* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download France - Henry County Schools
Charles X of France wikipedia , lookup
French Revolutionary Wars wikipedia , lookup
Reign of Terror wikipedia , lookup
Treaty of Amiens wikipedia , lookup
Vincent-Marie Viénot, Count of Vaublanc wikipedia , lookup
Germaine de Staël wikipedia , lookup
Causes of the French Revolution wikipedia , lookup
Hundred Days wikipedia , lookup
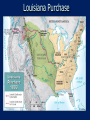
France Preview and Processing What is this picture of? Who was kept inside? The Monarchy • Louis XVI (16) is married to Marie Antoinette from Austria • • • Louis XVI was indecisive and had little patience for governing. Marie Antoinette was unpopular. “Madame Deficit” French Economy in trouble France is in debt because of the American Revolution and money spent by the monarchy. People were paying heavy taxes that made it hard to do business and make money for the merchants, factory owners and bankers. Estates General Louis tried taxing the nobility to get money, but they forced him to call an Estates General meeting. It was the first in 175 years to be held. Estates-General • 1st= Church 10% of the land • 2nd = nobles 2% pop. Owned 20% of the land • 3rd= bourgeoisie, urban lower class peasants 98% of pop. Owned less than 4% of the land The National Assembly 3rd estate eager for change Meet together and each delegate get a vote-3rd estate has the most votes The National Assembly June 17, 1789 Vote passes—end of absolute monarchy The Bastille July 14th, a mob storms into the Bastille Symbolic act for the Revolution Terror in France August 10th-20,000 people invade the palace where the royal family was. royal guards killed royal family imprisoned Great Fear-panic throughout France Riots over prices of bread Louis XVI and Marie Antoinette returned to Paris from Versailles Reforms National Assembly Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen men are born and remain free and equal in rights (liberty, property, security, and resistance to oppression) Equal justice, freedom of speech, and freedom of religion National Assembly Constitutional Monarchy 1791 Louis XVI agreed to National Assembly’s new constitution—limited constitutional monarchy Legislative Assembly power to create laws and to approve reject declarations of war(king has power to enforce laws) Monarchy Abolished Constitution of 1791declared the king deposed—abolished the monarchy and France becomes a republic New government=the National Convention Sept. 21 Jacobins take control. Louis XVI tried for treason. He is found guilty and was sentenced to death (January 21, 1793) Marie Antoinette killed as well Guillotine War France continues to fight outside forces such as Austria and Prussia along with Great Britain, Holland, and Spain Coalition Army 1793-300,000 1794-800,000 Making the Connection Why was Louis XVI killed? Do world leaders run the risk of being replaced in a revolution? How has the United States avoided violent revolution? Can you give a definition of social contract? Reign of Terror Maximilien RobespierreJacobin leader Republic of Virtue wiping out the trace of France’s past calendar 12 months of 30 days renamed months no Sundays- religion was dangerous July 1793- Robespierre became leader of the Committee of Public Safety Meant to protect France from its enemies Most of the enemies were usually fellow radials who challenged him. Thousands of people sent to their death (about 4,000) about 85% were peasants or urban class July 1794Robespierre arrested and executed-July 28 Shift in public opinion—too much terror Skyrocketing prices for bread, salt still exist New Government 1795—3rd new government put into place Power in the hands of upper middle class and had two-house legislation (Bicameral) Executive body Five men (The Directory) Napoleon Bonaparte Born in Corsica 1769 9 years old when he went to military school 1785-a lieutenant in old government’s military Post Revolution he joined the new Government Military hero as head of the French army Coup d’état Coup d’état: “blow to the state” and a sudden seizure of power Directory dissolved Napoleon becomes dictator The good things about the Age of Napoleon 1799-1815 Established peace Developed a plebiscite: vote on new Constitution Restored order Restoring Order 1. 2. 3. 4. Economic: national bank Social: promotion for merit not family & nobility allowed to return Religion: RCC official religion but everyone worship as they pleased Legal: Napoleonic Code Napoleonic Code: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Equality under the law Censored newspapers Woman could not hold property Restored slavery in the Caribbean None of the codes applied to Napoleon Making the Connection What would you give up in exchange for order? Napoleon Heads Off to Conquer the World “napoleon complex” Time Line 1799: came to power as dictator 1803: Louisiana Purchase 1804: self proclaimed Emperor of France 1805: Battle of Trafalgar 1808: Most of Europe under his control 1815-1821: attempts to take over Russia and thus Asia 1821: dies The French Empire Louisiana Purchase In 1803, Napoleon sold the Louisiana Purchase to the United States for $15 million. Louisiana Purchase The Battle of Trafalgar, 1805 Napoleon wants a European empire Napoleon’s only major loss Admiral Horatio Nelson—British Napoleon decided not to invade Great Britain The Continental System In 1806, a blockade was set up to prevent trade from Great Britain to Europe. Britain responded with its own blockade. Caused War of 1812 against the United States Spain King of Spain= Napoleon’s brother Joseph Spanish used Guerilla tactics. Peninsular War Nationalism had people fighting against Napoleon. Russia Napoleon invaded Russia in June 1812. Czar (tzar, tsar) Alexander I refused to stop selling grain to Britain Scorched earth policy Napoleon's Rule Comes to an End Napoleon faces a coalition army outside Leipzig and is defeated. Coalition: Great Britain, Prussia (Germany), Russia, Austria, Sweden 1814 exiled to the island of Elba 100 days 06-18-1815 Waterloo Exiled to St. Helena Died 1821 @ age 52 Congress of Vienna Congress of Vienna November 1814 to June 1815. Heads of European governments came together for security and stability for Europe Klemens von Metternich of Austria Balance of power