Napoleonic Code 1804 - Arlington Public Schools
... celebration, and Louis XVIII, the new king, fled to Belgium. With Louis only just gone, Napoleon moved back into the Tuileries. The period known as the Hundred Days had begun. ...
... celebration, and Louis XVIII, the new king, fled to Belgium. With Louis only just gone, Napoleon moved back into the Tuileries. The period known as the Hundred Days had begun. ...
napoleon`s rise and fall
... • 1798—French armies occupied Rome—a “Canossa in reverse” • The French Revolution had left the Church in France under state control • Napoleon recognized the need to come to terms with the Papacy in order that he might make use of it ...
... • 1798—French armies occupied Rome—a “Canossa in reverse” • The French Revolution had left the Church in France under state control • Napoleon recognized the need to come to terms with the Papacy in order that he might make use of it ...
The Napoleonic Wars
... Which of the following was most responsible for Napoleon's rise to power? A. his reputation as a military leader B. his devotion to republican ideals C. his use of absolute power D. the support given to him by the pope ...
... Which of the following was most responsible for Napoleon's rise to power? A. his reputation as a military leader B. his devotion to republican ideals C. his use of absolute power D. the support given to him by the pope ...
The Age of Napoleon and the Triumph of Romanticism
... Concordat with the Roman Catholic Church • For Napoleon religion was an instrument of social control. He was determined to mobilize it for the benefit of the state. • 1801: He concluded a concordat with Pope Pius VII. He restored the official status of the Roman Catholic Church, but not any power or ...
... Concordat with the Roman Catholic Church • For Napoleon religion was an instrument of social control. He was determined to mobilize it for the benefit of the state. • 1801: He concluded a concordat with Pope Pius VII. He restored the official status of the Roman Catholic Church, but not any power or ...
The Age of Napoleon
... French Revolution, including equality before the law, religious toleration, and economic freedom, through his empire. He urged his rulers to be constitutional kings. • He tried to destroy the feudal, hierarchical order in the French Empire and his dependent states. Nobility and clergy lost privilege ...
... French Revolution, including equality before the law, religious toleration, and economic freedom, through his empire. He urged his rulers to be constitutional kings. • He tried to destroy the feudal, hierarchical order in the French Empire and his dependent states. Nobility and clergy lost privilege ...
Chapter 11 Section 3 Study Notes
... C. Napoleon tried to use the Continental System to defeat Britain. The Continental System was intended to stop British goods from reaching continental markets. Allied states resented being told they could not buy British goods, and this strategy failed as well. Also due to new markets in Latin Ameri ...
... C. Napoleon tried to use the Continental System to defeat Britain. The Continental System was intended to stop British goods from reaching continental markets. Allied states resented being told they could not buy British goods, and this strategy failed as well. Also due to new markets in Latin Ameri ...
Napoleon Bonaparte
... Time period during the revolution when over 40,000 people were executed for being enemies of the state. King of France who would be executed. Peasants Pledge taken by the 3rd estate to stay together and create a fair constitution. Parisian mob stormed a prison in Paris looking for ammunition. Clergy ...
... Time period during the revolution when over 40,000 people were executed for being enemies of the state. King of France who would be executed. Peasants Pledge taken by the 3rd estate to stay together and create a fair constitution. Parisian mob stormed a prison in Paris looking for ammunition. Clergy ...
0.0_THE NAPOLEONIC ERA
... Established a secret police force. Censorship (media, laws, education) ...
... Established a secret police force. Censorship (media, laws, education) ...
Chapter 11 French Revolution
... F. Napoleon developed a powerful, centralized administrative machine with promotion based on ability. Opening government careers to individuals based on their ability was one change the middle class wanted. G. Napoleon created a new aristocracy based on merit in the state service. He created 3,263 n ...
... F. Napoleon developed a powerful, centralized administrative machine with promotion based on ability. Opening government careers to individuals based on their ability was one change the middle class wanted. G. Napoleon created a new aristocracy based on merit in the state service. He created 3,263 n ...
File - Springer`s World History
... F. Napoleon developed a powerful, centralized administrative machine with promotion based on ability. Opening government careers to individuals based on their ability was one change the middle class wanted. G. Napoleon created a new aristocracy based on merit in the state service. He created 3,263 n ...
