* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download plant tissues - WordPress.com
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Glossary of plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
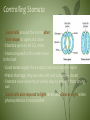
4.4 PLANT TISSUES Working Together LEAVES • Leaves are highly specialized structures with one primary function Photosynthesis: chlorophyll light energy + carbon dioxide + water glucose + oxygen • glucose produced can be converted into carbohydrates used as building blocks for plant’s structures and functions Absorbing Light • Thin, wide leaves with large surface area absorb sunlight best • In the chloroplasts, Chlorophyll absorbs the light • Chloroplasts are found in the palisade layer and the spongy mesophyll of a leaf • These are part of the ground tissue system • The tightly packed palisade layer capture the maximum amount of light while the loosely packed spongy mesophyll allow gases to move around (CO2 & O2) Obtaining Carbon Dioxide • the epidermis of the leaf has cells that produce a thin layer of wax called the cuticle • The cuticle prevents water loss and the diffusion of gases from the surface of the leaf • Gases enter and leave through openings called the stomata which are found on the underside of the leaf • They are surrounded by special epidermal cells called the guard cells Controlling Stomata • Guard cells around the stoma alter their shape to open and close • Stomata open to let CO2 enter. • Stoma respond to the water level in the leaf • Good water supply they expand and bend apart—open • Water shortage, they become soft and collapse—closed • Stomata close on sunny or windy days to prevent from drying out • Guard cells also respond to light levels and close at night when photosynthesis is not possible Obtaining Water • root hairs: Long thin epidermal cells on the roots absorb water from the soil by osmosis • Root hairs increase the surface area for water absorption • Water is then transported up the from the roots through xylem to the stem and leaves Comparing Plant & Animal Systems • Similarities • Vascular bundles are similar to veins and arteries • Differences • Animals actively use a heart to pump blood around organism • Plants passively acquire water and distribute it