* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter19
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketplace Fairness Act wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Music industry wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Bayesian inference in marketing wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
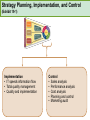
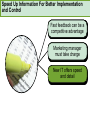
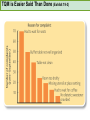
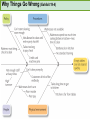
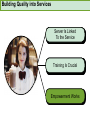
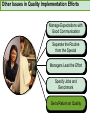
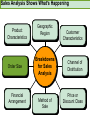
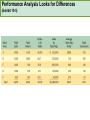
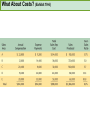
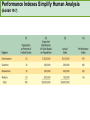
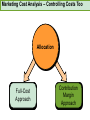
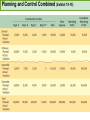
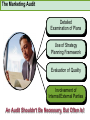
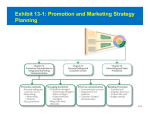
CHAPTER NINETEEN Implementing and Controlling Marketing Plans: Evolution and Revolution For use only with Perreault/Cannon/McCarthy or Perreault/McCarthy texts. © 2008 McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. McGraw-Hill/Irwin www.mhhe.com/fourps When we finish this lecture you should 1. 2. 3. 4. Understand how information technology speeds up feedback for better implementation and control. Know why effective implementation is critical to customer satisfaction and profits. Know how total quality management can improve implementation—including implementation of service quality. Understand how sales analysis can aid marketing strategy planning. When we finish this lecture you should 5. Understand the differences in sales analysis, performance analysis, and performance analysis using performance indexes. 6. Understand the difference between the full-cost approach and the contribution-margin approach. Understand how planning and control can be combined to improve the marketing management process. Understand what a marketing audit is and when and where it should be used. 7. 8. Strategy Planning, Implementation, and Control (Exhibit 19-1) Implementation • IT speeds information flow • Total quality management • Quality and implementation Control • Sales analysis • Performance analysis • Cost analysis • Planning and control • Marketing audit Speed Up Information For Better Implementation and Control Fast feedback can be a competitive advantage Marketing manager must take charge New IT offers speed and detail Effective Implementation Means That Plans Work As Intended On Saturday, July 8th, Amazon.com and FedEx made Harry Potter and the Goblet of Fire one of the largest book releases in Internet history. Dealing with Customer Complaints Complaints Bring Problems to Light Complaints Need a Response Using Information Technology to Improve Implementation (Exhibit 19-2) Technology and Implementation © 2008 McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., McGraw-Hill/Irwin Building Quality Into the Implementation Effort TQM is Easier Said Than Done (Exhibit 19-3) Why Things Go Wrong (Exhibit 19-4) Building Quality into Services Server Is Linked To the Service Training Is Crucial Empowerment Works Other Issues in Quality Implementation Efforts Manage Expectations with Good Communication Separate the Routine from the Special Managers Lead the Effort Specify Jobs and Benchmark Get a Return on Quality Sales Analysis Shows What’s Happening Product Characteristics Order Size Financial Arrangement Geographic Region Breakdowns for Sales Analysis Method of Sale Customer Characteristics Channel of Distribution Price or Discount Class Performance Analysis Looks for Differences (Exhibit 19-5) What About Costs? (Exhibit 19-6) Performance Indexes Simplify Human Analysis (Exhibit 19-7) Checking your knowledge A sales manager for Wilson Sporting Goods reviewed salesperson performance. Salesperson A had a performance index of 110, while Salesperson B had a performance index of 80. What might the sales manager conclude: A. Salesperson B’s performance should be a model for the whole sales force. B. Salesperson A should change her effort to bring her to the average. C. Salesperson A requires additional sales training D. Salesperson B may be having some problems. E. Salesperson B requires additional training. Marketing Cost Analysis – Controlling Costs Too Allocation Full-Cost Approach Contribution Margin Approach A Full-Cost Example (Exhibit 19-12) A Full-Cost Example (Exhibit 19-13) A Contribution-Margin Example (Exhibit 19-14) Planning and Control Combined (Exhibit 19-15) Checking your knowledge Mark Sun is a sales manager for Applied Robotics. He has asked his assistant to prepare a report that shows him how each of his sales reps has performed over the last year – showing their percentage above or below quota This is an example of: A. using natural accounts. B. the contribution margin approach. C. the marketing strategy planning process. D. performance analysis. E. sales analysis. Checking your knowledge Wendy Ball, sales manager for Applied Engineering Products, was reviewing the performance of her salespeople. One sales rep has sales 25% below quota. This analysis should lead the sales manager to conclude: A.that the sales rep has a great deal of competition in her territory. B.that the sales rep is not working hard enough. C.that the sales rep’s quota was set too high D.that there is no reason to worry, because the rest of the sales force is 25% over quota. E.Nothing at this point because of the iceberg principle. Checking your knowledge A marketing cost analysis conducted by Rosa Ruiz, marketing manager at Ruiz Windows, shows Watson Construction to be an unprofitable customer. Ruiz Windows should: A. change the delivery terms on Watson’s orders. B. raise prices on all items sold to Watson. C. assign a new salesperson to Watson. D. try to find out why Watson is unprofitable. E. refuse to sell to Watson Construction. The Marketing Audit Detailed Examination of Plans Use of Strategy Planning Framework Evaluation of Quality Involvement of Internal/External Parties An Audit Shouldn’t Be Necessary, But Often Is! Interactive Exercise: Sales and Performance Analysis © 2008 McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., McGraw-Hill/Irwin You now 1. 2. 3. 4. Understand how information technology speeds up feedback for better implementation and control. Know why effective implementation is critical to customer satisfaction and profits. Know how total quality management can improve implementation, including implementation of service quality. Understand how sales analysis can aid marketing strategy planning. You now 5. Understand the differences in sales analysis, performance analysis, and performance analysis using performance indexes. 6. Understand the difference between the full-cost approach and the contribution-margin approach. Understand how planning and control can be combined to improve the marketing management process. Understand what a marketing audit is and when and where it should be used. 7. 8. Key Terms • Control • Total quality • • • • • • • management (TQM) Continuous improvement Pareto chart Fishbone diagram Empowerment Benchmarking Sales analysis Performance analysis • Performance index • Iceberg principle • Full-cost approach • Contribution-margin • approach Marketing audit