* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Weather & Climate Chapter 1
Atmospheric circulation wikipedia , lookup
Surface weather analysis wikipedia , lookup
Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere wikipedia , lookup
History of climate change science wikipedia , lookup
Solar irradiance wikipedia , lookup
Satellite temperature measurements wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
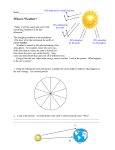
Chapter 1 Introduction to the Atmosphere Ecclesiastes 1:14-16 A generation goes, and a generation comes, But, the Earth remains forever. The Sun rises, and the Sun goes down, And hastens to the place where it rises. The wind blows to the south, and goes around to the north. Round and round goes the wind, and on its circuits the wind returns. “A Big Blue Marble” Seen from space, the Earth looks like no other planet that we know Its most conspicuous features are its atmosphere and hydrosphere From pre-history Man has been directly and indirectly affected by environment --- nothing as much as weather --- Sun God; Rain God; omens; reward/punishment; etc --- SAD Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD) Prolonged, but seasonal depression coinciding with shortening days and decreasing angle of insolation Recognized by National Institute of Mental Health; the AMA; the APA Variable: geographically [Fig 1-3]; demographically; physiologically Weather: the state of the Earth’s atmosphere with respect to heat or cold; wetness or dryness; clearness or cloudiness (Webster) --- atmospheric extent is conceptual --- manifest in wind; temperature and precipitation patterns; storms; etc Climate: weather of a location over an extended period of time, including its extremes [I do not like terming climate as “average weather” – look at variability in NYC temperature hidden in Average Daily Highs/Lows (Fig 1-4)] Meteorology Study of the atmosphere and processes that create weather and climate Atmospheric elements of: (1) temperature of the air (2) humidity of the air (3) type and amount of cloudiness (4) type and amount of precipitation (5) pressure exerted by the air (6) speed and direction of wind Atmospheric Hazards: Assault by the Elements “Natural hazards are a part of living on Earth” [understatement] They effect millions worldwide and cause billions of dollars damage --- Earth geologic hazards grab the press --- atmospheric hazards total more more lives; damage; dollars … unfortunately human lifestyles continue to make hazards worse The Atmosphere: A Part of the Earth System From the human perspective the Earth is huge [surface area – 500 mill sq. km /103 mill sq mi] It is a single global system of interrelated components operating as a single entity This Earth system is defined by four subsystems The Atmosphere: A Part of the Earth System, cont (1) Lithosphere – the outer, rigid portion of the “solid” Earth (upper mantle; crust) (2) Atmosphere – gaseous envelope surrounding the Earth; provides air we breath; protects from radiation; provides energy exchange The Atmosphere: A Part of the Earth System, cont (3) Hydrosphere – dynamic water and energy exchange processes that make Earth unique; 97% of Earth water is tied up in oceans (4) Biosphere – life portion of the Earth; a narrow band--- the interface of the other three zones Composition of the Atmosphere variant vs non-variant gases nitrogen oxygen water vapor trace elements (CO2; O3) dust industrial exhaust (NOx; SOx) insolation vs terrestrial radiation Ozone (O3) Stratospheric Tropospheric --- VOCs and NOx --- Corrosive --- Biological irritant (a secondary pollutant) --- compliance measured as hourly average (0.085ppm) Ozone (O3), cont Factors affecting O3 --- human/economic … industrial mix … transportation --- Physical … wind … atmospheric stability and inversions … topography … severe air pollution potential Origin of Atmosphere - First atmosphere of light gases disappear to space - “degassing” and “dissolving” - plants absorb CO2, release O2 Vertical Structure of the Atmosphere Atmosphere structure is based on: (1) pressure (2) temperature (3) vertical variation in composition --- Homosphere --- Heterosphere Vertical Structure of the Atmosphere, cont Earth atmosphere weight approx. 5.6 X 1018 Structure based on: (1) pressure (2) temperature (3) vertical variation in composition Vertical Structure of the Atmosphere, cont Homosphere Troposphere Tropopause normal lapse rate / inversions Stratosphere Mesosphere Heterosphere Thermosphere Ionosphere Exosphere Heating of the Atmosphere Radiation Conduction Convection / Advection Latent Heat of Condensation Controls on Weather and Climate (1) Latitude (2) Land-Water (3) Ocean Currents (4) Altitude (5) Physical Barriers (6) Human Activities (7) Pressure systems and storms Average Breakdown of Insolation Absorbed by atmosphere – 19%-22% Reflected into space – 34% Absorbed Earth surface – 43%-47% Heat Energy Budget Insolation to the Ground 47% of incoming solar radiation reaches the surface of the Earth … ultimately returned to the atmosphere terrestrial radiation – 14% conduction/convection – 10% latent heat – 23% Variation in the Heat Energy Balance Regions of Energy Surplus --- tropical zones --- seasonal Regions of Energy Deficit --- polar zones --- seasonal Air Temperature Temperature and Heat sensible temperature Temperature-Humidity Index [THI=T- 0.55(1-RH)(T-14)] wind chill Temperature Measure liquid-in-glass bi-metal electronic Scales Fahrenheit Celsius Kelvin Short Term Variations in Temperature Daily affects of insolation Cloud cover Differential heating (land/water) Reflection Horizontal Air Movement