* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Consumers Rule - Lampung University
Affiliate marketing wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Food marketing wikipedia , lookup
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Resource-based view wikipedia , lookup
Internal communications wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Bayesian inference in marketing wikipedia , lookup
Perfect competition wikipedia , lookup
Ambush marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
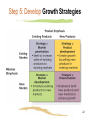
Strategic Marketing Planning Capturing the Big Picture Chapter Objectives • • • • Explain the strategic planning process Describe the steps in marketing planning Explain operational planning Explain the key role of implementation and control on marketing planning • Discuss some of the important aspects of an organization’s internal environment 2 Business Planning: Composing the Big Picture • Business planning: ongoing process of making decisions that guide the firm both in the short term and for the long haul Identifies/builds on firm’s strengths Helps managers make informed decisions Develops objectives before action is taken 3 3 Levels of Business Planning • 1. Strategic planning by top-level corporate management • 2. Functional planning by top functional-level management • such as the chief marketing officer • 3. Operational planning by supervisory managers 4 1. Strategic Planning • Managerial decision process that matches firm’s resources & capabilities to its marketing opportunities for long-term growth Top management • defines firm’s purpose and objectives Example: increase firm’s total revenues by 20% over next five years 5 2. Functional (Tactical) Planning • by various functional areas of firm • a broad 5-year plan to support strategic plan and a detailed annual plan • Example: to gain 40% of a particular market with three new products during coming year 6 3. Operational Planning • First-line managers focus on day-to-day execution of functional plans • includes detailed annual, semiannual, or quarterly plans • Example: units of a product a salesperson needs to sell per month 7 Business planning steps All Business Planning Is an Integrated Activity • Strategic, functional, and operational plans must work together for benefit of whole firm • must understand how they fit with the organization’s direction and resources 9 Strategic Planning: Framing the Picture • strategic business units (SBUs) divisions in Very large multiproduct firms Individual units within the firm that operate like separate businesses with each having its own mission, business objectives, resources, managers, and competitors • strategic planning done at both the corporate and SBU levels 10 Step 1: Define the Mission • Mission statement: a formal document that describes the organization’s overall purpose and what it hopes to achieve in terms of its customers, products, and resources • Mission should not be too broad, too narrow, too shortsighted 11 Step 1: Define the Mission • What business are we in? • • What customers should we serve? • How do we develop firm’s capabilities & focus its efforts? 12 Step 1: Define the Mission • Examples of mission statements MADD: “to stop drunk driving, support the victims of this violent crime, and prevent underage drinking” NeoMedia Technologies: “provide ground-breaking new technologies to companies everywhere” Xerox: provide “document solutions” 13 Step 2: Evaluate the Internal & External Environment • Situational /environmental analysis (business review) Includes a discussion of firm’s internal environment as well as the external environment 14 Internal Environment • All controllable elements inside a firm that influence how well the firm operates Strengths and weaknesses Technologies, physical facilities, financial stability, corporate reputation, quality products, strong brands, employees 15 External Environment • Elements outside the firm that may affect it either positively or negatively Opportunities and threats The economy, competition, technology, law, ethics, and sociocultural trends Firm cannot directly control external factors but can respond to them via planning 16 SWOT Analysis • • • • • • An analysis of an organization’s strengths (S) and weaknesses (W) and the opportunities (O) and threats (T) in the external environment 17 Step 3: Set Organizational or SBU Objectives • Long range goals • specific, measurable, and attainable • May relate to: sales, profitability, standing in market, return on investment, productivity, product development, customer satisfaction, social responsibility 18 Step 4: Establish the Business Portfolio • definition: • the group of different products or brands owned by an organization and having different income-generating and growth capabilities 19 Step 4: Establish the Business Portfolio • Portfolio analysis: • assessing the potential of a firm’s strategic business units Decisions: which SBUs should receive more or less of the firm’s resources 20 Step 5 : Growth Strategies • • • • Penetration Product development Market development Diversification 21 Step 5: Develop Growth Strategies 22 Which Growth strategy is this portraying? 23 Marketing planning Steps Cover on Friday Marketing Planning: Step 1 • Perform a situation analysis Builds on SWOT analysis about the environment • that specifically affects the marketing plan 25 Marketing Planning: Step 2 • Set marketing objectives Specific to the firm’s brands, sizes, product features, and other marketing mix-related elements State what the marketing function must accomplish if firm is to achieve overall business objectives 26 Marketing Planning: Step 3 • Develop marketing strategies to achieve marketing objectives Target market(s) where the firm’s offerings are best suited Marketing mix strategies: how marketing will accomplish its objectives in the firm’s target market by using product, price, promotion, and place 27 Marketing Mix Strategies • Product strategies include product design, packaging, branding, support services, and product variations/features • Pricing strategies include setting prices for final consumers, wholesalers, and retailers based on costs, demand, or competitors’ prices 28 Marketing Mix Strategies • Promotion strategies: advertising, sales promotion, public relations, direct marketing, personal selling • Distribution strategies: how, when, and where the product is available to targeted customers 29 Step 4: Implement & Control the Marketing Plan • Control: measuring actual performance, comparing performance to the objectives, making adjustments • Marketing metrics: return on marketing investment (ROMI) 30 Action Plans • Support plans that guide implementation and control of marketing strategies • Assign responsibility, time line, budget, measurement and control 31 Creating & Working with a Marketing Plan • Written marketing plans encourage concrete objectives and strategies • Operational plans focus on the day-to-day execution of the marketing plan 32 The Value of a Marketing Culture • A firm’s corporate culture determines much of its internal environment – the values, norms, and beliefs that influence everyone in the firm 33 The end 34 Real People, Real Choices • NeoMedia Technologies (Rick Szatkowski) • Rick choose option 2: leverage social networking Rick and his team are banking on early adopters to energize the market for Qode and push the product rapidly through the adoption cycle to more users 35 Keeping It Real: Fast-Forward to Next Class Decision Time at Tupperware • Meet Rick Goings, CEO of Tupperware Brands Corp. • Tupperware: one of the most recognized brands world-wide • The decision: How to refresh the Tupperware brand perception 36 Real People, Real Choices: Decision Time at Qode • What go-to-market strategies should Qode execute? Option 1: partner with cell phone carriers Option 2: leverage social networking Option 3: brand-driven distribution 37