* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Marketing Environment
Food marketing wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Affiliate marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Ambush marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
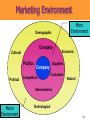
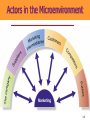
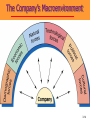
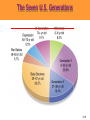
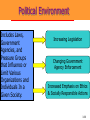
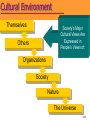
3 The Marketing Environment Marketing Environment The marketing environment consists of actors and forces outside the organization that affect management’s ability to build and maintain relationships with target customers. • Environment offers both opportunities and threats. • Marketing intelligence and research used to collect information about the environment. 3-2 The Company’s environment • Company’s Internal Environment: – Structure of company – Culture – Resources • Companies External Environment – Microenvironment: actors close to the company that affect its ability to serve its customers. – Macro environment: larger societal forces that affect the microenvironment. • Considered to be beyond the control of the organization. 3-3 Marketing Environment Micro Environment Demographic Company Cultural Publics Political Company Competitors Economic Suppliers Customers Natural Intermediaries Macro Environment Technological 3-4 Actors in the Microenvironment 3-5 The Company (Internal Marketing) – Marketing must consider other parts of the organization including • Finance • R&D • Purchasing • Operations and • Accounting – Marketing decisions must relate to broader company goals and strategies 3-6 The Company’s Microenvironment • Suppliers: – Provide resources needed to produce goods and services. – Marketers must watch supply availability and pricing – Important link in the “value delivery system.” – Most marketers treat suppliers like partners. 3-7 The Company’s Microenvironment • Marketing Intermediaries: – Help the company to promote, sell, and distribute its goods to final buyers • Resellers • Physical distribution firms • Marketing services agencies • Financial intermediaries 3-8 Partnering With Intermediaries Coca-Cola provides Wendy’s with much more than just soft drinks. It also pledges powerful marketing support. 3-9 The Company’s Microenvironment • Customers: – Five types of customer markets that purchase a company’s goods and services • Consumer • Business • Reseller • Government • International 3-10 The Company’s Microenvironment • Competitors: – Those who serve a target market with products and services that are viewed by consumers as being reasonable substitutes – Company must gain strategic advantage against these organizations – Conducting competitor analysis is critical for success of the firm – A marketer must monitor its competitors’ offerings to create strategic advantage 3-11 Publics Group that has an interest in or impact on an organization's ability to achieve its objectives 3-12 The Macroenvironment • The company and all of the other actors operate in a larger macroenvironment of forces that shape opportunities and pose threats to the company. 3-13 The Company’s Macroenvironment 3-14 The Company’s Macroenvironment • Demographic: – The study of human populations in terms of size, density, location, age, gender, race, occupation, and other statistics. – Marketers track changes with respect to • Age and Generations • House hold Patterns/ House hold makeup (FLCS) • Population size and growth rate • Geographic Shifts in Population • Better Educated Population • Ethnic mix. • Increasing Diversity 3-15 The Seven U.S. Generations 3-16 Baby Boomers • 78 million born between 1946 and 1964 • Account for 28% of population • Earn more than half of all personal income • Almost 25% belong to racial or ethnic minority • Spend a lot on anti-aging products and services • Are likely to postpone retirement 3-17 Generation X • 45 million born between 1965 and 1976 • Defined by their shared experiences – Increasing divorce rates – More of their mothers employed – First generation of latchkey kids • Cynical of frivolous marketing pitches • Care about the environment • Prize experience, not acquisition 3-18 Generation Y • 72 million born between 1977 and 1994 • Have large amount of disposable income • Comfortable with computer technology • Tend to be impatient and “Now-Oriented” • Many product lines targeted at Gen Ys 3-19 Interactive Student Assignment • Pair with another student to discuss the following questions: – In what ways does the buying behavior of you and your parents differ? – In what ways does the buying behavior of you and your grandparents differ? – What selling strategies would work best for: • You • Your parents • Your grandparents 3-20 Diversity-Based Advertising Based on careful study of cultural differences, Bank of America has developed targeted advertising messages for different cultural subgroups, here Asians and Hispanics. 3-21 Economic Environment Consists of factors that affect consumer purchasing power and spending patterns. it includes • Income • • • • Savings Gifts Debt Credit availability • Changes in Income level • Income Distribution – – – – Upper class Middle class Working class Underclass 3-22 Income Distribution Walt Disney markets two distinct Pooh bears to match its twotiered market. 3-23 Natural Environment • Involves • the natural resources that are needed as inputs by marketers or that are affected by marketing activities. Types of Resources – Infinite resources (air and water) – Finite renewable resources (forest and food) – Fininte nonrenueable resources (Oil and minerals) 3-24 Factors Impacting the Natural Environment Shortages of Raw Materials Increased Pollution Increased Government Intervention Environmentally Sustainable Strategies 3-25 Environmental Responsibility McDonald’s has made a substantial commitment to the so-called “green movement.” 3-26 Technological Environment • Most dramatic force now shaping our destiny. 3-27 Technological Environment • Changes rapidly. • Creates new markets • • and opportunities. Challenge is to make practical, affordable products. Safety regulations result in higher research costs and longer time between conceptualization and introduction of product. 3-28 Discussion Questions • Within the last ten years, which technological force has had the greatest impact on marketing? In what areas of marketing has this impact been seen? • What technological force has impacted you the most? In what ways has this occurred? 3-29 Political Environment Includes Laws, Government Agencies, and Pressure Groups that Influence or Limit Various Organizations and Individuals In a Given Society. Increasing Legislation Changing Government Agency Enforcement Increased Emphasis on Ethics & Socially Responsible Actions 3-30 Cultural Environment • The institutions and other • forces that affect a society’s basic values, Beliefs, Norms, perceptions, preference, and behaviors. Types of beliefs – Core beliefs – Secondary beliefs 3-31 Cultural Environment Themselves Society’s Major Cultural Views Are Expressed in People’s Views of: Others Organizations Society Nature The Universe 3-32 Responding to the Marketing Environment • Environmental Management Perspective • Taking a proactive approach to managing the environment by taking aggressive (rather than reactive) actions to affect the publics and forces in the marketing environment. • This can be done by: – Hiring lobbyists – Running “advertorials” – Pressing lawsuits – Filing complaints – Forming agreements to control channels 3-33 Rest Stop: Reviewing the Concepts • Describe the environmental forces that affect the • • • • company’s ability to serve its customers. Explain how changes in the demographic and economic environments affect marketing decisions. Identify the major trends in the firm’s natural and technological environments. Explain the key changes in the political and cultural environments. Discuss how companies can react to the marketing environment. 3-34 How to scan the environment • Value chain • Porters five forces model • SWOT analysis • PEST analysis • TOWS analysis 3-35