* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Microtubule Assembly and Disassembly
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
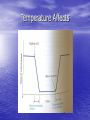
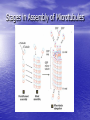
Microtubule Assembly and Disassembly By: Cherish Harmon Temperature Dependency • Assembly and stability of microtubules are temperature dependent. • If they are cooled to 4ºC, they depolymerize into αβ-tubulin dimers. • When they are warmed to 37ºC in the presence of GTP, the tubulin dimers polymerize into microtubules. • Change in temperature is used to purify. Temperature Affects Tubulin Polymerization • At αβ-tubulin concentrations above the critical • concentration (Cc), the dimers polymerize into microtubules, whereas at concentrations below the Cc, microtubules depolymerize. The nucleotide bound to the β-tubulin causes the Cc for assembly at the + and – ends of the microtubule to differ. Preferred assembly is at the + end. Tubulin Polymerization Cont. • At αβ-tubulin concentration higher than the Cc • for polymerization, dimers add to the + end. When the αβ-tubulin concentration is higher that the Cc at the + end but lower than the Cc at the – end, microtubules can treadmill by adding subunits to one end and dissociating subunits for the opposite end. Tubulin Polymerization Cont. • Because the intracellular concentration of the assembly-competent tubulin is much higher that the Cc of assembly, polymerization is highly favored in a cell. • The initial rate of tubulin polymerization is accelerated in the presence of nuclei (microtubule-based structures of fragments). Addition of Microtubule Fragments Microtubule Assembly • Three steps: • 1: Protofilaments assemble from αβ- tubulin subunits. • 2: Protofilaments associate to form the wall of the microtubule. • 3: The addition of more subunits to the ends of the protofilaments elongates the microtubule. Stages in Assembly of Microtubules Disassembly of Microtubules • Microtubule shortening: • Under shortening conditions, the microtubule • • ends are splayed, as if the lateral interactions between protofilaments may have been broken. When frayed apart and freed from lateral stabilizing interactions, the protofilaments may depolymerize by endwise dissociation of tubulin subunits. This provides clues about the instability of a microtubule. Observation of Disassembled Microtubules The End!!!