* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Neuron - VirtualAvenue
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
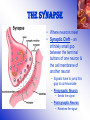
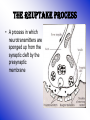
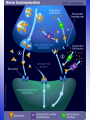
The Neuron Inter-workings of the Brain Drill #22 • Draw the neuron. • Label it correctly with the following parts: – Soma – Dendrites – Axon – Myelin Sheath – Terminal Buttons • Write the function of each of the parts Neural Impulse • NEURAL IMPULSES are complex electrochemical reactions involving IONS – electrically charged atoms that flow back and forth across the cell membrane – Positively charged ions – sodium & potassium – Negatively charged ions chloride • Positively & negatively charged ions DO NOT travel at the same rate – This leads to a slightly higher concentration of negatively charged ions inside the cell Resting vs. Action Potential Alan Hodgkin & Andrew Huxley • Resting Potential – when a neuron is at its stable, negative charge – When it is inactive • Action Potential – A very brief shift in a neuron’s electrical charge that travels along an axon – a voltage spike occurs • This occurs when channels open up, briefly allowing positively charged sodium ions to rush in Absolute Refractory Period & The All or None Law • Absolute Refractory Period – The minimum amount of time after an action potential during which another action potential CANNOT begin • All or None Law – Think of a Neuron like a gun – you cannot half-fire a gun – Either the neuron fires, or it doesn’t – Action potentials are all the same size – weaker stimuli do not produce smaller action potentials **Neurons can convey information about the strength of a stimulus by varying the rate at which they fire** The Synapse • Where neurons meet • Synaptic Cleft – an infinitely small gap between the terminal buttons of one neuron & the cell membrane of another neuron – Signals have to jump this gap to communicate – Presynaptic Neuron • Sends the signal – Postsynaptic Neuron • Receives the signal NeuroTransmitters Chemicals that transmit information from one neuron to another – fundamental to behavior & play a key role in everything from muscle movement to mood and mental health Common Neurotransmitters & Their Functions • Acetylcholine (can be stimulated by nicotine) – Activates motor neurons controlling skeletal muscles – Regulates attention, arousal, and memory • Dopamine (Cocaine & amphetamines elevate Dopamine activity) – Control of voluntary movement & pleasurable emotion – Overactivity is associated with Schizophrenia • Norepinephrine (Cocaine & amphetamines elevate NE levels) – Modulation of mood & arousal • Serotonin (Prozac & antidepressants affect Serotonin levels) – Regulation of sleep, eating & aggression – Abnormal levels contribute to depression & OCD • GABA (Valium & anti-anxiety drugs work at GABA synapses) – Seem to produce only inhibitory postsynaptic potentials – Regulation of anxiety in humans & plays a role in seizures • Endorphins (resemble opiate drugs in structure & effects) – Pain relief & pleasurable emotions Receiving Signals • Postsynaptic Potentials (PSP) – Voltage change at the receptor site on a postsynaptic cell membrane • DO NOT follow the All or None Law • Vary in size and increase or decrease probability of a neural impulse • Excitatory PSP – A positive voltage shift that increases likelihood that the postsynaptic neuron will fire action potentials • Inhibitory PSP – A negative voltage shift that decreases the likelihood that the postsynaptic neuron will fire action potentials The Reuptake Process • A process in which neurotransmitters are sponged up from the synaptic cleft by the presynaptic membrane