* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
The City and the Stars wikipedia , lookup
Kevin Warwick wikipedia , lookup
Autonomous car wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
History of artificial intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Intelligence explosion wikipedia , lookup
Ecological interface design wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive collaborative control wikipedia , lookup
Existential risk from artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Philosophy of artificial intelligence wikipedia , lookup
List of Doctor Who robots wikipedia , lookup
Self-reconfiguring modular robot wikipedia , lookup
Why Study Robots now?
MIT Kismet
Honda Asimo
2003
Sojourner 1996
NavLab (CMU)
Comp 3104 2009
1
Moore’s Law - Computers and Brains
AI
Comp 3104 2009
Figure from ROBOT, Moravec, Oxford, 1998, Chapter 3: Power and Presence, page 68
2
Why learn to program with Robots ?
1. Robots are becoming commercially viable – need developers
2. Serious promise of Artificial Intelligence – needs researchers
3. Fundamental aspects :
1. Good vehicle for teaching programming …
2. Important analogy of each living being … the Self
3. Important analogy of societies … Communication
N.B. we are thinking of Autonomous Robots
Comp 3104 2009
3
Comp 3104 2009
4
Human Robot
Human
Group Robot
Group
Comp 3104 2009
5
Human Qualities
Affective
Cognitive
Thinking
Feeling
s
Knowin
g
Emotions
Comp 3104 2009
Psychomotoric
Acting
Behavin
g
6
Behaviour Modules
Collision
Idea is to split overal desired
behaviour into a number of
“modules” of program code
which can run independently.
SearchLight
These may be arranged to
have priorities
Wander
Comp 3104 2009
7
Rod Brookes + Cogs
Comp 3104 2009
8
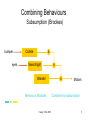
Combining Behaviours
Subsumption (Brookes)
bumper
eyes
Collide
s
Searchlight
Wander
Behaviour Modules
Comp 3104 2009
s
s
Motors
Combine by subsumption
9
DARPA ALV
(Autonomous Land Vehicle)
Internalized
Plans
Behaviour 3
Behaviour 2
Behaviour 1
sensors
s
s
s
Motors
There IS a global map !
Comp 3104 2009
10
Braitenberg (1984), Vehicles: Experiments in
Synthetic Psychology, MIT Press.
Comp 3104 2009
11
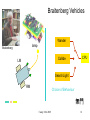
Braitenberg Vehicles
Wander
lamp
Braitenberg
Collide
LM
CPU
SearchLight
RM
Choice of Behaviour
Comp 3104 2009
12
Java Behaviour Routines
public void wander() {
forever {
wander_flag = true;
wanderOpL = 10;
wanderOpR = 10;
muMonDefer();
}
}
lamp
Braitenberg
LM
eyeLF
eyeRF
RM
public void searchlight() {
forever {
if(eyeLF > eyeRF) {
searchlight_flag = true;
searchlightOpR = ??;
searchlightOpL = ??;
muMonSleep(100);
searchlight_flag
= false;
Behaviour Routines
}
if(eyeLF > 0) {
Comp 3104 2009
13
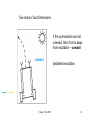
Two motors Two Dimensions
If the connections are not
crossed, then it turns away
from excitation – coward
Ipsilateral excitation
Comp 3104 2009
14
Uncrossed inhibitory
connections (note the –sign)
give ipsilateral inhibition:
Turns towards the light and
slows down as it gets close
Comp 3104 2009
15
Brood Sorting
The Emergence of Intelligence
robot
puck
Martijn Schut http://www.cs.vu.nl/~zos
Comp 3104 2009
16
Problem is to get one
(or more) autonomous
robots to clear the junk
into heaps …
• How to do the programming ?
• Imagine doing the clearing up yourself !
Program the Robots explicitly to
• find an object
• take an object
• go back to cluster
• find a cluster
• drop an object
Comp 3104 2009
17
Alternative
Program the robots to avoid things
Comp 3104 2009
18
Conclusions :
• Behaviour Emerges !
• Intelligence in the Indivudal or Group ?
Comp 3104 2009
19
• Messor Sancta ants
• 1,500 corpses
• 26 hours
• Put dead ants into graveyards by walking around
bumping into them
Comp 3104 2009
20
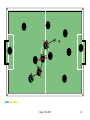
• Football as benchmark for AI advances
• Worldwide competitions since 1997
• Current Leagues
SmallSize
Simulation
MidSize
Sony Dog
Humanoide
Comp 3104 2009
21
Comp 3104 2009
22