* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 39 - Midway ISD
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Xenoestrogen wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Adrenal gland wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
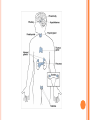
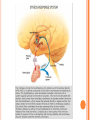
CHAPTER 39 Endocrine system and Reproductive system 39-1 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Hormones – chemicals released in one part of the body that travel through the bloodstream and affect the activities of cells in other parts of the body. Regulated by feedback mechanisms to maintain homeostasis. Exocrine Glands – release secretions directly into the organs that use them. Target Cells—The cells that hormones bind to and affect. Ex: Sweat, tears, digestive juices. Endocrine Glands – release secretions directly into blood stream. Ex: Hormones! 39-2 HUMAN ENDOCRINE GLANDS Pituitary Gland Divided into two parts: Anterior and Posterior. Base of the skull, secretes 9 hormones that directly regulate many body functions and endocrine glands. See pg. 1004 for hormones. Hypothalamus Attached to the posterior pituitary, controls the secretions of the pituitary gland through the usage of control hormones. Allows the nervous and the endocrine systems to work closely together. Thyroid Gland Wraps around trachea, major role in regulating metabolism by releasing 2 hormones with opposite effects. Parathyroid Gland Attached to thyroid, maintain homeostasis and calcium levels in blood Ex: if blood calcium levels are high, releases calcitonin to reduce calcium absorption; if levels are low, releases PTH to increase absorption of calcium Adrenal Glands Sit at the top of the kidneys, release hormones that help the body prepare for stress. Cortex – produces corticosteroids. Cortisol Medulla – releases epinephrine and norepinephrine (adrenaline) Fight or Flight response begins here! Pancreas Has exocrine and endocrine functions Releases digestive enzymes into the small intestine (exocrine) and releases hormones (insulin and glucagon) into the blood to regulate blood sugar levels Reproductive Glands Serve two functions: To produce gametes and also to secrete sex hormones. Ovaries – produce ova (eggs), secrete estrogen and progesterone (hormones) Testes – produce sperm, produce testosterone (hormone) 39-3 THE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Puberty – period of rapid growth and sexual maturation when the reproductive organs are fully developed Male Reproductive System Main function is to produce and deliver sperm • Structures scrotum – external sac that holds the testes seminiferous tubules – produces sperm epididymis – stores mature sperm vas deferans – some sperm move into this tube urethra – tube that connects to the vas deferens and leads to the outside of the body penis – anatomical structure of a male semen – combination of sperm and seminal fluid Female Reproductive System Main function to produce ova and nourish the embryo – produce one mature egg each month • Structures Follicles – clusters of cells surrounding an egg Ovulation – mature egg is released Fallopian tubes – tube that moves the egg to the uterus Uterus – organ where embryo grows Vagina – canal that leads to the outside of the body Menstrual cycle (4 phases) • Follicular phase – follicle matures and uterine lining thickens • Ovulation – egg released into fallopian tube • Luteal phase – at beginning of luteal phase is best chance for pregnancy; also when embryo implants in uterus • Menstruation – occurs if egg is not fertilized, uterine lining and ova exit the body 39-4 FERTILIZATION AND DEVELOPMENT Fertilization – process of an egg being joined by a sperm (N+N=2N) Zygote – fertilized egg cell Implantation – blastocyst attaches itself to the uterine wall Gastrulation – formation of three cell layers Neurulation – development of the nervous system Placenta – connection between mother and embryo Fetus – after eight weeks of development Control of development Still an unknown process End of three months all organs are developed • Later Development – 4th 5th and 6th month – tissues and organs become more highly developed • Last 3 Months – organ systems develop further and fetus grows in size Childbirth Hormone – Oxytocin – Causes contractions to start – cervix expands and baby is pushed out of the vagina Infancy – first 2 years of life Childhood – from infancy to puberty Adolescence – from puberty to adulthood Adulthood – 25 - 35 years of age and beyond