* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
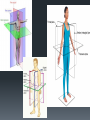
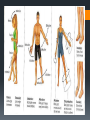
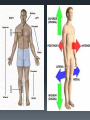
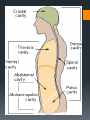
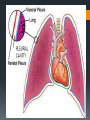
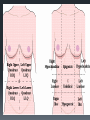
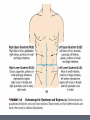
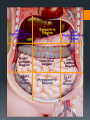
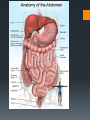
Human Body Orientation Dr Idara Objectives At the end of this slide, each student should be able to: List and describe the various body positions. Define the body planes and associated directional terms. Locate and describe the body cavities and their respective organs. List and describe the anatomical divisions of the abdominal region. Identify and locate the various body regions. Definition Anatomy is the study of structure and the physical relationships involved between body systems. It is from the Greek language which literally means “to cut apart”. The language of anatomy Body positions The body can assume many positions and therefore have different orientations. Scientists developed what is called the anatomical position to avoid confusion. The Anatomical position In the anatomical position, the body is assumed to be standing erect, face forward, with feet parallel and arms hanging at the side, with palms facing forward. Other body positions that are important to note are prone, supine e.t.c. In the supine position, the patient is lying face upward, on the back In the prone position, the patient is lying face downwards, on the stomach. Anatomical planes A plane is an imaginary line drawn through the body or organ to separate it into specific regions. Transverse or horizontal plane- divide the body into superior and inferior parts. Median or midsagittal plane- divides the body into right and left halves. Sagittal plane- run parallel to midsagittal but aren’t always in the midline. Frontal plane or coronal plane- divides the body into anterior and posterior sections. Terms of Movement Flexion Indicates bending or decreasing the angle between the bones or parts of the body. It usually occurs in an anterior direction. Dorsiflexion This describes ankle joint flexion. This occurs when walking uphill or lifting the front of the foot and toes off the ground. Extension Straightening or increasing the angle between the bones or parts of the body. It usually occurs in a posterior direction. Plantarflexion This occurs when one stands on his/her toes. Hyperextension This refers to extension of a limb or part beyond the normal limit. It can cause injury, such as “whiplash”. Abduction Means moving away from the median plane. Adduction Means moving towards the median plane. Circumduction A circular movement involving sequential flexion, abduction, extension, and adduction in such a way that the distal end of a part moves in a circle. Rotation Involves turning or revolving a part of the body around it’s longitudinal axis, such as turning one’s head to face sideways. Medial rotation- brings the anterior surface of a limb closer to the median plane. Also called internal rotation. Lateral rotation- Takes the anterior surface away from the median plane. Also called external rotation. Pronation Rotates the radius medially so that the palm of the hand faces posteriorly and it’s dorsum faces anteriorly. Supination Rotates the radius laterally and uncrosses it from the ulna, returning the pronated forearm to the anatomical position. Eversion Moves the sole of the foot away from the median plane, turning the sole laterally. Inversion Moves the sole of the foot towards the median plane, turning the sole medially. Opposition Is the movement by which the pad of the first digit ( thumb) is brought to another digit pad. This is the movement used when buttoning a shirt, pinch e.t.c. Reposition Describes the movement of the first digit back to it’s anatomical position. Protrusion Is an anterior movement as in protruding the mandible ( chin). Elevation Raises or moves a part superiorly e.g. raising the shoulders when shrugging Retrusion Posterior movement as in retruding the mandible. Depression Lowers or moves a part inferiorly e.g. Depressing the shoulders when standing at ease. Similar terms include Protraction and Retraction. Directional terms Superior (cranial or cephalic) means toward the head or upper body. Inferior (caudal) means away from the head or toward the lower part of the body. Anterior (ventral) refers to body parts toward or on the front of the body. Posterior (dorsal) refers to body parts toward or on the back of the body. Medial refers to body parts located near the middle or midline of the body. Lateral refers to body parts located away from the midline Note: any body part can be either superior or inferior depending on your reference point. Proximal refers to body parts close to the point of reference of the body. Distal refers to the body parts away from the point of reference. External means on the outside. Internal refers to structures on the inside. Superficial means toward or at the body’s surface. Deep means away from the body’s surface. Central refers to locations near the center of the body. Peripheral refers to the extremities or the surrounding. Body cavities The body has 2 cavities that house and protect organs, the dorsal (posterior) cavity and the ventral (anterior) cavity. The larger anterior cavity is subdivided into the thoracic cavity and abdominopelvic cavity. These two cavities are separated by the diaphragm. The thoracic cavity contains the heart, lungs and large blood vessels. The abdominopelvic cavity contains digestive organs, urinary and reproductive organs. Posterior Cavity Also called the cranial cavity. It houses the brain and spinal cord It is the smaller of the two cavities. Body regions The abdomen can be divided into 4 quadrants and 9 regions. 4 quadrants -upper left quadrant ULQ -upper right quadrant URQ Lower left quadrant LLQ -lower right quadrant LRQ 9 regions Epigastic region- located superior to the umbilical region. Right and left hypochondriac- located on either side of the epigastric region and contain the lower ribs. Umbilical- centrally placed, houses the naval or belly button. Right and left lumbar- lateral to the umbilical region. Hypogastric region- lies inferior to the umbilical region. Left and right iliac or inguinal region- lateral to the hypogastric region. Any questions? References Clinically Oriented Anatomy 6th Edition Keith L. Moore , Arthur F. Daley, Anne M. R. Agur Google images