* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 2
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Planned obsolescence wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Customer relationship management wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Grey market wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Online shopping wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketplace Fairness Act wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Music industry wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Visual merchandising wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
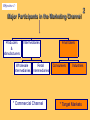
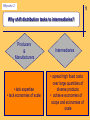
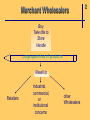
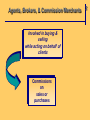
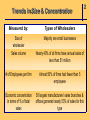
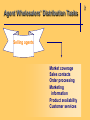
Chapter 2 The Channel Participants Objective 1: Major Participants in the Marketing Channel Producers & Manufacturers Intermediaries Wholesale Retail Intermediaries Intermediaries * Commercial Channel 2 Final Users Consumers Industries * Target Markets Objective 2: 1 Why shift distribution tasks to intermediaries? Producers & Manufacturers • lack expertise • lack economies of scale Intermediaries • spread high fixed costs over large quantities of diverse products • achieve economies of scope and economies of scale 2 Example: Distribution of Crayons Manufacturer direct to customers • Huge order processing facility • Huge inventory • Several warehouse locations • Transportation of product to consumers = cost prohibitive Objective 3: 2 Major Types of Wholesalers All Wholesale Firms Independent middlemen Merchant wholesaler Agents, brokers, & commission merchants Manufacturer owned Manufacturers' sales branches & offices Merchant Wholesalers Buy Take title to Store Handle Large quantities of products Resell to Retailers Industrial, commercial, or institutional concerns other Wholesalers 2 Agents, Brokers, & Commission Merchants Involved in buying & selling while acting on behalf of clients Commissions on sales or purchases 2 Manufacturers’ Sales Branches & Offices Separated from manufacturing plants Owned & operated by manufacturers Distribute manufacturer’s products at wholesale Some wholesale allied & supplementary products purchased from other manufacturers. 2 Objective 4: 2 Major Trends in Wholesale Structure 1987—1997 69.7% Manufacturer’s sales branches & offices 60.8% Wholesale trade 57.8% Merchant wholesalers 50.0% Agents, brokers, & commission merchants Trends in Size & Concentration Measured by: Types of Wholesalers Size of wholesaler Majority are small businesses Sales volume Nearly 40% of all firms have annual sales of less than $1 million # of Employees per firm Almost 50% of firms had fewer than 5 employees Economic concentration in terms of % of total sales 50 largest manufacturers’ sales branches & offices garnered nearly 53% of sales for this type 2 Objective 5: 2 Merchant Wholesalers Specialize in Performance Distribution Tasks Provide market coverage Make sales contacts Hold inventory Process orders Gather market information Offer customer support • Operate at high levels of effectiveness and efficiency • Average cost curves lower than those for their suppliers Merchant Wholesalers’ Distribution Tasks Serve Customers Assure product availability Provide customer service Extend credit & financial assistance Offer assortment convenience Break bulk Help customers with advice & technical support 2 Agent Wholesalers’ Distribution Tasks Manufacturers’ Agents Market coverage Sales contacts 2 Agent Wholesalers’ Distribution Tasks Selling agents Market coverage Sales contacts Order processing Marketing information Product availability Customer services 2 Agent Wholesalers’ Distribution Tasks Brokers Market coverage Sales contacts Order processing Marketing information Product availability Customer services 2 Agent Wholesalers’ Distribution Tasks Commission Merchant Market coverage Sales contacts Order processing Breaking bulk Credit Holding inventory 2 Objective 6: 2 Retail Structure Alternative Bases for Classifying Retailers • By Ownership of Establishment • By Kind of Business (Merchandise Handled) • By Size of Establishment • By Degree of Vertical Integration • By Type of Relationship with other Business Organizations • By Method of Consumer Contact • By Type of Location • By Type of Service Rendered • By Legal Form of Organization • By Management Organizations or Operational Technique 2 Kind-of-Business Classifications Retail Trade • Motor vehicle & parts dealers • Furniture & home furnishings stores • Electronics & appliance stores • Building material & garden equip. & supply dealers • Food & beverage stores • Health & personal care stores • Gasoline stations • Clothing & clothing accessories stores • Sporting goods, hobby, book, & music stores • General merchandise stores • Miscellaneous store retailers • Nonstore retailers Objective 7: 1 Retail Structure Trends Decreasing number of establishments Increasing sales = increase in size of retail establishments measured by average sales volume per store Concentration in Retailing In 1997 4% of all retail firms accounted for nearly 80% of total sales!! 1 Objective 8: 2 Distribution Tasks Performed by Retailers The role of the retailer in the distribution channel, regardless of his size or type, is to interpret the demands of his customers and to find and stock the goods these customers want, when they want them, and in the way they want them. This adds up to having the right assortments at the time customers are ready to buy. — Charles Y. Lazarus 2 Distribution Tasks Performed by Retailers • Offer manpower & physical facilities close to consumers’ residences • Provide personal assistance to help sell products • Interpret and relay consumer demand • Divide large quantities into consumer-sized lots • Offer storage • Remove risk by ordering in advance of the season Objective 9: 2 Retailers’ Growing Power in Marketing Channels Increased size & buying power Become power retailers & category killers Application of advanced Technologies Information technology & the Internet; threetailing Use of modern marketing strategies Modern techniques; relationship marketing Objective 10: Facilitating Agencies in Marketing Channels • • • • • • • Transportation agencies Storage agencies Order processing agencies Advertising agencies Financial agencies Insurance companies Marketing research firms 2