* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Welcome to Anatomy and Physiology!
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
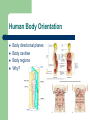
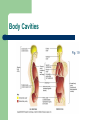
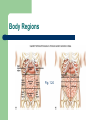
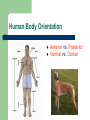
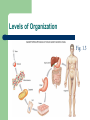
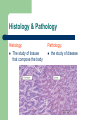
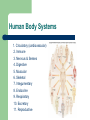
Unit 1: Body Organization and Homeostasis Tamalpais High School Honors Physiology Hippocrates Greek physician born in 460 BC “Hippocratic Oath” Today Hippocrates is known as the "Father of Medicine" What exactly will we study in physiology? Anatomy vs. Physiology STRUCTURE vs. FUNCTION Human Body Orientation Body directional planes Body cavities Body regions Why? Body Directional Planes Sagittal Midsagittal Frontal (aka Coronal) Transverse Fig 1.21 Body Cavities Fig. 1.9 Body Regions Fig. 1.24 Human Body Orientation Anatomical position Superior vs. Inferior Medial vs. Lateral Distal vs. Proximal Deep vs. Superficial Ipsilateral vs. Contralateral Fig. 1.20 Human Body Orientation Anterior vs. Posterior Ventral vs. Dorsal Fig 1.7 Homeostasis The body’s ability to maintain a stable internal environment – examples: human body temperature, water balance, salt/ion balance, oxygen/CO2 balance, blood pH, etc A Homeostatic Mechanism Fig 1.6 Example mechanism Gross vs. Fine Anatomy Gross anatomy Fine anatomy – – involves cells and tissues Histology = study of tissues Levels of Organization Fig. 1.3 Histology & Pathology Histology: The study of tissues that compose the body Pathology: the study of disease Tissues Cells organize into tissues – Tissue = Cells + extracellular matrix (EM) Nonliving Made by the cells Fig. 5.24 4 Main Tissue Types 1. Epithelial tissue • • • • • Protective covering Fig. One “free” side Other side: basement membrane Tightly packed, little EM Classified according to shape and # of layer of cells 5.6 4 Main Tissue Types Epithelial cell # of layers: – – Fig. 5.4 Simple – one layer Stratified – two or more layers Epithelial cell shape: – – – Squamous - flat Cuboidal – cube Columnar – tall, elongated What would simple cuboidal epithelial tissue look like? 4 Main Tissue Types 2. Connective Tissue – – Lots of EM Binds structures, provides support and protection, fills spaces, stores fat, produces blood cells, and protects against infections Figs 5.21 & 5.24 4 Main Tissue Types Types of Connective Tissue: – – – – – – Loose CT– under most layers of epithelium Adipose – stores fat Dense CT – very strong but stretchy; tendons & ligaments Bone Blood Cartilage Hyaline Elastic Fibrocartilage Figs 5.26 & 5.27 4 Main Tissue Types 3. Muscle Tissue – Skeletal muscle – Cardiac muscle – Smooth muscle Figs 5.28, 29, and 30 4 Main Tissue Types 4. Nervous tissue – – Communication Example cells include neurons (nerve cells) Fig. 5.31 Major Chemical Elements in the Body 65% Oxygen (O2) 18.5% Carbon (C ) 9.5% Hydrogen (H) 3.2% Nitrogen (N) Total O,C,H, & N = approx 96% of the body by weight Organic substances contain both C & H The rest are inorganic substances – electrolytes = inorganic substances that dissolve in water Electrolytes Electrolyte: any substance containing free ions that make the substance electrically conductive Examples: Na+, Cl-, Ca2+, K+, Why are they important? Trace Elements A trace element – – needed in very small ( i.e. “trace”…) amounts crucial to human survival Examples – – – – iron (Fe) - part of hemoglobin molecule zinc (Zn) – in several enzymes copper (Cu) – bone and melanin development iodine (I ) – synthesis of thyroid hormones Iodized salt! Human Body Systems 1. Circulatory (cardiovascular) 2. Immune 3. Nervous & Senses 4. Digestive 5. Muscular 6. Skeletal 7. Integumentary 8. Endocrine 9. Respiratory 10. Excretory 11. Reproductive