* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Leaves
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
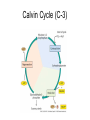
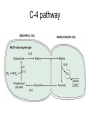
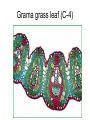
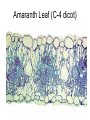
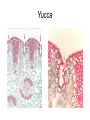
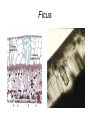
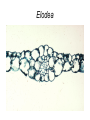
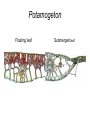
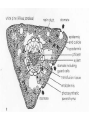
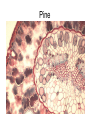
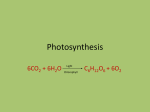
Leaves - II Corn leaves show Kranz anatomy Photosynthesis • Light Reactions produces ATP and NADPH • Carbon fixation reaction incorporates CO2 into sugars – Normal fixation is by Calvin Cycle: C-3 pathway • CO2 + Ribulose-1,6-bisphosphate forms 2 molecules of PGA – C-4 plants prefix CO2 into oxaloacetic acid and malic acid prior to the Calvin Cycle Calvin Cycle (C-3) C-3 plant leaves C-4 pathway Sugar Cane Leaf Grama grass leaf (C-4) Corn leaf Amaranth Leaf (C-4 dicot) Schematic of Atriplex leaf (a C-4 dicot) 1 = vascular bundle 2 = bundle sheath cell 3 = radially arranged palisade mesophyll (Kranzmesophyll) cell 4 = water-storage parenchyma cell 5 = stomatal complex 6 = sub-stomatal cavity 7 = cuticle of adaxial epidermis Adaptations to Xeric Environments Thickened cuticle Sunken stomata Beach grass Yucca Oleander has many xeromorphic adaptations Ficus Succulency Succulents Lithops Saguaro cactus Hydrophytes Nymphae spp Nymphae leaves Elodea Potamogeton Floating leaf Submerged leaf Submerged Vallisneria leaf Gymnosperm leaves Pine needles Pine Cooksonia earliest vascular plant Evolution of microphylls as enations Evolution of Megaphylls by •Overtopping •Plannation •Webbing