* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
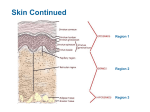
Skin Department of Histology and Embryology Li jinxin No.1020603 The following are emphasized 1.General structure of the skin. 2.The five layers of the epidermis. 3.Components of the cutaneous appendages. 1. General characteristics Skin is composed of two parts: epidermis and dermis.Under the dermis is the hypodermis or subcutaneous tissue. The skin appendages consist of sweat glands,sebaceous glands,hair and nails.Most of them are located among the dermis. epidermis dermis Sweat gland Section of skin from fingertip Function of skin • • • • Protection Sensory reception Excretion and absorption Thermoregulation 2. Epidermis • The epidermis consists of stratified squamous epithelium of keratinised type. • Its cells are arranged in five layers: stratum basale (basal layer) stratum spinous (spinous layer) stratum granulosum (granular layer) stratum lucitum (clear layer) stratum corneum (cornified layer) cornified layer clear layer granular layer spinous layer basal layer Section of skin from fingertip Epidermis • All the epidermis cells divide into two types: keratinocyte and non- keratinocyte • Most of the cells are keratinsed cells .In the deeper layer,cells are continuously produced and in the superficial layer they are keratinised and shed away. 2.1 layers of epidermis 2.2.1 Basal layer • This is a layer of columnar or cuboidal cells. • The cytoplasm is basophilic. •Large numbers of ribosomes, tonofibrils and desmosomes. 2.2.2 Spinous layer *It is composed of 4-10 layers of polygonal cells. *Many spinous processes are to be found on the cell surface. *The cytoplasm is basophilic. *Numerous ribosomes, desmosomes, lamellar granules. 2.1.3 Granular layer It is composed of 3-5 layer of flattened cells.The cytoplasm contains abundant keratohyalin granules. 2.2.4 Clear layer It is made up of 3-4 layers of transparent cells which are stained red by eosin. No nucleus and organelles. 2.1.5 Cornified layer The nuclei and organelles of which have degenerated and become lost.The cytoplasm has become keratin.Intercellular spaces are filled by material derived in part from discharged lamellated granules. 2.2 Non- keratinocyte • 2.2.1 Melanocytes • Melanocytes are large cells with long branched processes. They are located among the stratum basale cells. •Numerous ribosomes, rough endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi complexes. Melanocytes • • • • Melanosome (It contains tyrosinase) Melanin Melanin granule Melanin granules can absorb ultraviolet light and protect the body against ultraviolet irradiation. 2.2.2 Langerhans cells 2.2.3 Merkel cells 3 Dermis It is composed of dense connective tissue.The dermis is subdivided into two layers:the papillary layer and the reticular layer. Dermis • 3.1 Papillary layer • Numerous dermal papillaes.It has a rich blood capillary network,free nerve ending,tactile corpuseles. • 3.2 Reticular layer • Dense connetive tissue.It has blood vessels,lymphatics,nerves and skin appendages. 4 Hypodermis • This is a layer of loose connective tissue between the skin and deeper structures. 5 Skin appendages Including hair,sweat glands,sebaceous glands and nails. epidermis hair muscle sebaceous gland hair follicle sweat gland 5.1 Hair hair shaft hair root hair bulb hair papilla hair follicle hair muscle 5.2 Sweat glands • There are two types:small sweat glands and large sweat glands. • A sweat gland is divided into two parts:a secretory portion and a duct. secretory portion duct 5.3 Sebaceous glands • The secretory portion consists of two types of cells:the periphery cells and the center cells. duct periphery cell center cell Sebaceous glands • The periphery cells grow large toward the center. • As the cells become mature,the cytoplasm is gradually filled with fatty droplets,the nuclei shrink and even disappear. • At last,the cells break down and turn into sebum. • The ducts open to the upper part of hair follicles. Exercise • Statement the structure of epidermis. • Statement the structure and function of Melanocyte.