* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The French Revolution - Mrs. Duvall
Charles Maurice de Talleyrand-Périgord wikipedia , lookup
French Revolutionary Wars wikipedia , lookup
Treaty of Amiens wikipedia , lookup
Vincent-Marie Viénot, Count of Vaublanc wikipedia , lookup
War of the Fifth Coalition wikipedia , lookup
Reign of Terror wikipedia , lookup
Causes of the French Revolution wikipedia , lookup
Hundred Days wikipedia , lookup
Germaine de Staël wikipedia , lookup
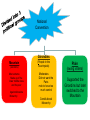
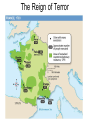
The French Revolution Chapter 6 6.1 The Revolution Begins Old Order • King Louis and wife Marie Antoinette (Austria) • • Spent to much $, Divided into estates 1. First – Catholic clergy, 1%, no taxes, some very wealthy 2. Second – nobility, 2%, important positions in gov’t and military, few taxes, large estates or king’s court 3. Third – largest, 97%, • • • bourgeoisie (merchants, factory owners, pro’s), sans culottes (artisans and workers) peasants (farmed nobles land, pay taxes, labor w/o pay Inequality and Enlightenment (Colonists) ideas inspired French revolution First Events of the Revolution • 1789 – King calls Estates General – (1st meeting in175 years) • Each estate brought a list of grievances • One vote each • Third Estate –formed the National Assembly • King locked them out of their meeting • met in indoor tennis court – (tennis court oath) • new constitution • King sent troops to Paris and Versailles • Members of National Assembly stormed the Bastille to get weapons (symbol of French Rev.) Storming of the Bastille Creating a New Nation • National Assembly (members of the 3rd Estate) • • • • • Removed First Estate’s privileges Sold church land Clergy public employees Monarchs to commoners Adopted Declaration of Rights of Man and the Citizen • Basic principle of revolution – All men were equal and able to vote • National Assembly, now controlled by radicals • Elected new legislature National Convention • Abolished monarchy, created Republic Declaration Rights of Man Guillotine • The new killing machine • pulley system with a sharp razor • 3rd Estate wanted equality in death. • Creator, Joseph Guillotin, a doctor who wanted a more humane way to die. 6.2 The Republic: A Radical Government • Three men important roles in new gov’t • all members of Mountain (Montagnards) political party – Jean-Paul Marat » Leader of the Paris Sans culottes » One of the National Convention’s most radical leaders – George-Jacques Danton » Beginning was radical, then compromise » Opposed the violent excess – Maximilien Robespierre » Lead the National Convention » Lead Committee of Public Safety » Started the Reign of Terror National Convention Girondins Mountain (Jacobins) Most extreme Made up of the lower middle class and the poor Against Aboslute Monarchy (People in the countryside) Moderates Did not want the Paris mob to have too much control Constitutional Monarchy Plain (swing voters) Supported the Girondins but later switched to the Mountain The end of the Monarchy • National Convention placed Louis XVI on trial – accused of treason-going against own country. – January 23, 1793 guillotined • Foreign troops deployed at French borders – Fight against Austria and Prussia • France transformed – – – – no monarch churches shut down new religion – worship rev. not God calendar – months renamed/10 day week Committee of Public Safety • 12 members lead by Robespierre – Drafted 18-45 men, fight against counterrevolutionaries (Foreign countries) • Set up Revolutionary Tribunal. – Used scare tactics on peasants to gain information – A counter-revolutionist-people rising up again the French Rev. – Secret police would stand in bread lines, listen for gossip. The Reign of Terror (10 months) During • Anyone who opposed the Revolution • executions drew crowds daily • Nobles, peasants, and revolutionaries died • 300,000 arrested • 17,000 were killed • One month in Paris 800 people • Govt. too radical End/After • Robespierre would later die because the majority people wanted to end to the killings • The Directory (1795) – – – – Run by 5 directors Weak Corrupt When in 1799 Napoleon seized power The Reign of Terror French Revolution Song 6.3 Napoleon • Young man achieved several military victories. • Admiral Horatio Nelson, commander of the British navy, trapped Napoleon’s ships in Egypt, Nile River. (lied about losses) • Became national hero. • Napoleon would then mix winning wars with govt. • Asked to run the govt. after the Committee of Public Safety would dissolve. • Napoleon ruled like a dictator, called himself Emperor. • Napoleon sold the Louisiana Territory to the United States. Napoleonic Wars • Great Britain was France’s biggest enemy. • British navy prevented Napoleon from conquering all of Europe. • Continental SystemFrench and its allied ships were not allowed to trade with Britain. Napoleon’s Policies • Recognized the Roman Catholic Church • Established the Bank of France, and set up an efficient way to collect taxes. • Napoleon set up high schools, universities and technical schools to educate young men. • Great sense of nationalism-feelings of pride on one’s country. 6.4 Napoleon Falls • Napoleon helped give the French something to support. • France fought against Austria, Prussia, and Great Britain. • These countries took advantage of France, during the French Rev. Napoleon’s Empire, 1812 Napoleon • Napoleon attacks Russia in1812 because of their – increasing military – decreasing support for Continental System • Napoleon had – new recruits – scarce resources – could not find the Russians – Russians used the scorched-earth policy (burned everything down) Napoleon’s defeat – Russian city Moscow was in flames – Russian winter and little food defeated Napoleon's army – 600,000 94, 000 – October 1813 Battle of Nations • Russia, Prussia, Austria, Great Britain – Napoleon surrendered in March 1814 – Exiled (forced to leave) to Elba, tiny island of coast of Italy The Last Campaigns • Napoleon returns to Paris after one year – France had returned to monarchy – Louis XVIII – fled to Belgium • March 20, 1815 – Hundred Days – Battle of Waterloo – British Duke of Wellington • Dutch, German, Prussian help – unsuccessful escape to America, exiled to St. Helena, tiny island in the South Atlantic • Napoleon dies at age 51 The Congress of Vienna • met to restore order in Europe – change boundaries, strengthen nations France gave up conquered territory and paid indemnity –fee to countries damaged during war – Charles Maurice de Talleyrand • represented France on behalf of king • made sure territory distributed fairly – Prince Klemens von Metternich • Austria, reactionary views – Europe before Napoleon • Revolution’s Legacy – nobility realized Enlightenment Ideas would not go away – ideas inspired political movements around the world