* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Anxiety Disorders
Antisocial personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders wikipedia , lookup
Test anxiety wikipedia , lookup
Causes of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
Dissociative identity disorder wikipedia , lookup
Conversion disorder wikipedia , lookup
Depersonalization disorder wikipedia , lookup
Asperger syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Conduct disorder wikipedia , lookup
Spectrum disorder wikipedia , lookup
Diagnosis of Asperger syndrome wikipedia , lookup
History of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
Child psychopathology wikipedia , lookup
Claustrophobia wikipedia , lookup
Anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Panic disorder wikipedia , lookup
Externalizing disorders wikipedia , lookup
Social anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Death anxiety (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
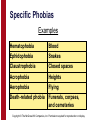
Abnormal Psychology Clinical Perspectives on Psychological Disorders 5e Richard P. Halgin Susan Krauss Whitbourne University of Massachusetts at Amherst slides by Travis Langley Henderson State University Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Anxiety Disorders Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. The Nature of Anxiety Disorders Fear is an innate alarm response to a dangerous or life-threatening situation. Anxiety is the state in which an individual is inordinately apprehensive, tense, and uneasy about the prospect of something terrible happening. People with anxiety disorders are incapacitated by chronic and intense feelings of anxiety. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Panic Disorder Frequent and Recurrent Panic Attacks Unexpected (Uncued) Attacks Situationally Bound (Cued) Attack Situationally Predisposed Attack or Constant Worry and Apprehension About Possible Panic Attacks Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Panic Disorder Panic disorder is often associated with agoraphobia. Agoraphobia: Intense anxiety about being trapped or stranded in a situation without help if a panic attack occurs. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Panic Disorder Suggested explanations include: Neurotransmitters Anxiety Sensitivity Conditioned Fear Reactions Biological relatives of people with panic disorder are 8 times more likely to develop this condition. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Panic Disorder Treatments Benzodiazepines Antidepressants Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors Relaxation Training Panic Control Therapy (PCT) Drugs used- Valium, Klonopin, Zoloft Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Specific Phobias Specific Phobia: An irrational and unabating fear of a particular object, activity, or situation that provokes an immediate anxiety response, disrupts functioning, and results in avoidance behavior. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Specific Phobias Examples Hematophobia Blood Ephidophobia Snakes Claustrophobia Closed spaces Acrophobia Heights Aerophobia Flying Death-related phobia Funerals, corpses, and cemeteries Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Specific Phobias Some Less Common Phobias Ailurophobia Cats Chionophobia Snow Erythrophobia The color red Metallophobia Metals Ponophobia Work Triskaidekaphobia The number 13 Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Specific Phobias Treatments Systematic Desensitization Flooding Imaginal Flooding Graduated Exposure Thought Stopping Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Specific Phobias Virtual reality software is sometimes used to treat people with phobias such as fear of heights or flying. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Social Phobia A social phobia involves a fear in virtually all social situations. People with social phobia: • recognize their own fears as unreasonable • show low self-esteem • underestimate their own abilities • ruminate about how they could have acted differently in a social event. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Social Phobia Treatments In Vivo Exposure Cognitive Restructuring Social Skills Training Sometimes Medication Drugs used- Nardil, Inderal, Klonopin Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Generalized Anxiety Disorder Generalized Anxiety Disorder: An anxiety disorder characterized by anxiety that is not associated with a particular object, situation, or event, but seems to be a constant feature of a person's day-to-day existence. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder: An anxiety disorder characterized by recurrent obsessions or compulsions that are inordinately time-consuming or that cause significant distress or impairment. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder Obsession: A persistent and intrusive idea, thought, impulse, or image. Compulsion: A repetitive and seemingly purposeful behavior performed in response to uncontrollable urges or according to a ritualistic or stereotyped set of rules. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder 4 Major Dimensions Obsessions associated with checking compulsions. Need for symmetry and order. Obsessions about cleanliness associated with washing compulsions. Hoarding-related behaviors. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder OCD is increasingly being understood as a genetic disorder. So far, treatment with clomipramine or other serotonin reuptake inhibiting medications, such a fluoxetine (Prozac), is the most effective biological treatment available for OCD. Drugs Used- Anafranil, Luvox, Prozac, Paxil, and ©Zoloft Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. TRAUMA Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Trauma-Induced Disorders Acute Stress Disorder: An anxiety disorder that develops during the month after a traumatic event. Lasts 2-4 weeks. Symptoms may include depersonalization, numbing, dissociative amnesia, intense anxiety, hypervigilance, and impairment of everyday functioning. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Trauma-Induced Disorders Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder: More than a month after a traumatic event, stress interferes with the individual’s ability to function. Symptoms fall into two related clusters: Intrusions and Avoidance Hyperarousal and Numbing Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Perspectives on TraumaInduced Disorders Brain Changes Conditioned Fear Economic Disadvantage Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Treatment of TraumaInduced Disorders Medication “Covering” “Uncovering” Drugs used- Depakote, Topomax, Seroquel, Risperdal Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Anxiety Disorders: The Biopsychosocial Perspective These disorders intermingle biological, psychological, and sociocultural phenomena. Relatively straightforward behaviorally based treatments can alleviate symptoms. Other strategies can enhance effectiveness of behavioral techniques: cognitive insight-oriented psychopharmacological Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. For more information on material covered in this chapter, visit our Web site: http:/www.mhhe.com/halgin6e Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.