* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Goiter
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
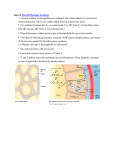
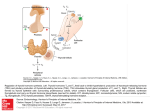
Goiter Thyroid Gland Thyroid Hormones: Functions • PERMISSIVE ACTIONS – Growth and development – Reproduction • DIRECT EFFECTS – Metabolic/thermogenic What makes thyroid hormones different from every other class of hormones? IODINE Thyroid Gland Thyroid Gland Synthesis of Thyroid Hormones OH OH • 3 main steps: CH2 – Synthesize thyrogobulin CH2 thyroglobulin – Alter tyrosine residues to create thyroxine and triiodothyronine OH OH I I I O O I CH2 I I I CH2 OH OH CH2 CH2 thyroglobulin OH OH I I I O O I CH2 I I I CH2 Synthesis of Thyroid Hormones OH • 3 main steps: – Synthesize thyrogobulin OH CH2 CH2 thyroglobulin – Alter tyrosine residues to create thyroxine and triiodothyronine – Use enzymes to cleave T3+4 from thyroglobulin I OH I I O I I CH2 enzymes OH I O I I CH2 Follicular Cells 1. Synthesis of thyrogolulin 2. Alteration of tyrosine colloid What does TSH do? 1. Stimulates I- uptake 2. Stimulates thyroglobulin synthesis 3. Stimulates re-uptake of thyroglobulin into the cell 4. Stimulates breakdown of thyroglobulin 5. Follicle cell enlargement and cell division 3. Enzymatic breakdown of thyroglobulin There is 50X more T4 than T3 in the blood • More T4 is produced in the thyroid gland • Binding globulin: – T4 has a much higher affinity for Thyroid-bindingglobulin than T3 – So a higher proportion of T4 will be bound, less will be free – More of T3 will be free to enter cells • In fact, it is thought that T3 is the ‘active’ form of thyroid hormone – Thyroid hormone receptors in cells have higher affinity for T3 – Most cells contain an enzyme to remove one of the iodines off of T4 – The liver converts T4 to T3 Thyroid Hormone Receptors • Can be nuclear: – Regulate gene transcription • Can be in the mitochondria: – Can regulate gene transcription of mitochondrial DNA • Effects on Metabolism – Thyroid hormones increase ATP production in the mitochondria – Increases oxygen consumption, and therefore basal metabolic rate • Effects on Thermoregulation: – Decreases the efficiency of ATP production • Less ATP produced, more heat let off • Increases Na+ transport pumps in cells (pumps produce heat) Clinical Aspects of Thyroid Hormones Clinical Aspects of Thyroid Hormones Clinical Aspects of Thyroid Hormones Clinical Aspects of Thyroid Hormones ? Clinical Aspects of Thyroid Hormones