* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Natural Selection - Liberty Union High School District
The Selfish Gene wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Organisms at high altitude wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness wikipedia , lookup
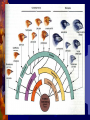
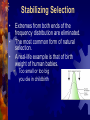
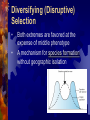
Slides 1-13 Evidence for Evolution 1. Fossils show change over time • • scientists can date fossils & use them to support the theory of evolution common ancestors reveal whether species are related – Anatomy of living species also shows relatedness How Anatomy supports Evolution 2. Homologous Structures • • Traits similar in different species because they share a common ancestor Ex: human arm, dog front limb, horse leg, whale fin “ Look the Same” How Anatomy supports Evolution 3. Analogous structures • Distantly related species have structures that have the same function but are different in structure • Ex: wing of butterfly & bird “ Work the Same” 4. Vestigial structures • • • Structures reduced in size & often unused Remains of functional structures inherited from an ancestor Ex: leg & hip bones in pythons & whales How do new species form? 1. Geographic Isolation • • When members of a population are separated Ex: polar, grizzly, & black bears 2. Reproductive Isolation • When members of a population can’t breed even though they live nearby • Ex: different mating seasons or different mating calls Different Types of Evolution 1. 2. 3. 4. Divergent evolution Convergent evolution Coevolution Adaptive radiation 1. Divergent Evolution Isolated populations evolve independently Ex: polar & grizzly bears changed independently due to different habitats 2. Convergent Evolution Unrelated species become more alike because they live in similar environments Ex: shark & dolphin 3.Coevolution Species that interact closely adapt to one another Ex: flowers & hummingbirds 4. Adaptive Radiation Evolution of many diverse species from one common ancestor Ex: Galapagos finches discovered by Darwin Population Genetics: Evolution at the Gene Level Population all of the individuals of a species that live together in one place at one time. Natural Selection: populations changing in response to their environment as individuals better adapted to the environment leave more offspring 4 Steps of Natural Selection: 1. 2. 3. 4. Overproduction Genetic Variation Struggle to survive (limited resources) Successful reproduction Allele Frequency • The relative amount of an allele of a gene within a population (%) • Example • If 100 individuals make up a population and 50 are homozygous dominant, 25 are heterozygous, and 25 are recessive, what is the allele frequency of the dominant allele? Allele Frequency • You Try! • If 300 individuals make up a population, 150 are homozygous dominant, 100 are heterozygous, and the rest are recessive, what is the allele frequency of the recessive trait? How does Natural Selection Affect Allele Frequency • Mutations provide the raw material on which natural selection acts • Evolution depends on variations because it is the only way that differences among organisms are created • Acts on Populations not individuals by changing the % of alleles in the population Survival of the Fittest If individuals having certain genes are better able to produce mature offspring than those without them, the frequency (#) of those genes will increase Survival: Fitness: Making it to reproductive age Producing enough offspring Different Lines of Evidence •Wolf Lineage: all dogs are descendent from the Grey wolf •Darwin’s Finches: all 13 species are descendent of a South American species •Whale DNA Genetic Drift Mutations that take place because of random fluctuations of gene frequencies due to small population size • Example: Ellis-van Creveld syndrome • A rare form of dwarfism that includes extra fingers and toes– • Amish population of eastern Pennsylvania, which has intermarried over many generations. Gene Flow Changes in the gene pool of a population because of the introduction of genes from another population by migration. • Example: the gene pool in southeast Asia was changed when U.S. Soldiers had children with Vietnamese women during the Vietnam war. Founder Effect Changes in a population when a small population moves to a new location bringing only a small fraction of the genes and variation of the parent population. • Example: Galapagos Finches Bottleneck Effect Over-hunting, predation or natural disaster leads to a population that no longer represents the original. • Organisms are recessive at almost all alleles • Mutations: deformed Claws, low sperm count, coat variation • Example: Cheetahs (2 bottleneck events) 1st :10,000 years ago 2nd: 1980’s Types of Natural Selection • Stabilizing • Directional • Diversifying Stabilizing Selection • Extremes from both ends of the frequency distribution are eliminated. The most common form of natural selection. A real-life example is that of birth weight of human babies. • • • Too small or too big you die in childbirth Directional Selection • Individuals at either end of the distribution are favored. The distribution shifts towards the left or right, depending on which one is favored. • What we usually think of as natural selection Diversifying (Disruptive) Selection • • Both extremes are favored at the expense of middle phenotype A mechanism for species formation without geographic isolation CLADISTICS •A Cladogram is a branching diagram that depicts species divergence from common ancestors. •They show the distribution and origins of shared characteristics. •Cladograms are testable hypotheses of phylogenetic relationships. Questions?