* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Market positioning
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Service parts pricing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Planned obsolescence wikipedia , lookup
Grey market wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Dumping (pricing policy) wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Darknet market wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Product placement wikipedia , lookup
Perfect competition wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Product lifecycle wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Food marketing wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
Market analysis wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Predictive engineering analytics wikipedia , lookup
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Market segmentation wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
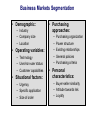
Segmentation, Targeting and Positioning: Building the Right Relationships with the Right Customers Steps in Market Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning • Market segmentation: dividing market into distinct groups which will require separate marketing mixes • Target marketing: choosing which group(s) to appeal to • Market positioning: creating a clear, distinctive position in the consumer’s mind relative to competition Consumer Market Segmentation • Geographic: – Regions – Size/density – Climate • Demographic: – – – – – – – Age/generation Gender Family size/life-cycle Income Occupation Religion Ethnic origin • Psychographic: – Social class – Lifestyle – Personality • Behavioral: – – – – – – – Occasions Benefits User status Usage rate Loyalty status Readiness state Attitude toward product Business Markets Segmentation • Demographic: – Industry – Company size – Location • Operating variables: – Technology – User/non-user status – Customer capabilities • Situational factors: – Urgency – Specific application – Size of order • Purchasing approaches: – – – – – Purchasing organization Power structure Existing relationships General policies Purchasing criteria • Personal characteristics: – Buyer-seller similarity – Attitude towards risk – Loyalty Segmenting International Markets • International markets can be segmented by: – – – – Geographic location Economic factors Political and legal factors Cultural factors • Intermarket segmentation: – Forming segments of consumers who have similar needs, even though they live in different countries Requirements for Effective Segmentation • To be useful, market segments must be: – Measurable: • Size, purchasing power, and profiles can be measured – Accessible: • Segments can be reached – Substantial: • Large enough to be profitable – Actionable: • Programs can be developed to attract and serve the segments Target Marketing Strategies • Three factors used to evaluate segments: – Segment size and growth – Structural attractiveness • Competition, substitute products, power of buyers/suppliers – Company objectives and resources Choosing a Target Marketing Strategy • Factors to be considered: – Company resources – Product variability – Product’s life-cycle stage – Market variability – Competitor’s marketing strategies Positioning for Competitive Advantage • Product position: the way the product is defined by consumers on important attributes, relative to competing products • Competitive advantage: an advantage gained over competitors by offering (and delivering) greater value • Sources of differentiation: – – – – – Product Service Marketing channels People Image Which Differences to Promote? • Unique selling proposition (USP): aggressively promoting one benefit to the target audience • Three major positioning errors: – Under-positioning – Over-positioning – Confused positioning • Differences should be: – – – – – – – Important Distinctive Superior Communicable Pre-emptive Affordable Profitable Possible Value Propositions • Value proposition: – Full positioning of a brand – Mix of benefits used for positioning Sliced Bread and other marketing delights… Seth Gordin Marketing Expert, book author and Entrepreneur Former Vice President of Marketing at Yahoo! Class Assignment Select one of below brands and do research to learn more about the brand. Then answer the below questions with a short group presentation. 1)Give a brief description of your product and define the target market and segment it serves 2)At what stage in its life cycle is this product? What are your reasons for believing it is at this point? 3)How do the product’s packaging and labeling help boost its consumer appeal? 4)How is the product promoted? 5)Is this product sold in international markets? If so, does the company use a standardized or customized strategy? 6)How is the product priced in relation to competing products? Nescafe coffee Samsung “Galaxy” tablet computers Levi’s jeans Play Station 2 Metersbonwe clothing Coca-Cola drinks L’Oreal shampoo and hair products Snickers chocolate Apple ipod Haier refrigerators Lenovo laptops KFC Restaurants BYD Automobiles Casio Watches Huawei mobile telephones