* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Specialized Tissues In Plants
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
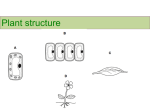
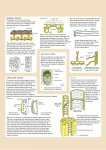
Specialized Tissues In Plants Types of Plant Tissue • Dermal tissue – the tissue covering the outside of the plant body • Periderm – the part of the dermal tissue in plants that makes up the outer bark in trees and other woody plants • Epidermis – the outermost tissue layer • Cuticle – waxy, waterproof coating secreted by epidermal cells • Stomata – (singular - stoma) the pores on plant surfaces that function in gas exchange • Vascular tissue – the plant tissue composed of conducting tubes of xylem and phloem • Xylem – transfers • Phloem – transfers sugars water and minerals throughout the plant upwards from the roots • Companion cells – load to the leaves sugars into sieve-tube members • Tracheids – the elongated cells that provide structure • Sieve-tubes – the cells that as well as conducting water join end to end forming a and minerals tube through which sugars are transported through the • Vessel elements – the shortened cells that connect end to end as vessels in plant order to transport water and minerals • Ground tissue – the tissue system that makes up the bulk of the plant body • Parenchyma – the cells of the ground tissue of plants where sugars are synthesized and stored • Collenchyma – gives support to young and growing parts of the plant • Sclerenchyma – the rigid cells of the ground tissue that contain a hardening agent to give support to the plant Biology 16.2 – Specialized Tissues In Plants Specialized Tissues In Plants Stems • Plant organs grouped into two systems • Root system - underground structures • Shoot system – above ground structures • Stems – vertical stalk or main trunk • Provides support • Transports water, minerals, and food • Stem structures • Epidermis provides structural support • Sclerenchyma cells in ground tissue provide additional support • Cortex – ground tissue between epidermis and vascular bundles • Parenchyma cells store carbohydrates and oils Roots • • • • Anchor plants Absorb water through outermost epidermis Store food in the cortex Root cap – the area that surrounds and protects the epidermal cells and apical meristem at the tip of the plant root • Osmosis moves water • Into roots • Through tissues into xylem • Transpiration – the evaporation of water through the stomata on the leaves of plants • Evaporating water pulls water molecules through cohesion • Water moves up toward the leaves Biology 16.2 – Specialized Tissues In Plants Specialized Tissues In Plants Leaves • Leaves – photosynthetic organs of the plant • Epidermis protects and prevents water loss • Mesophyll – the area between the upper and lower epidermis of a leaf where the majority of photosynthesis occurs • Palisade layer – cells just below the upper epidermis where most of the chloroplasts are located • Spongy layer – the bottom layer of the mesophyll that contains many open spaces that connect to stomata Flowers • Angiosperms produce flowers • Used as reproductive organs for the plant • Tissue structure is similar to leaves • Flower structure • Sepals – an outer ring of modified leaves on the flower that provide protection to the flower before it opens and are usually green • Petals – colorful and often scented • Stamens – male structures • Anther and filament • Pistil – female structure • Stigma, style, and ovary Biology 16.2 – Specialized Tissues In Plants