* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Fossil Record-Homologies-Mechanisms of Evolution Notes
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Sociobiology wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Organisms at high altitude wikipedia , lookup
The Selfish Gene wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
The eclipse of Darwinism wikipedia , lookup
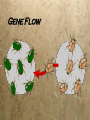
Fossil Record & Homologies Scientists have used the fossil record to construct a history of life on Earth. This is only a theory Fossil record is not complete Homologous Body Structures Structures That Have Different Mature Forms But Develop From The Same Embryonic Tissues A cladogram is a theoretical evolutionary tree made using cladistics. – A clade is a group of species that are thought to share a common ancestor. – Each species in a clade shares some traits with the ancestor. – Each species in a clade has traits that have changed. Mechanisms of Evolution There are several: 1. Natural Selection 2. Gene Flow 3. Genetic drift 4. Mutations 5. Non-random mating 1. Natural Selection: Affects variation in a population as the better adapted (more fit) individuals survive and reproduce, passing on their genes to the successive generations. Acts only upon an organism’s phenotype (its physical characteristics). If the phenotype is better suited for a changing environment, the individual can survive and pass on its genes. Natural Selection 2. Gene Flow: Is the movement of alleles into or out of a population (immigration or emigration). Gene flow can introduce new alleles into a gene pool or can change allele frequencies. The overall effect of gene flow is to counteract natural selection by creating less differences between populations. Example: Plant pollen being blown into a new area Gene Flow 3. Genetic Drift The change in allele frequencies as a result of chance processes. These changes are much more pronounced in small populations. Examples of Genetic Drift A) The Founder Effect: Small population that branches off from a larger one may or may not be genetically representative of the larger population from which it was derived. Only a fraction of the total genetic diversity of the original gene pool is represented in these few individuals. Examples of Genetic Drift B) Population Bottleneck: Occurs when a population undergoes an event in which a significant percentage of a population is killed or otherwise prevented from reproducing. •The event may eliminate alleles entirely or also cause other alleles to be overrepresented in a gene pool. EX. Cheetahs 4. Mutations: Are inheritable changes in the genotype (genes). Provide the variation that can be acted upon by natural selection. Mutations provide the raw material on which natural selection can act. Exp. Frog mutation 5. Non-Random Mating: In animals, non-random mating can change allele frequencies as the choice of mates is often an important part of behavior. Many plants self-pollinate, which is also a form of non-random mating (inbreeding).