* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Welcome to Meteorology 10
The Weather Channel wikipedia , lookup
Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric circulation wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Storm Prediction Center wikipedia , lookup
History of climate change science wikipedia , lookup
Severe weather wikipedia , lookup
Automated airport weather station wikipedia , lookup
Space weather wikipedia , lookup
Surface weather analysis wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric convection wikipedia , lookup
Atmosphere of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of numerical weather prediction wikipedia , lookup
Weather Prediction Center wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Weather forecasting wikipedia , lookup
Lockheed WC-130 wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric model wikipedia , lookup
Marine weather forecasting wikipedia , lookup
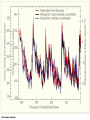
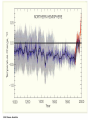
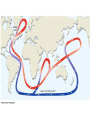
Welcome to Meteorology 10 Professor Jeff Gawrych De Anza College Meterology Definition • The science that deals with the phenomena of the atmosphere, especially weather and weather conditions Part of the Geosciences Meteorology Oceanography - Atmospheric science - Atmospheric chemistry/physics - Climatology/Paleoclimatology - Biometeorology •study of the ocean and its phenomena Geology Geography/ Environmental Science •Studies origin, history, and structure of the earth. Similar in many ways to meteorology - A large factor in many area of meteorology. E.g. Land use What is Weather/Climate? • Weather: The atmospheric conditions at a particular place and time – E.g. It’s currently 80º with a relative humidity of 40% – Today’s high temeprature was 50º • Climate: The time-averaged conditions at a particular location – San Francisco is prone to summertime fog – It hardly ever rains in San Jose during the summertime – The average high temeprature in January is 52.9º Part of a bigger system • • • • • Atmosphere: this course Hydrosphere: Oceans/lakes/rivers Cryosphere: Ice caps Lithosphere: Solid ground/rock Biosphere: All living things including plants and animals – ALL OF THESE ARE CO-DEPENDENT ON ONE ANOTHER 385 ppm in 2007 Concept of a Balance • The weather serves to keep earth in a heat balance. Pure and simple. • Without it, the poles would be much colder and the tropics much warmer • Maintains earth’s heat balance along with the oceans • Earth tries to achieve balance, but never fully does. This is VERY GOOD for me as a meteorologist. Who cares? – We must always be able to answer this question. • Why we care about the atmosphere? – we live with it and it sustains life » not all planets have atmosphere meaning: » there’s no life (air to breathe) » temperatures are usually too hot or too cold – Affects our day-to day activites » What to wear. Stay in or go out. – Affects business » Flight delays/crop forecasts/weather shutdowns What do meteorologists do? • Study the sun and its phenomena: physicists • Study climate history of earth • Use math in numerical models to aid research and practical tools, like forecast models • Work in the solar and wind energy fields • Air pollution--A big issue everywhere now. • Study planetary atmospheres, like Mars • Forecasting (air, sea, business, land use, building design) • Teach, por supuesto! Course Outline • Our study of the atmopshere will focus on weather forecasting: predicting future weather events • We will learn the meteorlogical tools to effectively observe,diagnose and predict future weather events •