The primary is: epidermis The secondary is: periderm Epidermis is closely packed, without intercellular spaces or chloroplasts. The outer walls may be covered waxy, waterproof cuticle Guard cells contain chloroplasts and regulate gas exchange between the inside of the leaf and the surrounding air. Trichomes- on plants are epidermal outgrowths of various kinds. Trichomes may be unicellular or multicellular, branched or unbranched Branched hairs can be dendritic (tree-like), tufted, or stellate (star-shaped). Epidermal hairs lower water loss by decreasing the flow of air over the plant surface, which in turn, slows the loss of water from the plant. Glandular hairs (secretory) prevent herbivory by storing substances that are harmful to insects. Root hairs increase water uptake by increasing the surface area of the cell. Epidermis is short lived in many plants. When epidermis ruptures a secondary dermal tissue periderm that concist of phellogen (cork cambium), phellem (cork), phelloderm (secondary cortex) replaces it. SECRETORY TISSUES OF PLANS secretory structures: external secretory structures (nectaries, hydathodes, secretory hair) - internal secretory structures (secretory cells, canals, ducts, cavities, laticifers). Resin canals Internal secretory structure: - laticifers (of dantelion); OIL CANALS Parenchyma Types parenchyma 1. Chlorenchyma 2. Aerenchyma 3. Storage parenchyma Chlorenchyma : contains chloroplasts and functions in photosynthesis Chlorenchyma of leaves STORAGE PARENCHYMA: characterized by large accumulations of storage products such as starch, protein, oil, hemicellulose or water. Aerenchyma contains large intracellular air spaces and functions in gas exchange.