* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Modern Physics - Politechnika Wrocławska
Molecular Hamiltonian wikipedia , lookup
Tight binding wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Delayed choice quantum eraser wikipedia , lookup
Bremsstrahlung wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Auger electron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Particle in a box wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Ultrafast laser spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
Double-slit experiment wikipedia , lookup
Low-energy electron diffraction wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Wave–particle duality wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
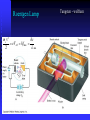
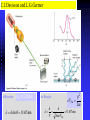
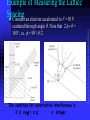
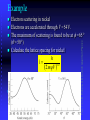
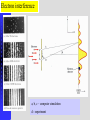
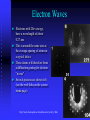
Modern Physics Lecture IX The Quantum Hypothesis In this lecture we examine the evidence for “light quanta” and the implications of their existence Waves as Particles The photoelectric effect Compton scattering Particles as Waves Electron diffraction The Double Slit Revisited Photoelectric effect When light strikes the cathode, electrons are emitted Electrons moving between the two plates constitute a current Photoelectric Effect Properties of the photoelectric effect Electrons are only emitted above a certain “cut-off” frequency This frequency is different for different materials It is called the “work function” Below the “work function” no electrons are emitted no matter how intense the light is The maximum energy of the ejected electron is Kmax=eDVs Photoelectric Effect Properties No photoelectrons are emitted if the frequency falls below some cut-off frequency fc The maximum energy of the photons is independent of the light intensity The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons increases with increasing frequency Photoelectrons are emitted almost instantaneously from the surface Photoelectric Effect Explanation Einstein extended Planck’s explanation for blackbody radiation to suggest that in fact the quanta of energy used in blackbody radiation are in fact localised “particle like” energy packets Each having an energy given by hf Emitted electrons will have an energy given by K max hf f Where f is known as the “work function” of the material Photoelectric Effect Quantum interpretation If the energy of a photon is less than the work function f, the photon cannot give enough energy to the electron to leave the surface Kmax does not depend on light intensity, because doubling the number of photons would only double the number of electrons and not double their energy Kmax increases with frequency because energy and frequency are related If light is particle-like, then all of the energy will be delivered instantaneously thus liberating an electron with no time delay between the light hitting the surface and the electron escaping Inverse photoelectric effect - Production of X-rays X-rayphoton s E lectrons High vol tage 1. Photons are absorbed in whole - electrons can transfer part of their energy. 2. Brehmsstrahlung - electrons decelerate in electromagnetic field of nuclei: Ef = Ei - h , wide distribution 3. Maximal frequency - minimal wavelength (observed empirically first) eV = h max = h c / min 4. Also discrete spectrum (atomic levels) Roentgen Lamp me v 2 hc eVAC hf max 2 min Tungsten - wolfram Compton Scattering If light is like a particle does it have momentum? In Compton scattering x-rays impart momentum to matter, scattering electrons like billiard balls Thus photons also have momentum. The momentum of a photon is given by E hf h p c c Recoiling electron f Incident Photon, 0 0 Scattered Photon, ’ h (1 cos ) me c Photons and Electromagnetic Waves How can light be considered a photon (particle) when we know it is a wave Light has a dual nature: it exhibits both wave and particle characteristics There is a smooth transition of these properties across the electromagnetic spectrum At low frequencies (radio waves) photons have a vanishingly small energy and the wave properties dominate At high frequencies (x-rays, g-rays) it is the particle properties that dominate But… Louis de Broglie 1892 - 1987 Wave Properties of Matter In 1923 Louis de Broglie postulated that perhaps matter exhibits the same “duality” that light exhibits Perhaps all matter has both characteristics as well Previously we saw that, for photons, p E hf h c c Which says that the wavelength of light is related to its momentum Making the same comparison for matter we find… h h p mv de Broglie Wavelength of Electrons We now calculate the wavelength of a charged particle accelerated through potential V Assume that the particles have mass m and charge q Equate kinetic energy of the particles with the electrostatic energy K = m v 2/2 = q V momentum p=mv We can express kinetic energy in terms of momentum K = p 2/(2 m) = q V Reorganise to get p = (2 m q V )1/2 de Broglie’s hypothesis gives =h/p h λ Substitute for p to get 1/2 2 m q V Does Matter Really Have a Wavelength The wavelength of matter waves is very small. This is why we do not see them in our every day experience To see diffraction a grating a very small slit width is required (eg the space between two atoms in a crystal) This is exactly how electron diffraction was first found! G. P. Thompson of Scotland and Davisson and Germer from the USA used the close spacing between atoms in a crystal lattice to diffract electron waves thus proving that matter can also exhibit diffraction and interference Sir Joseph John (JJ) Thomson C.J.Davisson and L.G.Germer diffraction dNi=0.215nm d sin 0.165nm de Broglie eVba p2 2m h h 0.167 nm p 2meVba scattered through angle . Note that 2 f + = 180°, i.e. f 90°- /2 • The condition for constructive interference is 2 d sinf = n n integer Figs. from R. Eisberg & R. Resnick Quantum Physics Example of Measuring the Lattice Spacing Consider an electron accelerated to V = 50 V Example Electron scattering in nickel Electrons are accelerated through V = 54V. The maximum of scattering is found to be at f = 65 ° ( = 50 °) Calculate the lattice spacing for nickel h 1/2 2 m qV 2 d = n / sinf Verify that d = 0.092 nm Figs. from R. Eisberg & R. Resnick Quantum Physics Electron interference a, b, c – computer simulation d - experiment Electron Microscope Electron Waves Electrons with 20ev energy, have a wavelength of about 0.27 nm This is around the same size as the average spacing of atoms in a crystal lattice These atoms will therefore form a diffraction grating for electron “waves” Several pictures are shown left (see the web links on the course home page) http://www.chem.qmw.ac.uk/surfaces/scc/scat6_2.htm from this lecture… The solution to the blackbody spectrum leads to the concept of photons, and to a solution for the photoelectric effect The maximum excess energy of a photoelectron is K max hf f The particle nature of light is also shown by Compton scattering of electrons by photons 0 Scattering shows that photons have momentum given by p E hf h c c This implies that matter also has wavelike properties given by the de Broglie formula h (1 cos ) me c h h p mv The de Broglie wavelength leads to phenomena such as electron diffraction. A common tool in modern crystallography