* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Physiology of hearing. Vestibular analyzer
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
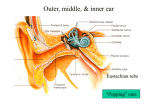
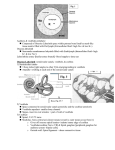
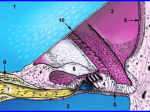
Physiology of hearing. Vestibular analyzer 1 – cochlear nerve; 2 – ventral cochlear nucleus; 3 – dorsal cochlear nucleus; 4 – olivar complexes; 5 – accessory nucleus; 6 – lateral lemniscus; 7 – lower hillocs of quadrigeminal body; 8 – medial genicular body; 9 – auditory cortex/ Semicircular canal function • Ampula is enlargement at one end of semicircular canal. It has a small crest on top of which is a gelatinous mass known as cupula. Hair cells have two kinds of cilia – kinocilium and stereocilia. • Kinocilium is large cilium located at one end of hair cell. Stereocilia are small. When stereocilia are bent towards kinocilium, hair cell is depolarized, i.e. stimulated. • When stereocilia are bend away from kinocilium, hair cell is hyperpolarized, i.e. inhibited. It occurs because acceleratory force acts to flow of fluid in semicircular canals during circular motion of the head or whole the body. • Hair cells are located along crista ampularis and protect their cilia in cupula. Hair cells are secondary sensor cells, which synapse with neurons. Axons of these nerve cells compose vestibular nerve.