* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Thyroid Physiology and Thyroiditis
Survey
Document related concepts
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (menopause) wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Growth hormone therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hypopituitarism wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
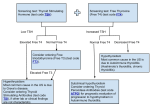
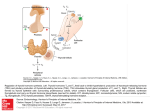
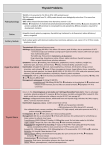
Thyroid Physiology and Thyroiditis Heidi Chamberlain Shea, MD Endocrine Associates of Dallas Case Presentation 23 year old female G2P2 6 months post partum Palpitations that were intermittent for a couple of weeks and now resolved Now with 1 month of increased fatigue, hair loss and 10 pound weight gain Case Presentation What is her diagnosis? Tests that should be done? Pathophysiology of her disease process? Thyroid Trivia “Bronchocele” Greek for tracheal outpouch 1500 AD described by Leonardo da Vinci 1656 AD “thyroid” Thomas Wharton Shield shaped cartilage Thyroid Trivia Largest endocrine gland 20 grams in adult Each lobe 2-2.5cm in width and thickness 4cm in height Isthmus 0.5cm thick 2cm height and width Thyroid Derived from endoderm at base of tongue Recognizable after 1 month of fetal life Isthmus lies over 2nd and 3rd tracheal rings 2cm wide x 2 cm height x 0.5cm thick Adult 15-20 grams Thyroid Largest of the endocrine glands Blood flow 5x the weight of the gland/minute Hormones produced 93% thyroxine (T4) 7% triiodothyronine (T3) 4x the potency of thyroxine Responsible for the basal metabolic rate Deficiency = 40-50% fall in metabolic rate Excess = 60-100% increase in metabolic rate Thyroid Histology Multiple closed follicles (100-300 micrometers) Cuboidal epithelial cells secrete colloid into the follicles Colloid = thyroglobulin Large glycoprotein with 70 tyrosine amino acids Endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus synthesize and secrete HYPOTHALAMUS (-) HYPOTHALAMICPITUITARY PORTAL SYSTEM (-) TRH (+) ANTERIOR PITUITARY POSTERIOR PITUITARY TSH THYROID GLAND T4, T3 (T4 --> T3) TRH Produced by Hypothalamus Release is pulsatile, circadian Downregulated by T4, T3 Travels through portal venous system to adenohypophysis Stimulates TSH formation TSH Produced by Adenohypophysis Thyrotrophs Upregulated by TRH Downregulated by T4, T3 Travels through portal venous system to cavernous sinus, body. Stimulates several processes Iodine uptake Colloid endocytosis Growth of thyroid gland Thyroid Physiology Uptake of Iodine by thyroid Coupling of Iodine to Thyroglobulin Storage of MIT / DIT in follicular space Re-absorption of MIT / DIT Formation of T3, T4 from MIT / DIT Release of T3, T4 into serum Breakdown of T3, T4 with release of Iodine Thyroid and Iodine 50 mg of iodides are needed per year 1 mg/week Iodized salt 1 part Na iodide to 100,000 parts NaCl Iodides are ingested and oxidized to iodine in the thyroid Nascent iodine(Io) or I3Peroxidase enzyme (hydrogen peroxide) 1/5 of ingested iodine utilized for hormone synthesis Iodide Circulation Iodine uptake Na+/I- symport protein controls serum Iuptake Based on Na+/K+ antiport potential Stimulated by TSH Inhibited by Perchlorate Iodide Pump Thyroid gland actively pumps iodide into the cell via the basal membrane (iodide trapping) Iodide 30x the concentration of blood Able to concentrate to 250x the concentration in blood Rate of iodide trapping TSH dependent Thyroid Hormone Synthesis Tyrosine backbone Iodine Iodinase enzyme (enzyme I) attaches iodine to thyroglobulin Number of iodines determine activity of thyroid hormone Thyroxine (4 iodines) Triiodothyronine (3 iodines) MIT / DIT Formation Thyroid Peroxidase (TPO) Apical membrane protein Catalyzes iodide oxidation to reactive iodine Binds to Tyrosine residues of Thyroglobulin Antagonized by thionamides Coupling enzyme MIT with DIT= T3 Two DIT’s= T4 Pre-hormones secreted into follicular space Transport of T3 and T4 When in circulation 93% thyroxine and 7% triiodothyronine Conversion to active (T3) is by slow deiodination process 99% of T4 and T3 bound to plasma proteins Causes slow release of hormone to tissue Thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG) Tyroxine-binding prealbumin and albumin Secretion of Thyroid Hormone Stimulated by TSH Endocytosis of colloid on apical membrane Coupling of MIT & DIT residues Catalyzed by TPO MIT + DIT = T3 DIT + DIT = T4 Hydrolysis of Thyroglobulin Release of T3, T4 Release inhibited by Lithium Thyroid Hormones Thyroglobulin Storage Thyroglobulin molecule 30 thyroxine molecules Few triiodothyronine Sufficient supply for 2-3 months Deiodinase enzyme recycles iodine when thyroglobulin utilized Thyroid Hormone Metabolic effect of thyroxine noticed 2-3 days after release Steady state of thyroid hormone 10-12 days after ingestion Half life of 15 days Due to steady state, thyroid hormone is typically adjusted every 4-6 weeks Check T4 vs. TSH in the short term assessment Thyroid Hormone Majority of circulating hormone is T4 98.5% T4 1.5% T3 Total Hormone load is influenced by serum binding proteins Thyroid Binding Globulin 70% Albumin 15% Transthyretin 10% Regulation is based on the free component of thyroid hormone Hormone Binding Factors Increased TBG High estrogen states (pregnancy, OCP, HRT, Tamoxifen) Liver disease (early) Decreased TBG Androgens or anabolic steroids Liver disease (late) Binding Site Competition NSAID’s Furosemide IV Anticonvulsants (Phenytoin, Carbamazepine) Hormone Degradation T4 is converted to T3 (active) by 5’ deiodinase T4 can be converted to rT3 (inactive) by 5 deiodinase T3 is converted to rT2 (inactive)by 5 deiodinase rT3 is inactive but measured by serum tests Hypothyroidism Symptoms Nervous system Forgetfulness and mental slowing Paresthesias Carpal tunnel Ataxia and decreased hearing Tendon jerk slowed with prolonged relaxation phase Cardiovascular Bradycardia Decreased cardiac output Pericardial effusion Reduced voltage on EKG and flat T waves Dependent edema Hypothyroidism Symptoms Gastrointestinal Constipation Achlorhydria with pernicious anemia Ascitic fluid with high protein Renal Reduced excretion of water load Decreased renal blood flow and glomerular filtration Responses to hypoxia and hypercapnia are decreased Pleural effusions high protein Musculoskeletal Hyponatremia Pulmonary Arthralgia Joint effusions Muscle cramps CK can be elevated Anemia Normochromic normocytic Megaloblastic Pernicious anemia Hypothyroidism Symptoms Skin and hair Loss of lateral eye brows Dry, cool skin Facial features Coarse and puffy Metabolism Orange skin Carotene Decreased lipoprotein receptors Reproductive system Menorrhagia from anovulatory cycles Hyperprolactinemia No inhibition of thyroid hormone Hypothermia Intolerance to cold Increased cholesterol and triglyceride Weight gain Thyroid Hormone Metabolic effect of thyroxine noticed 2-3 days after release Steady state of thyroid hormone 10-12 days after ingestion Half life of 15 days Due to steady state, thyroid hormone is typically adjusted every 4-6 weeks Check T4 vs TSH in the short term assessment Hypothyroidism Etiologies Thyroiditis Thyroid ablation External radiotherapy Pharmacologic agents Infiltrative disorders Embryologic variants Thyroiditis Decreased uptake on uptake scan Transient Euthyroidism