... F. Napoleon developed a powerful, centralized administrative machine with promotion based on ability. Opening government careers to individuals based on their ability was one change the middle class wanted. G. Napoleon created a new aristocracy based on merit in the state service. He created 3,263 n ...
Napoleon Bonaparte PowerPoint - Mrs. Darling`s Digital Classroom.
... hearts of the many French men and women Helped defend the Directory (government) Won a series of remarkable victories for France By 1799, the government lost control of the political situation and the confidence of the French people People urged Napoleon to take over the government Napoleo ...
... hearts of the many French men and women Helped defend the Directory (government) Won a series of remarkable victories for France By 1799, the government lost control of the political situation and the confidence of the French people People urged Napoleon to take over the government Napoleo ...
Le Monde - christinelewh
... several time before, but only under Napoleon’s rule did it succeed. The new banking system regulated the economy, preventing any future economic crises from occurring. A new system of tax collection was created that was more efficient. Another major cause of the Revolution was the inequality among ...
... several time before, but only under Napoleon’s rule did it succeed. The new banking system regulated the economy, preventing any future economic crises from occurring. A new system of tax collection was created that was more efficient. Another major cause of the Revolution was the inequality among ...
Section 3: Radical Days of the Revolution
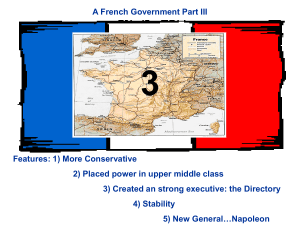
... • Directory held power from 1795-1799 • They were able to end war with Prussia and Spain but war continued with Austria and Great Britain • The Directory failed to deal with pressing problems-instead they focused on lining their own pockets. • Supporters of a constitutional monarchy won the majority ...
... • Directory held power from 1795-1799 • They were able to end war with Prussia and Spain but war continued with Austria and Great Britain • The Directory failed to deal with pressing problems-instead they focused on lining their own pockets. • Supporters of a constitutional monarchy won the majority ...
Napoleon blanks ppt
... was a popular soldier in the French military who supported the republic In 1796, the leaders of the French republic gave Napoleon command of the army to defend France from this European coalition ...
... was a popular soldier in the French military who supported the republic In 1796, the leaders of the French republic gave Napoleon command of the army to defend France from this European coalition ...
Napoleon Lecture
... Spanish people revolt and win with British help Napoleon commits 250,000 troops there for 6 years Hurts French economy badly Spanish set up a limited monarchy and include many ideals from the French Revolution Think about the Spanish peasants that fought in the war… ...
... Spanish people revolt and win with British help Napoleon commits 250,000 troops there for 6 years Hurts French economy badly Spanish set up a limited monarchy and include many ideals from the French Revolution Think about the Spanish peasants that fought in the war… ...
Napoleon - Warren County Schools
... • A blockade preventing all French or allied ships from trading with Great Britain • Napoleon hoped disrupting their trade would weaken Great Britain, therefore weakening the rebellion against ...
... • A blockade preventing all French or allied ships from trading with Great Britain • Napoleon hoped disrupting their trade would weaken Great Britain, therefore weakening the rebellion against ...
Napoleon Bonaparte - Greensburg Salem School District
... insisting that the government view all manuscripts before they are published, and having government police read people’s mail. Once when asked who the greatest woman of history was, he answered, “The one who had the most children.” ...
... insisting that the government view all manuscripts before they are published, and having government police read people’s mail. Once when asked who the greatest woman of history was, he answered, “The one who had the most children.” ...
Independence High School Global History Regents Mr. Wisell Unit 2
... realized the need for a pause in the war. He remarked, “the French Revolution is not finished so long as the scourge of war lasts…I want peace, as much to settle the present French government, as to save the world from chaos.” Napoleon achieved a peace treaty in 1802, but it did not last long. War w ...
... realized the need for a pause in the war. He remarked, “the French Revolution is not finished so long as the scourge of war lasts…I want peace, as much to settle the present French government, as to save the world from chaos.” Napoleon achieved a peace treaty in 1802, but it did not last long. War w ...
Napoleon Notes- Powerpoint
... Revolution? a) the storming of the Bastille b) the Reign of Terror c) the establishment of the Napoleonic Code d) Napoleon’s rise to power ...
... Revolution? a) the storming of the Bastille b) the Reign of Terror c) the establishment of the Napoleonic Code d) Napoleon’s rise to power ...
