* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download marketing
Bayesian inference in marketing wikipedia , lookup
Planned obsolescence wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Service parts pricing wikipedia , lookup
Price discrimination wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Product placement wikipedia , lookup
Consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Product lifecycle wikipedia , lookup
Dumping (pricing policy) wikipedia , lookup
Food marketing wikipedia , lookup
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Grey market wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Perfect competition wikipedia , lookup
Supermarket wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Predictive engineering analytics wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Segmenting-targeting-positioning wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
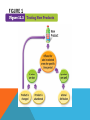
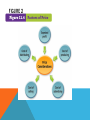
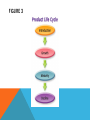
Chapter Introduction Section 1: The Changing Role of Marketing Section 2: The Marketing Mix Section 3: Distribution Channels Visual Summary The profit motive acts as an incentive for people to produce and sell goods and services. Do you think advertisements influence your buying habits? In this chapter, read to learn how businesses market and distribute their goods and services. The Development of Marketing The focus of marketing is to maximize sales by satisfying consumer wants and needs. SECTION 1 The Development of Marketing (cont.) • Marketing’s main purpose today is to convince consumers that a certain product will add to their utility. • Utility can be divided into four types: – Form – Place – Time – Ownership SECTION 1 Market Research Through market research, businesses can determine what products consumers are likely to buy and at what prices. SECTION 1 Market Research (cont.) • In today’s global market, it is vital that businesses find out what consumers want through market research. • Issues considered by market researchers: – Who is their target audience? – What advertising method will be most effective? SECTION 1 Market Research (cont.) • Purposes of early market research: – It helps producers determine whether there is a market for their good or service. – It helps determine what the market is. – It can indicate any changes in quality, features, or design that should be made. SECTION 1 Market Research (cont.) • Market research can be done immediately after a product is released for sale or after it has been on the market for a while. Changes in marketing strategy are made accordingly. • The first step in market research is conducting a market survey. SECTION 1 Market Research (cont.) • The survey may be in the form of: – a written questionnaire – individual interviews – focus group interviews – an online questionnaire SECTION 1 Market Research (cont.) • Test-marketing is the final step before offering a product for national distribution. • If the product is not successful here, it may be redesigned or discontinued. View: Testing New Products SECTION 2 The “Four P’s” of Marketing The “four Ps” of marketing are product, price, place, and promotion. SECTION 2 The “Four P’s” of Marketing (cont.) • Product—market research helps determine what services to offer with the product, how to package it, and what kind of product identification to use. – Product identification is meant to attract consumers to look at, buy, and remember a particular product. SECTION 2 The “Four P’s” of Marketing (cont.) • Price—in setting a price, a company has to consider the costs of producing, advertising, selling, and distributing the product, as well as the amount of profit it hopes to make. – Penetration price is one common marketing strategy for a new product. – Some industries may rely on price leadership. View: Factors of Price SECTION 2 The “Four P’s” of Marketing (cont.) • Place—where the product should be sold is another decision of the marketing department. – The location of the product within the store itself is another consideration. – Geographic location is also a factor. SECTION 2 The “Four P’s” of Marketing (cont.) • Promotion—use of advertising to inform consumers that a new or improved service is available and to persuade them to purchase it. SECTION 2 The “Four P’s” of Marketing (cont.) • The type of promotion that a producer uses depends on three factors: – The product. – The type of consumer that the company wants to attract. – The amount the company plans to spend. SECTION 2 The “Four P’s” of Marketing (cont.) • Direct-mail advertising, free samples, cents-off coupons, gifts and rebates are all forms of promotion. SECTION 2 Product Life Cycle Most products go through a four-stage life cycle consisting of introduction, growth, maturity, and decline. SECTION 2 Product Life Cycle (cont.) • Most products go through a product life cycle. View: Product Life Cycle SECTION 2 Product Life Cycle (cont.) • The four stages of a typical product life cycle include: – Introduction – Growth – Maturity – Decline SECTION 3 Wholesalers, Retailers, Storage, and Transportation Goods are usually moved from producers to consumers through middlemen such as wholesalers and retailers. SECTION 3 Wholesalers, Retailers, Storage, and Transportation (cont.) • Few goods go directly from producer to consumer. • The channels of distribution are: – Wholesalers – Retailers – E-commerce View: Distribution of Consumer Goods SECTION 3 Wholesalers, Retailers, Storage, and Transportation (cont.) • Part of the distribution process includes storing goods for future sales. • Transportation involves the physical movement of goods from producers and/or sellers to buyers. • Businesses must consider the type of product, size and weight of the product, speed, and cost in transporting goods within the channels of distribution. SECTION 3 Other Distribution Channels Direct marketing is done mainly through catalogs and over the Internet. SECTION 3 Other Distribution Channels (cont.) • Distribution channels have expanded rapidly in the last 15 to 20 years because of club warehouse stores and direct marketing. • Direct marketing is done mainly through catalogs and over the Internet. VS 1 The main purpose of marketing is to convince consumers that a certain product or service will add to their utility. Product testing helps marketers predict whether or not a new good will sell well. VS 2 When introducing a new product, businesses need to keep the “Four Ps” of marketing in mind. VS 3 Goods are usually moved from manufacturers to consumers through various distribution channels like wholesalers and retailers. FIGURE 1 FIGURE 2 FIGURE 3 FIGURE 4 DFS TRANS 1 DFS TRANS 2 DFS TRANS 3 VOCAB1 marketing: all the activities needed to generate consumer demand and to move goods and services from the producer to the consumer VOCAB2 consumer sovereignty: the role of the consumer as ruler of the market when determining the types of goods and services produced VOCAB3 utility: the amount of satisfaction one gets from a good or service VOCAB4 market research: gathering, recording, and analyzing data about the types of goods and services that people want VOCAB5 market survey: information gathered by researchers about possible users of a product based on such characteristics as age, gender, income, education, and geographic location VOCAB6 test-marketing: offering a product for sale in a small area for a limited period of time to see how well it sells before offering it nationally VOCAB7 penetration pricing: selling a new product at a low price to attract customers away from an established product VOCAB8 price leadership: a practice in some industries in which the largest firm publishes its price list ahead of its competitors, who then match those announced prices VOCAB9 promotion: use of advertising to inform consumers that a new or improved product or service is available and to persuade them to purchase it VOCAB10 direct-mail advertising: type of promotion using a mailer that usually includes a letter describing the product or service and an order blank or application form VOCAB11 product life cycle: series of stages that a product goes through from first introduction to complete withdrawal from the market VOCAB12 channels of distribution: routes by which goods are moved from producers to consumers VOCAB13 wholesalers: businesses that purchase large quantities of goods from producers for resale to other businesses VOCAB14 retailers: businesses that sell consumer goods directly to the public VOCAB15 e-commerce: business transactions conducted over the Internet