* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Islam, Judaism & Christianity
Survey
Document related concepts
The Invention of the Jewish People wikipedia , lookup
The Reform Jewish cantorate during the 19th century wikipedia , lookup
Homosexuality and Judaism wikipedia , lookup
Hamburg Temple disputes wikipedia , lookup
Orthodox Judaism wikipedia , lookup
Jewish views on sin wikipedia , lookup
Supersessionism wikipedia , lookup
Interfaith marriage in Judaism wikipedia , lookup
Jewish views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
Pardes (Jewish exegesis) wikipedia , lookup
Index of Jewish history-related articles wikipedia , lookup
Jewish religious movements wikipedia , lookup
Origins of Rabbinic Judaism wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
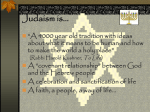
Judaism • religion of just one people: the Jews. • first to teach belief in only one God. • Two other important religions developed from Judaism: Christianity and Islam. Judaism • Founder/Prophets/ Important people: 1. Abraham, Isaac, and Jacob (name changed to Israel) 2. Twelve Tribes (sons of Israel) 3. Moses 4. David, Solomon Daniel in the Lion’s Den • Languages: 1. Hebrew • Percent of followers in the world: – 2% – Jewish influence on the world has been vast -- far more than their numbers would indicate. David and Goliath Judaism • Important Teachings & Beliefs: 1. 2. 3. 4. Monotheistic 10 commandments Prayer Still Awaiting Messiah (Savior) Holy Book(s): (Old Testament) 1. Torah • First 5 books of Bible • According to Torah, it is disrespectful to spell out name of deity (G_ D) [Yahweh] in full. 2. Talmud • record of rabbinic discussions pertaining to Jewish law, ethics, customs, and history. Moses breaks the first set of the 10 Commandments Judaism Beliefs • Jews believe that there is a single God (Yahweh) who not only created the universe, but with whom every Jew can have an individual and personal relationship. • They await the Messiah, who will be an earthly king. They believe in heaven, but that God determines where they go after life on earth. • Ten Commandments is the basic code of law. Judaism Briefly • Judaism is around 3500 years old and is the oldest of the world's four great monotheistic religions (religions with only one God). • It's also the smallest, with only about 12 million followers around the world. • Its holy city is Jerusalem. • The Jewish calendar is based on 29 or 30 days therefore they have 12.13 months. Judaism Beliefs • Jews believe that there is a single God who not only created the universe, but with whom every Jew can have an individual and personal relationship. • They believe in heaven, but that God determines where they go after life on earth. • Give a tithe (10%). • Ten Commandments is the basic code of law. Judaism • Jews think that God will send a Messiah (a deliverer) to unite them and lead them in His way. • Christians believe that Jesus was the Messiah. – The Jewish people do not agree; they anticipate His arrival in the future. Jewish Philosophy • • • • • • • • • • God is one and unique God is the creator God is transcendent God is immanent. God is lawgiver God is personal We have the obligation to worship The Torah is God's law God is judge The Messiah will come. Judaism Holy Book • The most holy Jewish book is the Torah (the first five books of the Christian Bible) • Others include Judaism's oral tradition, the written form of which is known as the Talmud. • The Torah (scroll of teachings) contains the five books revealed to Moses by God on Mount Sinai. – Genesis, Exodus, Leviticus, Numbers & Deuteronomy • Another important book is the "Talmud," serving primarily as a guide to the civil and religious laws of Judaism. • Hebrew is read right to left. Judaism Place of Worship • Jews worship in Synagogues or temples. • Men and women usually sit separately. • Worship is led by a Rabbi. • Friday evening is time for worship. Stamford Hill, London The Temple • According to the Bible, the First Temple for Jewish worship was built around 900-1000 BCE and destroyed by Babylonians in 586 BCE. • The Jews were then sent out of Canaan, but returned after 50 years in exile. • A Diaspora occurs when a group of people leave their homeland and move to many different locations separately. • All of the world’s Jewish communities today that do not live in present-day Israel are part of the Jewish Diaspora. The Temple • A new temple was finished 70 years later on the site of the First Temple, but was badly plundered by invading Romans about 54 BCE. • King Herod, a Jew, ruled Judea for the Romans. Under him the second temple was rebuilt in 20 BCE. • When the Romans attacked Jerusalem again in 70 CE(AD), they destroyed Herod’s temple. • Today, the single remaining temple wall, the Western Wall, is a place of prayer for Jewish pilgrims. • Jews moved away from the land again, until the modern state of Israel was formed in the late 1940s. Judaism • Important Cities 1. Jerusalem • Major Groups: 1. Orthodox Jews: • adheres faithfully to the principles and practices of traditional Judaism. 2. Conservative Jews: • modern denomination of Judaism that arose in United States in the early 1900's. 3. Reform Jews: • largest denomination of Jews. They are more liberal in their thinking about Judaism. Samson destroys the Philistine temple 7 Holy Days • Rosh Hashanah-Jewish New Year • Yom Kippur-A day of fasting and praying which occurs 10 days after the first day of Rosh Hashanah. The holiest day in the year • Sukkot-8 day festival of thanksgiving • Hanukkah-The Feast of Lights is an 8 day Feast of Dedication. It recalls the war fought by the Maccabees in the cause of religious freedom • Purim-The Feast of Lots recalls the defeat by Queen Esther of the plan to slaughter all of the Persian Jews, circa 400 BC • Pesa(Passover)-The 8 day festival recalls the exodus of the Israelites from slavery in Egypt circa 1300 BCE. A holiday meal, the Seder, is held at home • Shavouth-Pentecost recalls God's revelation of the Torah to the Jewish people • The Star of David is the international symbol of Judaism • Flag of Israel has it • Menorah-It is a symbol of the nation of Israel and a mission to be "a light unto the nations. • A Yarmulke is worn during prayer to shoe respect to G_d Kosher Foods • Foods are kosher when they meet all criteria that Jewish law applies to food • Characteristics that make a food non-kosher: – the mixture of meat and milk – the use of cooking utensils which had previously been used for non-kosher food – The type of animal it is • Leviticus 11:3 says that Jews may eat all animals that have cloven hooves and chew their cud • Leviticus 11:4 explicitly prohibited the consumption of animals that do not have these characteristics designating them "unclean to you." • Six mammals are specifically not allowed: – The camel – The hyrax – The hare – The pig – Whales and dolphins • Kosher animals are as follows: – Cows, goats, sheep, antelope, deer, giraffes, okapis and pronghorns – Most fish(excluding shellfish, sharks, octupus, eels and squid) – Chicken, duck, turkey – Milk and cheese are kosher but cannot be eaten with meat or mixed with meat. • Preparation – the slaughter of animals is designed to minimize the pain—usually done by a slice across the throat – this eliminates the practice of hunting for food unless it can be captured alive and ritually slaughtered. – All blood and veins must be removed from meat(salting and broiling are common methods) Judaism – Map! Judaism in 1500 C.E. Judaism Today In 1500, located in Europe and Middle East Today, located in Israel and U.S.