* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download variation
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Organisms at high altitude wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Vestigiality wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
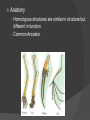
10.1 KEY CONCEPT There were theories of biological and geologic change before Darwin. What are some reasons why this creature would have the specific traits it has; tentacles on its mouth and long claw like nails? Early scientists proposed ideas about evolution. Evolution is the biological change process by which descendants come to differ from their ancestors. A species is a group of organisms that can reproduce and have fertile offspring. Discussion Questions: 1. What are some examples of species? 2. Would a donkey and a horse be considered the same species? Scientist Contribution Linnaeus (1700s) Classification System; hybridization Buffon (1700s) Species shared ancestors; earth is older E. Darwin (1750s) Common ancestor Lamarck (1809) Inheritance of acquired characteristics Cuvier (early 1700s) Catastrophism Hutton (late 1700s) Gradualism Lyell (1830s) Uniformitarianism 10.2 KEY CONCEPT Darwin’s voyage provided insight on evolution. Darwin observed differences among island species. Variation is a difference in a physical trait. Examples: Tortoises and Finches in the Galapagos Islands What variation do you see in the tortoises below? An adaptations is a feature that allow an organism to better survive in its environment. – Species are able to adapt to their environment. – Adaptations can lead to genetic change in a population. HOW?? Variation v. Adaptation For each trait, give a variation and then explain how it could become an adaptation. Example: Neck rotation in owls Variation: amount of rotation, some small, medium, large, etc Adaptation – Owls with larger amount of rotation can seen more to get food and survive Neck length in giraffes Size of dolphins Sense of smell in dogs Muscle amount in Huskies Amount of blubber on penguins Darwin’s Evidence • Fossils • Earthquake Adaptation Scenario Imagine that you are a scientist, studying sea lions on the Galapagos Islands. The sea lions lose their main food source when anchovies are kept away from the island. The only other food available is a small species of crab that lives on the seafloor 100 feet below. What kind of traits would the sea lions adapt and how would they help? Discuss as a group and write your response 10.3 Several key insights led to Darwin’s idea for natural selection. Darwin noticed a lot of variation in domesticated plants and animals. Artificial selection is the process by which humans select traits through breeding. What are some examples of humans using this process? neck feathers crop tail feathers Natural selection is a mechanism by which individuals that have inherited beneficial adaptations produce more offspring on average than do other individuals. Heritability - ability of a trait to be passed down. Overpopulation and limited resources cause struggle for survival So how long does natural selection take? ○ Darwin proposed that adaptations arose over many generations. Natural selection explains how evolution can occur. • There are four main principles to the theory of natural selection. – Variation: heritable differences that exist in every population – overproduction: too many offspring compete for resources – adaptation: certain variation allows individuals to survive better than others – descent with modification: more individuals have an adapted trait with each generation VARIATION Natural selection acts on EXISTING variation. • Fitness is the measure of survival ability and ability to produce more offspring. • Natural selection can act only on traits that already exist. • Structures take on new functions in addition to their original function. five digits wrist bone Natural Selection Example Jaguar Example: Overproduction – not enough food for all offspring to survive Variation – teeth and jaw size, some are born with slightly larger than others Adaptation – larger teeth and jaws allow jaguars to eat more things; survive more than those who don’t have this trait Descent with modification – because larger teeth and jaws are beneficial to survival, they will be passed on more often and become more common in the population With the person sitting next to you: Look at the example of the Jaguar on page 307 in the books Choose your own animal and explain how that animal could fit all 4 principles of natural selection in the same way as the example. Create an environmental change that would cause natural selection in the organism you chose. Write it down and turn in. 10.4 KEY CONCEPT Evidence of common ancestry among species comes from many sources. Several Sources of Evidence Fossils Fossils in older layers are more primitive than those in the upper layers. Geography – island species most closely resemble nearest mainland species – populations can vary from one island to another Embryology – identical larvae, different adult body forms – similar embryos, diverse organisms Larva Adult crab Adult barnacle Anatomy – Homologous structures are similar in structure but different in function. – Common Ancestor Anatomy Analogous structures have a similar function. Common environment, not common ancestor Fly wing Bat wing Structural patterns are clues to the history of a species. • Vestigial structures are remnants of organs or structures that had a function in an early ancestor. • Ostrich wings • Other examples? 10.5 KEY CONCEPT New technology is furthering our understanding of evolution. Fossils provide a record of evolution. Paleontology is the study of fossils or extinct organisms. Paleontology provides evidence to support evolution. Molecular and genetic evidence support fossil and anatomical evidence. Hox genes indicate a very distant common ancestor. – control the development of specific structures – found in many organisms Evolution unites all fields of biology. • Scientist from any fields contribute to the understanding of evolution. • The basic principles of evolution are used in many scientific fields. Evidence for Evolution – Opinion Statement Do you believe the evidence we discussed is enough to justify belief in evolution? Why or why not? Homework 1. 2. 3. 4. Create a Venn Diagram Comparing and Contrasting Analogous, Homologous, and Vestigial Structures Do the VOCABULARY CONNECTIONS (#1-5) on page 323 in your book Due Tomorrow Quiz Friday on Ch. 10!!