* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 2, Section 3
Index of Egypt-related articles wikipedia , lookup
Art of ancient Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Thebes, Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Egyptian medicine wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Egyptian funerary practices wikipedia , lookup
Amenhotep I wikipedia , lookup
Prehistoric Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Egyptian race controversy wikipedia , lookup
Amenhotep III wikipedia , lookup
Egypt (Roman province) wikipedia , lookup
Middle Kingdom of Egypt wikipedia , lookup
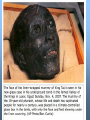
Chapter 2, Section 3 The Egyptian Empire A new dynasty of pharaohs came to power, moved their capital to Thebes and restored order and stability. This brought about a new period called…. THE MIDDLE KINGDOM 2050 B.C. to 1670 B.C. ACHIEVEMENTS DURING THE MIDDLE KINGDOM • Egypt took control of new lands including Nubia and what is now Syria. • Pharaohs added more waterways and dams which increased farming. • Built a canal between the Nile River and Red Sea. MORE MIDDLE KINGDOM ACHIEVEMENTS… • Arts, literature and architecture blossomed. • Instead of building pyramids, pharaohs had their tombs cut into cliffs west of the Nile River. This area became known as the Valley of the Kings. End of Middle Kingdom • Ended in 1670 B.C. when the Hyksos, from Western Asia attacked Egypt. • Hyksos were mighty warriors who came in horse-drawn chariots and had weapons made of bronze and iron. • Hyksos ruled Egypt for about 120 years. THE NEW KINGDOM 1550 B.C. – 1080 B.C. • An Egyptian prince named Ahmose led and uprising that drove the Hyksos out of Egypt and the New Kingdom began. • Egypt became very rich and powerful during the New Kingdom. Hatshepsut • A queen who came to power in 1473 B.C. • After her husbands death she made herself pharaoh. • One of the few women to rule Egypt. Hatshepsut’s Reign • More interested in trade than conquest. • Egyptians often traded with the Phoenicians. The Phoenicians had furniture and wood that the Egyptians needed. In return, Egyptians traded wheat, paper, gold, copper and tools. Thutomose III • When Hatshepsut died, her nephew Thutmose III became pharaoh. • He expanded Eygpt’s borders, and his empire grew rich from trade. • During his reign, Egypt enslaved many prisoners of war. Slavery became common during the New Kingdom. Amenhotep • Came to the throne in 1370 B.C. • Introduced a new religion in an attempt to maintain power of the pharaohs. • New religion directed Egyptians to worship only one god called Aton. • Priests resisted this religion so Amenhotep took away their titles, closed their temples, etc. Amenhotep • Amenhotep then changed his name to Akhenaton, which means “Spirit of Aton” • While Akhenaton became obssessed with this new religion, most Egyptians rejected it. • Akhenaton was not a strong pharaoh and during his rule lost most of his lands in Western Asia to the Hittites, which greatly shrunk the Egyptian empire. Tutankhamen • After Akhenaton died, his son-in-law inherited the throne. • Tutankhamen was only 10 years old when he became king. • Under the advice of palace officials and priests King “Tut” restored Egypts old religion. • He died after only 9 years of rule. Tutankhamen’s Tomb • King Tut, the boy king, played only a small part in Egypt’s history. • He is very famous because his tomb was discovered by a British archaeologist, Howard Carter, in 1922. • It was one tomb that had not yet been looted by robbers and contained the king’s mummy and incredible treasures. What King Tut looked like based on 3-D Xrays scans of his corpse!!