returns with time Lead to chronic thyroid dysfunction Etiology Infectious Post-partum Auto-immune Transient Chronic Drug Thyroiditis Thyrotoxic phase Short phase Increased T3 and T4 Symptoms of hyperthyroidism Thionamides not effective Thyroid synthesis low Can use beta-blockers Hypothyroid phase Transient or permanent Symptomatic patients need replacement Can check for recovery with stopping after 3-6 months Thyroiditis Time Course Williams Text of Endocrinology, Fig 11.50 Infectious Thyroiditis Etiology Bacterial 90% Fungal Mycobacterial Parasitic Syphilitic Symptoms Thyroid pain and tenderness Fever Dysphagia Dysphonia Treatment Treat the infection Autoimmune Thyroiditis Chronic Lymphocytic Silent Thyroiditis Hashimoto’s Women 3.5/1000 Men 0.8/1000 Frequency increases with age Familial history Associated with autoimmune diseases Antibodies Thyroid peroxidase More specific Thyroglobulin Elevated in many types of thyroid inflammation Thyroiditis Postpartum thyroiditis 2-21% of pregnancies Can occur up to one year post partum Usually transient and returns to euthyroid state Treat Hypothyroidism Symptoms with ‘hyperthyroidism’ Presence of TPO AB increases risk of long term hypothyroidism Transient/Destructive Thyroiditis Subacute 20% of thyrotoxic cases De Quervain’s thyroiditis Giant cell thyroiditis Pseudogranulomatous thyroiditis Subacute painful thyroiditis Symptoms Pain Fever Increased ESR Hoarseness or dysphagia Treatment ASA, NSAID Steroid rarely Comparison of Thyroiditis Characteristic Silent thyroiditis Subacute thyroiditis Age of onset (yr) 5-93 20-60 Sex ratio (F:M) 2:1 5:1 Etiology Autoimmune Viral Pathology Lymphocytic infiltration Giant cells, granulomas Prodrome Pregnancy Viral illness Goiter Non-painful Painful Fever/malaise No Yes TPO/thyroglobulin AB High and rising Low, absent or transient ESR Normal High RAIU <5% <5% Relapse Common Rare Permanent hypothyroidism Common Infrequent Drug Induced Thyroid Dysfunction Lithium Inhibits thyroid hormone secretion Hypothyroidism 3.4% prevalence Interferon-α Hyper/Hypothyroidism Transient thyroiditis TPO AB increases risk of thyroid dysfunction Interleukin-2 Aminoglutethimide Ethionamide Sulfonamides Drug Induced Thyroid Dysfunction Amiodarone 75 mg iodine/200 mg Hypothyroidism Thyrotoxicosis Type I and Type II Increased blood flow vs. decreased blood flow Not responsive to thionamides Hypothyroidism Infiltrative Disorders Amyloidosis Sarcoidosis Hemochromatosis Cystinosis Pneumocystis carinii Lymphoma Riedel’s thyroiditis Invasive Fibrous Thyroiditis Thyroid tissue replaced by fibrous tissue Rapidly enlarging neck mass Compressive symptoms Surgical removal Steroids and tamoxifen Thyroid Hormone Replacement 1.3 ug/kg/day 75-100 ug per day Elderly or patients with angina 12.5-25 ug/day Carefully increase every month IV dosing Use 60% of oral dose Levothyroxine Synthroid Levoxyl Unithroid Armour Thyroid T3/T4 preparation Dessicated pig thyroid Not a consistent amount of T3/T4 Most T3 preparations give higher than 1:11 ratio of T3:T4 Case Presentation 23 year old female G1P1 6 months post partum Palpitations that were intermittent for a couple of weeks and now resolved Now with 1 month of increased fatigue, hair loss and 10 pound weight gain Case Presentation What is her diagnosis? Post partum thyroiditis Tests that should be done? TSH 15 uIU/ml, Free T4 1.2 ng/dl TPO AB negative Pathophysiology of her disease process? Transient Treatment Levothyroxine therapy Recheck every 6-8 months After 3-6 months may be able to wean replacement Post Partum Thyroiditis Time Course Changes in free T4 Williams Text of Endocrinology, Fig 11.51 Williams Text of Endocrinology, Fig 12.6