Napoleon: Hero or a Villain?
... Napoleon’s Background • From Corsica • Sent to school in France at age 9 • Became a General in the French military under Robespierre • When the country was in grave ...
... Napoleon’s Background • From Corsica • Sent to school in France at age 9 • Became a General in the French military under Robespierre • When the country was in grave ...
Napoleon - White Plains Public Schools
... • After Napoleon’s defeat in Russia, the other European powers combined to overthrow him. • After invading France, the foreign powers brought the old French royal family back to power in 1814. E. Napp ...
... • After Napoleon’s defeat in Russia, the other European powers combined to overthrow him. • After invading France, the foreign powers brought the old French royal family back to power in 1814. E. Napp ...
The French Revolution and Napoleon
... Ex: Just as it helped France in the late 1700’s. It will help Germany and Spain protect themselves against Napoleon. ...
... Ex: Just as it helped France in the late 1700’s. It will help Germany and Spain protect themselves against Napoleon. ...
File - Hjelm`s History Class
... by strengthening the government. “Order, security and efficiency” replaced “liberty, equality and fraternity” as France’s slogan. • To restore economic prosperity, Napoleon controlled prices, encouraged new industry and built roads and canals. He set up gov’t schools to ensure well-trained officials ...
... by strengthening the government. “Order, security and efficiency” replaced “liberty, equality and fraternity” as France’s slogan. • To restore economic prosperity, Napoleon controlled prices, encouraged new industry and built roads and canals. He set up gov’t schools to ensure well-trained officials ...
French Revolution
... After Napoleon’s defeat the major European powers and their monarchies tried to restore order, keep the peace, and suppress the ideas of Revolution. The Congress of Vienna was setup to achieve these goals. The Congress focused on three principles. • The countries that had suffered the most under Nap ...
... After Napoleon’s defeat the major European powers and their monarchies tried to restore order, keep the peace, and suppress the ideas of Revolution. The Congress of Vienna was setup to achieve these goals. The Congress focused on three principles. • The countries that had suffered the most under Nap ...
Charles Maurice de Talleyrand-Périgord

Charles Maurice de Talleyrand-Périgord (/ˈtæləˌrænd ˈpɛrɪˌɡɔr/; French: [ʃaʁl moʁis də tal(ɛ)ʁɑ̃ peʁiɡɔʁ]; 1754–1838), prince de Bénévent, then prince de Talleyrand, was a French bishop, politician and diplomat. Due to a lame leg, he was not able to pursue the military career that had originally been foreseen for him by his family. Instead he studied theology. In 1780, he became Agent-General of the Clergy and represented the Catholic Church to the French Crown. He worked at the highest levels of successive French governments, most commonly as foreign minister or in some other diplomatic capacity. His career spanned the regimes of Louis XVI, the years of the French Revolution, Napoleon, Louis XVIII, and Louis-Philippe. Those he served often distrusted Talleyrand but, like Napoleon, found him extremely useful. The name ""Talleyrand"" has become a byword for crafty, cynical diplomacy.He was Napoleon's chief diplomat in years when French military victories were bringing one European state after another under French hegemony. Most of the time, though, Talleyrand worked for peace so as to consolidate France's gains. He succeeded in obtaining peace with Austria in the 1801 Treaty of Luneville and with Britain in the 1802 Treaty of Amiens. He could not prevent the renewal of war in 1803. By 1805, he opposed his emperor's renewed wars against Austria, Prussia, and Russia in 1805–1806; he resigned as foreign minister in August 1807, but Napoleon still trusted him. Talleyrand connived to undermine Napoleon's plans and secretly dealt with Tsar Alexander of Russia and the Austrian minister Metternich. He sought a negotiated secure peace so as to perpetuate the gains of the French revolution. Napoleon rejected peace and when he fell in 1814, Talleyrand took charge of the Bourbon restoration based on the principle of legitimacy. He played a major role at the Congress of Vienna in 1814–1815, where he negotiated a favourable settlement for France while undoing Napoleon's conquests.Talleyrand polarizes scholarly opinion. Some regard him as one of the most versatile, skilled and influential diplomats in European history, and some believe that he was a traitor, betraying in turn the Ancien Régime, the French Revolution, Napoleon, and the Restoration.