* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Option A.3 Pt 1 - Peoria Public Schools
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
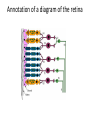
Perception of stimuli Option A.3 Receptors detect changes in the environment. • List and describe the types of specialized receptors in humans. a. Mechanoreceptors- respond to movement. b. Chemoreceptors- respond to chemicals. c. Thermoreceptors- heat. d. Photoreceptors- light. Labelling a diagram of the structure of the human eye Rods and cones are photoreceptors located in the retina. • Describe the retina. a. A thin layer of light sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. • Describe what rods and cones do for the eye. a. Rods and cones work together to detect the image focused on the retina. Rods and cones differ in their sensitivities to light intensities and wavelength. • Compare and contrast rods and cones. a. They are both photoreceptors in the retina. Rods work well in dim light and give us black and white vision. Cones work well in bright light and give us color vision. • List the three types of cones. a. Red, blue, green Red-green color blindness as a variant of normal trichromatic vision • What is red-green color blindness caused by? a. The absence or a defect in a gene for photoreceptors for red or green cone cells. • Why is it more common in males? a. It is more common in males because it is a recessive allele carried on the X chromosome. Males have only one X so will show the trait if recessive. Annotation of a diagram of the retina Bipolar cells send the impulses from rods and cones to ganglion cells • Describe the job of bipolar cells. a. Bipolar cells synapse with rod and cone cells to carry a message to the ganglion cells. Ganglion cells send messages to the brain via the optic nerve • Describe the structure of ganglion cells. a. Ganglion cells have cell bodies in the retina and dendrites that synapse with bipolar cells. They also have long axons that pass impulses to the brain. The information from the right field of vision from both eyes is sent to the left part of the visual cortex and vice versa • Name the spot where axons from the left and right sides cross over. a. Optic Chiasma